NASA saw Tropical Depression 3-E coming together
2015-06-11
(Press-News.org) The third tropical depression of the active Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season formed and NASA's RapidScat saw its winds coming together as it formed. NASA's Terra satellite provided an image of the storm's cloud extent showing bands of thunderstorms wrapping into its center.
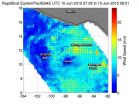
RapidScat is a scatterometer instrument that flies aboard the International Space Station and can measure surface winds over the ocean. On June 10 from 07:28 to 09:01 UTC (3:28 to 5:01 a.m. EDT) RapidScat collected wind data on the strengthening tropical low pressure area known as System 94E. Strongest sustained winds during that time period were near 15 meters per second (mps)/33.5 mph/54 kph) in areas north and east of the center. Sustained winds around the rest of the low were weaker. The RapidScat image also showed that the low had good circulation.
As System 94E continued organizing NASA's Terra satellite passed overhead at 17:25 UTC (1:25 p.m. EDT). The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard captured infrared data on the tropical low pressure area, revealing a powerful, thick band of thunderstorms spiraling into the center from the northern quadrant of the storm. The storm continued to consolidate overnight and by June 11, Tropical Depression 03E was born.
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) the National Hurricane Center (NHC) placed the center of Tropical Depression Three-E near latitude 13.1 North and longitude 100.2 West. That's about 265 miles (425 km) south of Acapulco, Mexico. Maximum sustained winds remain near 35 mph (55 kph) with higher gusts. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1003 millibars (29.62 inches). The depression is moving toward the northwest near 8 mph (13 kph). A turn toward the north and a decrease in forward speed are expected to occur later today or tonight.
TD03E is close enough to the coast to cause ocean swells, bring rainfall and gusty winds. The NHC noted that locally heavy rains could spread over portions of the southern coast of Mexico, primarily in the states of Oaxaca and Guerrero, during the next couple of days. In addition, swells associated with the depression are expected to increase near the coast of southern Mexico during the next few days.
These swells could cause life-threatening surf and rip current conditions.
Strengthening is forecast during the next 48 hours, and the depression is expected to become a tropical storm later today.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-11
Researchers have identified two critical mutations allowing the deadly Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) virus to transmit from bats to humans. The findings were published in the most recent edition of the Journal of Virology.
Leading the research was Fang Li, Ph.D., associate professor of Pharmacology at the University of Minnesota Medical School. Graduate students Yang Yang and Chang Liu from Professor Fang Li's lab participated in the research. The study was conducted in collaboration with Shibo Jiang, M.D. , Ph.D., and Lanying Du, Ph.D., from the New York Blood ...
2015-06-11
Comparing the genomes of different species -- or different members of the same species -- is the basis of a great deal of modern biology. DNA sequences that are conserved across species are likely to be functionally important, while variations between members of the same species can indicate different susceptibilities to disease.
The basic algorithm for determining how much two sequences of symbols have in common -- the "edit distance" between them -- is now more than 40 years old. And for more than 40 years, computer science researchers have been trying to improve upon ...
2015-06-11
PHILADELPHIA -- More than one-third of counties in the Unites States are located more than 50 miles from the nearest gynecologic oncologist, making access to specialty care for ovarian and other gynecologic cancers difficult for nearly 15 million women. While most of these "low access" counties are located in the Mountain-West and Midwest regions, the findings of a recent study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania also reveal that 47 states have at least one county located more than 50 miles from the nearest gynecologic oncologist. ...
2015-06-11
PHILADELPHIA - According to a new study, women experiencing difficulty with time management, attention, organization, memory, and problem solving - often referred to as executive functions - related to menopause may find improvement with a drug already being used to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The study led by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania is the first to show that lisdexamfetamine (LDX) improved subjective and objective measures of cognitive decline commonly experienced in menopausal women. Results ...
2015-06-11
Researchers from Boston Children's Hospital and Merck have built the beginnings of "digital phenotype" of insomnia and other sleep disorders based on data from Twitter. This study, published today in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is one of the first to look at relationships between social media use and sleep issues, and--based on assessments the sentiments expressed in users' tweets--gives preliminary hints that patients with sleep disorders may be a greater risk of psychosocial issues.
The study--led by Jared Hawkins, PhD; David McIver, PhD; and John Brownstein, ...
2015-06-11
Philadelphia, PA - "The impact of human mobility on disease dynamics has been the focus of mathematical epidemiology for many years, especially since the 2002-03 SARS outbreak, which showed that an infectious agent can spread across the globe very rapidly via transportation networks," says mathematician Gergely Röst. Röst is co-author of a paper to be published this week in the SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems that presents a mathematical model to study the effects of individual movement on infectious disease spread.
"More recently, the risk of polio ...
2015-06-11
Washington D.C., June 11, 2015 - A study published in the June 2015 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry demonstrates that the atypical trajectory of cortical/brain development in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) extends well beyond young childhood and into late adolescence and young adulthood.
A considerable amount of work has focused on early structural brain development in ASD utilizing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This body of work has revealed evidence for brain overgrowth during the early postnatal years that appears ...
2015-06-11
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--An MIT team has developed a way of making soft materials, using a 3-D printer, with surface textures that can then be modified at will to be perfectly smooth, or ridged or bumpy, or even to have complex patterns that could be used to guide fluids.
The process, developed using detailed computer simulations, involves a material that is composed of two different polymers with different degrees of stiffness: More rigid particles are embedded within a matrix of a more flexible polymer. When squeezed, the material's surface changes from smooth to a pattern ...
2015-06-11
June 11, 2015 - The well-known "fight or flight" response is part of the inborn series of defense/fear responses activated in reaction to threats. Understanding the steps of the defense cascade can help in forming effective treatments for patients dealing with persistent aftereffects of trauma, according to a review in the Harvard Review of Psychiatry. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
Child and adolescent psychiatrist Kasia Kozlowska of The Children's Hospital at Westmead, Australia, and colleagues explain the five steps of the defense cascade, in a framework ...
2015-06-11
In a study that seems to defy conventional dietary wisdom, University of Iowa scientists have found that adding high salt to a high-fat diet actually prevents weight gain in mice.
As exciting as this may sound to fast food lovers, the researchers caution that very high levels of dietary salt are associated with increased risk for cardiovascular disease in humans. Rather than suggest that a high salt diet is suddenly a good thing, the researchers say these findings really point to the profound effect non-caloric dietary nutrients can have on energy balance and weight gain.
"People ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA saw Tropical Depression 3-E coming together