New web tool allows public to compare quality of long-term care homes
2015-06-10
(Press-News.org) The public can now make a more informed choice about long-term care thanks to a new online tool launched today that compares facilities across Canada based on nine indicators such as safety, quality of life and general health of residents.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo led the development of the assessment criteria and quality measures that will allow people to compare data of more than 1,000 facilities. They are members of interRAI, a global network developing assessment and screening tools to support vulnerable populations.
'This website provides Canadians with an authoritative source of information about quality of care in nursing homes,' said professor John Hirdes, of the School of Public Health and Health Systems at Waterloo, and who developed the indicators in collaboration with researchers at the University of Michigan and Harvard University. 'It creates an opportunity for transparency and accountability in long-term care.'
The searchable database is an extension of 'Your Health System: In Depth,' an interactive website of the Canadian Institute for Health Information (CIHI). The launch marks the first time CIHI has made this information about nursing homes publicly available. The organization has been collecting and reporting on the information for the last 10 years.
'The results are really a starting point for conversation,' said professor Chris Perlman, also at the School of Public Health and Health Systems in Waterloo's Faculty of Applied Health Sciences. 'The indicators create an opportunity for collaboration, for administrators to talk with each other and learn from best practices.'
INFORMATION:
Your Health System first launched in 2013 in order to provide health-care professionals and the general public with information on health-care access, quality and outcomes. The site has two sections: an In-Depth section for managers to identify areas for improvement based on 45 health-system indicators from both the acute care and long-term care sectors, and an In Brief section for the public to review how their health system is performing within a city, region, province or territory. The addition of the long-term care indicators provides Canadians with an even greater perspective of how the health care system is performing.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-10
A large data-mining study carried out by investigators at the Stanford University School of Medicine has linked a popular class of heartburn drugs to an elevated risk of heart attack.
Proton-pump inhibitors, or PPIs, are among the world's most widely prescribed drugs, with $14 billion in annual sales. They are effective at lowering the acidity of the stomach, in turn preventing heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest that occurs when stomach acid rises up into the esophagus. In any given year, more than 20 million Americans -- about one in every 14 -- use PPIs such ...
2015-06-10
Chimpanzee may be able to use facial expressions and vocalizations flexibly, notably during physical contact play, according to a study published June 10, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Marina Davila-Ross from University of Portsmouth, UK and colleagues.
The ability to flexibly produce facial expressions and vocalizations has a strong impact on the way humans communicate, but scientists' understanding of nonhuman primate facial expressions and vocalizations is limited. The authors of this study investigated whether chimpanzees produce the same types of ...
2015-06-10
People reflecting on a roundtrip walk estimated that the return trip took less time than the outward trip, according to a study published June 10, 2015 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Ryosuke Ozawa from Kyoto University, and colleagues.
Many have experienced the "return trip effect," where the return trip seems shorter than the outward trip, even when the trips actually took the same amount of time. Scientists have studied the effect, but haven't confirm its existence in the context of the environment and duration of the real-life trip. To better understand the ...
2015-06-10
This news release is available in French.
A study at the University of Montreal shows that the market share of the five largest research publishing houses reached 50% in 2006, rising, thanks to mergers and acquisitions, from 30% in 1996 and only 20% in 1973. "Overall, the major publishers control more than half of the market of scientific papers both in the natural and medical sciences and in the social sciences and humanities," said Professor Vincent Larivière of the School of Library and Information Science, who led the study. "Furthermore, these large commercial ...
2015-06-10
Most Americans are aware that food waste is a problem, are concerned about it, and say they work to reduce their own waste, but nearly three-quarters believe that they waste less food than the national average, new research suggests.
The findings, from the Johns Hopkins Center for a Livable Future (CLF) at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, are significant given that 31 to 40 percent of the American food supply goes to waste, primarily in homes, stores and restaurants. The top foods wasted, by weight, are fruits and vegetables, due in part to their perishability ...
2015-06-10
People hospitalized for heart failure had a significantly lower chance of being readmitted within 30 days of discharge when treated with a cardiac resynchronization therapy device, or CRT, equipped with an algorithm to automatically deliver and adjust therapy when compared to those receiving the standard CRT optimized with echocardiography, according to a study today in JACC: Heart Failure.
A CRT device is a defibrillator that sends electrical impulses to the heart to help the chambers beat in synchronization and improves the heart's pumping function. It is an established ...
2015-06-10
Although hypertension is more common in African-Americans, they have significantly lower levels of a hormone produced in response to cardiac stress than white and Hispanic individuals, a finding that may indicate a target for prevention or treatment of heart disease, according to a study published today in JACC: Heart Failure.
Using data from the Dallas Heart Study, researchers assessed 3,148 patients and examined the association between race and ethnicity and levels of natriuretic peptides -- which are hormones produced in response to increased cardiac wall stress common ...
2015-06-10
In preliminary experiments with mice and lab-grown cells, Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center scientists have found that a protein-signaling process accelerates the work of the gene most frequently mutated in a common form of adult leukemia and is likely necessary to bring about the full-blown disease.
The Kimmel team, in a report published in the June 10 issue of Science Translational Medicine, demonstrated the impact of the so-called Hedgehog protein signaling pathway by successfully using a combination of two drugs to both block the activity of the mutated gene, called ...
2015-06-10
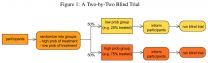
PRINCETON, N.J.--Double-blind clinical trials for new drugs are considered the "gold standard" of medical research because they're designed to determine the efficacy of a treatment free from doctor and participant bias.
But one effect these trials fail to measure is how a medication's performance can vary based on patients' lifestyle choices, especially if patients change their habits because they are anticipating treatment, according to a new study published in PLOS ONE.
A recent meta-analysis of six clinical trials, led by researchers from Princeton University, the ...
2015-06-10
A key potential 'benefit' of global warming--namely, that plants at northern latitudes will thrive in a warmer world--is challenged by a new study released by University of Hawai'i scientists today.
The prevailing assumption ignores the fact that plants in the North will remain limited by solar radiation, curbing positive effects of warming and additional CO2 availability. In addition, that same warming could surpass plant temperature tolerances in tropical areas around the world, and further be accompanied by drought.
"Those that think climate change will benefit plants ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New web tool allows public to compare quality of long-term care homes