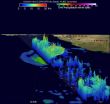
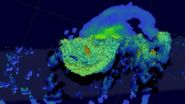
(Press-News.org) Tropical cyclones are not too common in the Arabian Sea, but tropical cyclone 01A, now renamed Ashobaa, formed this week. NASA/JAXA's Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core satellite flew over Ashobaa and gathered data that provided a 3-D look at the rainfall in the storm.
The GPM core observatory satellite flew over Ashobaa on the morning of June 8 at 0811 UTC (4:11 a.m. EDT). Tropical cyclone Ashobaa had sustained wind speeds of about 40 knots (46 mph) when the satellite passed overhead.
On June 9 at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), tropical cyclone Ashobaa had maximum sustained winds near 50 knots (57.5 mph/92.6 kph). Ashobaa was centered near 20.7 north latitude and 64.1 east longitude, about 290 nautical miles (333.7 miles/ 537.1 km) south-southwest of Karachi, Pakistan. Ashobaa is moving west-northwest at 8 knots (9.2 mph/14.8 kph).
Satellite data on June 9 showed that the storm is tightly wrapped, although elongated as clouds and showers are being pushed to the west because of persistent moderate easterly wind shear.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) predicts that tropical cyclone Ashobaa will become more powerful and have winds of 65 knots (about 75 mph) by June 10 as it moves through warm sea surface temperatures. Ashobaa is then predicted to weaken as dry stable air is expected to affect the system. It is forecast to turn west where it expected to make landfall on June 12 near Ras al Hadd, a village in the Ash Sharqiyah district in Oman.
As Ashobaa continues curving to the west in the Arabian Sea, it is generating rough surf along the coasts of Oman, southeastern Iran and Pakistan.
GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) and Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) instruments measured rain falling at a rate of over 60 mm (2.3 inches) per hour in strong thunderstorms southwest of the storm's center of circulation.
INFORMATION:
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., a 3-D view was constructed using data from DPR Ku band radar data. The 3-D view of GPM revealed Ashobaa had very powerful thunderstorms near the center of the newly formed storm reaching heights above 17 km (10.5 miles). These tall thunderstorms near the center of a tropical cyclone can be as sign that intensification will occur in the future.
MADISON, Wis. -- Scientists have prior evidence that the hormone estrogen is a major driver in the growth of cervical cancer, but a new study examining genetic profiles of 128 clinical cases reached a surprising conclusion -- estrogen receptors all but vanish in cervical cancer tumors.
This counterintuitive finding, reported June 8 in the online Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, further bolsters the understanding of cervical cancer's progression and offers valuable new targets to fight the disease.
Lead author Johan den Boon, associate scientist with ...
The economic impact of the Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) was $872.3 million nationwide in fiscal year 2014, according to a study by the University of Colorado Boulder's Leeds School of Business.
The study estimates NREL's impact to Colorado's economy totaled $701 million, a decline of 1.6 percent from the prior year. The slight year-over-year drop was largely attributed to a decline in major construction spending that came as NREL completed the planned build-out of its sustainable campus.
Jefferson County, where the largest concentration ...
Two of our nation's most advanced wind energy research and test facilities have joined forces to help the wind energy industry improve the performance of wind turbine drivetrains and better understand how the turbines can integrate more effectively with the electrical grid.
Through a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement (CRADA), the Energy Department's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) and Clemson University will partner to share resources and capabilities in the operation and development of testing facilities. The CRADA also includes the exchange ...
DOWNERS GROVE, Ill. - June 9, 2015 - The percentage of U.S. female physician authors of original research in major gastroenterology journals has grown over time, yet the percentage of women in the senior author position remains lower than expected based on the proportion of female gastroenterologists in academia. A look at the evolution of gender in the GI publishing landscape is presented in "Female authorship in major academic gastroenterology journals: a look over 20 years," published in the June issue of GIE: Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, the monthly peer-reviewed scientific ...
SAN FRANCISCO--Seismologists studying the recent dramatic upswing in earthquakes triggered by human activity want to clear up a few common misconceptions about the trend.
There is increasing evidence that these earthquakes are caused by injecting fluids from oil and gas operations deep into the earth. These human-caused earthquakes are sometimes called "induced earthquakes."
A Seismological Research Letters focus section to be published online June 10 addresses some common misconceptions about induced seismicity--the biggest of which is that it is primarily related ...
Scientists at the University of York have made a significant advance that could make cell-based treatments for arthritis less of a lottery.
Researchers in the Departments of Biology and Physics at York, working with colleagues at the Erasmus Medical Centre in Rotterdam, have identified individual stem cells that can regenerate tissue, cartilage and bone.
The stem cells are mixed within human bone marrow stromal cells (MSCs) but are similar in appearance and previously, scientists had difficulty in distinguishing between them. The York researchers isolated individual MSCs ...
An unexpected finding by an international team of scientists based at The University of Manchester and National Institutes of Health in America has shed new light on how immune cells are programmed to either repair or protect the body.
It's hoped the discovery will inform the development of better treatments for a range of conditions from inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) to certain cancers.
The research, led by Dr John Grainger from the Manchester Collaborative Centre for Inflammation Research (MCCIR) and Dr Yasmine Belkaid from the National Institute of Allergy and ...
Large magnetic storms from the Sun, which affect technologies such as GPS and utility grids, could soon be predicted more than 24 hours in advance.
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are eruptions of gas and magnetised material from the Sun that have the potential to wreak havoc on satellites and Earth-bound technologies, disrupting radio transmissions and causing transformer blowouts and blackouts.
These mass ejections can cause problems with GPS technology - used by all kinds of vehicles, from cars to oil tankers to tractors. For example, they can affect the ability of ...
What:
The Makona strain of Ebola virus (EBOV) circulating in West Africa for the past year takes roughly two days longer to cause terminal disease in an animal model compared to the original 1976 Mayinga strain isolated in Central Africa, according to a new National Institutes of Health (NIH) report. The results provide important information to scientists who have wondered if the Ebola virus in West Africa is becoming more severe. In fact, the new study suggests the current virus has a decreased ability to cause disease in their animal model compared to the 1976 strain.
Using ...
This news release is available in Spanish.
CRG scientists describe a new mechanism shaping cells and generating cell contractile forces during development and organogenesis.
The new mechanism, which has been published today in the journal Developmental Cell, includes strategies shared with programmed cell death but which have not previously been directly associated with force generation.
Studying developmental processes such as the one presented in the Dev. Cell paper contributes to a better understanding of organ development and maintenance. Also, ...