(Press-News.org) DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. - June 9, 2015 - The percentage of U.S. female physician authors of original research in major gastroenterology journals has grown over time, yet the percentage of women in the senior author position remains lower than expected based on the proportion of female gastroenterologists in academia. A look at the evolution of gender in the GI publishing landscape is presented in "Female authorship in major academic gastroenterology journals: a look over 20 years," published in the June issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE).
Researchers looked at authorship of articles at five-year intervals in five major journals from 1992 to 2012: Gastroenterology; Hepatology; American Journal of Gastroenterology; Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology (CGH); and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (GIE). They compared the percentage of female first (lead) and senior authors with the percentage of gastroenterologists in academic practice who were female. Their total sample included 2,275 original research articles.
Overall, 18 percent of first authors and 10.1 percent of senior authors were women. For first authors, the percentage increased from 9.1 percent in 1992 to 29.3 percent in 2012. (In 1992, women represented approximately 10 percent of academic gastroenterologists. In 2012, that figure had risen to approximately 26 percent.)
With the exception of 1997, the proportion of women authors in the senior position (typically the author whose name appears last in the list of contributors) was significantly lower than expected throughout the 20-year timeline based on the proportion of female academic gastroenterologists at the same time. The proportion of female lead authors kept pace with the increasing percentage of women in the field.
Having a female first author was associated with the gender of the senior author. Of the female senior authors, 37 percent had a female lead author. Of male senior authors, 20.7 percent had a female lead author. The research topic also was associated with gender; for example, the odds of female authorship were greater for liver-related publications, but lower for both pancreaticobiliary and endoscopy journals.
According to the study's lead author, Michelle Long, MD, "Future research should explore potential reasons for the lower rates of female authorship in the senior author position, and whether this relates to individual preferences or more systemic issues."
ASGE immediate past president Colleen Schmitt, MD, FASGE, wrote an accompanying editorial, "Flute or tuba: women and publishing success in top gastroenterology journals." According to Dr. Schmitt, "The American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy has stepped out to invest in this idea in a real way, by supporting a cohort of young women and minority faculty with a substantial skills-training program called Leadership Education and Development, or LEAD." She notes that women need strong mentors to help with career management in this area, including funding ideas, requests and reiterations.
INFORMATION:
Editor's Note: A video interview featuring lead author Michelle Long is available as part of the "GIE Author Interview" series. http://www.giejournal.org/content/video_interviews
About the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Since its founding in 1941, the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) has been dedicated to advancing patient care and digestive health by promoting excellence and innovation in gastrointestinal endoscopy. ASGE, with more than 13,000 members worldwide, promotes the highest standards for endoscopic training and practice, fosters endoscopic research, recognizes distinguished contributions to endoscopy, and is the foremost resource for endoscopic education. Visit http://www.asge.org and http://www.screen4coloncancer.org for more information and to find a qualified doctor in your area.
About Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures allow the gastroenterologist to visually inspect the upper gastrointestinal tract (esophagus, stomach and duodenum) and the lower bowel (colon and rectum) through an endoscope, a thin, flexible device with a lighted end and a powerful lens system. Endoscopy has been a major advance in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases. For example, the use of endoscopes allows the detection of ulcers, cancers, polyps and sites of internal bleeding. Through endoscopy, tissue samples (biopsies) may be obtained, areas of blockage can be opened and active bleeding can be stopped. Polyps in the colon can be removed, which has been shown to prevent colon cancer.
http://www.giejournal.org/article/S0016-5107(15)00049-8/abstract
SAN FRANCISCO--Seismologists studying the recent dramatic upswing in earthquakes triggered by human activity want to clear up a few common misconceptions about the trend.
There is increasing evidence that these earthquakes are caused by injecting fluids from oil and gas operations deep into the earth. These human-caused earthquakes are sometimes called "induced earthquakes."
A Seismological Research Letters focus section to be published online June 10 addresses some common misconceptions about induced seismicity--the biggest of which is that it is primarily related ...
Scientists at the University of York have made a significant advance that could make cell-based treatments for arthritis less of a lottery.
Researchers in the Departments of Biology and Physics at York, working with colleagues at the Erasmus Medical Centre in Rotterdam, have identified individual stem cells that can regenerate tissue, cartilage and bone.
The stem cells are mixed within human bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs) but are similar in appearance and previously, scientists had difficulty in distinguishing between them. The York researchers isolated individual MSCs ...
An unexpected finding by an international team of scientists based at The University of Manchester and National Institutes of Health in America has shed new light on how immune cells are programmed to either repair or protect the body.
It's hoped the discovery will inform the development of better treatments for a range of conditions from inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) to certain cancers.
The research, led by Dr John Grainger from the Manchester Collaborative Centre for Inflammation Research (MCCIR) and Dr Yasmine Belkaid from the National Institute of Allergy and ...
Large magnetic storms from the Sun, which affect technologies such as GPS and utility grids, could soon be predicted more than 24 hours in advance.
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are eruptions of gas and magnetised material from the Sun that have the potential to wreak havoc on satellites and Earth-bound technologies, disrupting radio transmissions and causing transformer blowouts and blackouts.
These mass ejections can cause problems with GPS technology - used by all kinds of vehicles, from cars to oil tankers to tractors. For example, they can affect the ability of ...
What:
The Makona strain of Ebola virus (EBOV) circulating in West Africa for the past year takes roughly two days longer to cause terminal disease in an animal model compared to the original 1976 Mayinga strain isolated in Central Africa, according to a new National Institutes of Health (NIH) report. The results provide important information to scientists who have wondered if the Ebola virus in West Africa is becoming more severe. In fact, the new study suggests the current virus has a decreased ability to cause disease in their animal model compared to the 1976 strain.
Using ...
This news release is available in Spanish.
CRG scientists describe a new mechanism shaping cells and generating cell contractile forces during development and organogenesis.
The new mechanism, which has been published today in the journal Developmental Cell, includes strategies shared with programmed cell death but which have not previously been directly associated with force generation.
Studying developmental processes such as the one presented in the Dev. Cell paper contributes to a better understanding of organ development and maintenance. Also, ...
Simple steps that include the consistent use of experienced medical teams for a single type of surgery, preemptive antibiotics before the procedure, less reliance on potent opioids during recovery and urging patients to get out of bed and move around sooner can not only prevent infections, blood clots and other serious complications in people undergoing colorectal operations, but can also accelerate recovery and reduce cost of care, according to results of an ongoing program at The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
The approach, dubbed Integrated Recovery Pathway, or IRP, and its ...
In a small clinical trial, scientists at Johns Hopkins' Kimmel Cancer Center and James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute found that men with advanced prostate cancer and detection of androgen receptor splice variant-7 (AR-V7) respond to chemotherapy just as well as men who lack the variant.
The findings, the researchers say, may be significant for patients who carry the AR-V7 variant, because they are more likely to develop resistance to one of two hormone drugs routinely used to treat their disease. Results of the trial are published online in the June 4 issue of JAMA ...
Young adults who use social media to quit smoking are twice as successful in their efforts as those who use a more traditional method, according to new research from the University of Waterloo.
The study, published last week in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, compared the success of the social media-based campaign Break It Off with Smokers' Helpline, a telephone hotline for young adults looking to quit smoking.
After three months in the program, 32 per cent of smokers who used Break It Off apps and web tools had quit smoking, compared to 14 per cent of their peers who ...
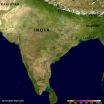
Monsoon rainfall, although a little later than normal, started on June 5, 2015, in southern India. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core satellite gathered rainfall data that was used to create an animation that shows where the precipitation fell as the season started.
Due to El Nino conditions some meteorologists predict that monsoon rainfall will be below normal this year. Cooling rainfall comes to the country after high temperatures preceding the monsoon have caused the reported deaths of more than 2,300 people.
Data from the NASA's Integrated Multi-satellitE ...