(Press-News.org) Boston, MA - More than half of all children and adolescents in the U.S. are not getting enough hydration--probably because they're not drinking enough water--a situation that could have significant repercussions for their physical health and their cognitive and emotional functioning, according to the first national study of its kind from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The study also found racial/ethnic and gender gaps in hydration status. Black children and adolescents were at higher risk of inadequate hydration than whites; boys were at higher risk than girls.
The study appears online June 11, 2015 in the American Journal of Public Health.
"These findings are significant because they highlight a potential health issue that has not been given a whole lot of attention in the past," said lead author Erica Kenney, a postdoctoral research fellow in the Department of Social and Behavioral Sciences at Harvard Chan School. "Even though for most of these kids this is not an immediate, dramatic health threat, this is an issue that could really be reducing quality of life and well-being for many, many children and youth."
Drinking enough water is essential for physiological processes such as circulation, metabolism, temperature regulation, and waste removal. Although excessive dehydration is associated with serious health problems, even mild dehydration can cause issues, including headaches, irritability, poorer physical performance, and reduced cognitive functioning.
The researchers looked at data from 2009-2012 on more than 4,000 children and adolescents aged 6 to 19 years who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a study of the health of U.S. children and adults conducted each year by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They used urine osmolality--a measure of how concentrated a person's urine is--to determine whether or not participants were adequately hydrated.
They found that a little more than half of all children and adolescents weren't getting enough hydration. Boys were 76% more likely than girls, and non-Hispanic blacks were 34% more likely than non-Hispanic whites, to be inadequately hydrated.
Notably, nearly a quarter of the children and adolescents in the study reported drinking no plain water at all.
"The good news is that this is a public health problem with a simple solution," said senior author Steven Gortmaker, professor of the practice of health sociology. "If we can focus on helping children drink more water--a low-cost, no-calorie beverage--we can improve their hydration status, which may allow many children to feel better throughout the day and do better in school."
INFORMATION:
Other Harvard Chan School authors of the study included Angie Cradock, senior research scientist and deputy director of the Harvard Prevention Research Center, and research fellow Michael Long.
This study was supported by Cooperative Agreement No. 1U48DP001946 (including the Nutrition and Obesity Policy Research and Evaluation Network) from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Prevention Research Centers Program and a grant in memory of Melvin R. Seiden.
"Prevalence of Inadequate Hydration among US Children and Disparities by Gender and Race/Ethnicity: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2009-2012," Erica L. Kenney, Michael W. Long, Angie L. Cradock, Steven L. Gortmaker, American Journal of Public Health, online June 11, 2015, doi:10.2105/AJPH.2015.302572.
Visit the Harvard Chan website for the latest news, press releases, and multimedia offerings.
Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health brings together dedicated experts from many disciplines to educate new generations of global health leaders and produce powerful ideas that improve the lives and health of people everywhere. As a community of leading scientists, educators, and students, we work together to take innovative ideas from the laboratory to people's lives--not only making scientific breakthroughs, but also working to change individual behaviors, public policies, and health care practices. Each year, more than 400 faculty members at Harvard Chan teach 1,000-plus full-time students from around the world and train thousands more through online and executive education courses. Founded in 1913 as the Harvard-MIT School of Health Officers, the School is recognized as America's oldest professional training program in public health. END
Though many people believe they can recognize when someone is lying, detecting deception is difficult. Accuracy rates in experiments have proven to be only slightly greater than chance, even among trained professionals.
But a new study published recently in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) finds that groups are consistently more accurate in distinguishing truths from lies than one individual is.
In 'Group discussion improves lie detection,' by University of Chicago Booth School of Business Professor Nicholas Epley and Chicago Booth doctoral student ...
Not all of America's most admired companies are killing it on social media. In fact, some are almost flat lining, according to a team of researchers.
Several firms on Fortune Magazine's list of America's most admired companies are failing to achieve basic social media standards, let alone best practices, according to Marcia DiStaso, associate professor of public relations, Penn State.
"We were surprised that not all the companies had a Twitter account, for instance, and not every company had a Facebook page, or a YouTube page," said DiStaso. "There are top companies ...
Beverly, MA, June 11, 2015 - Cardiac surgeons often "crack open" the flat bone that forms the middle front section of the chest, known as the sternum, in order to reach important structures. When a sternal wound infection (SWI) occurs, serious complications and even death may result. Implanting antibiotic-laden sponges between the sternal halves before closure has been adapted to prevent infections. While a recent report questioned this practice, a meta-analysis in The Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, the official publication of the American Association for ...
Nursing home residents with dementia are less likely to be apathetic if they live in an appropriately stimulating environment, according to nursing researchers.
Nearly half of all residents in nursing homes have dementia, according to a 2013 report by the Centers for Disease Control. Apathy is one of the most common neurobehavioral symptoms in dementia, with about 90 percent of older adults with dementia experiencing it. Those with mild dementia will decline more quickly into severe dementia if they also suffer from apathy, making it important to help them stay engaged. ...
Lehigh University engineers, materials scientists and chemists will present their innovative breakthroughs to a national showcase of investors and industrial partners at the TechConnect 2015 World Innovation Conference and National Innovation Showcase in Washington on June 14-17.
Working at the junction of engineering and health, the Lehigh innovations include a nanoscale device that captures tumor cells in the blood, a bioengineered enzyme that scrubs microbial biofilms and the creation of a safe and efficient chemical reagent that is stable at room temperature.
These ...
DARIEN, Ill. -- A new study suggests that bright light at the end of a night shift may have potential as a countermeasure to improve driving performance, particularly for low light work environments and commutes that occur before dawn.
Results show that temperature, subjective alertness and psychomotor vigilance performance decreased significantly across the night. Bright light significantly suppressed melatonin, but did not improve subjective alertness or psychomotor vigilance performance. Sleep deprivation markedly increased incidents, accidents, and the average lane ...
LEXINGTON, Ky., June 12 -- In a new University of Kentucky study published today in Cell Reports, a leading scientific journal in cell biology, researchers describe a new molecular mechanism that contributes to age-related macular degeneration (AMD) due to accumulation of excessive iron within the cells of the retina.
Cells of the body use iron in dozens of normal metabolic processes. However, excessive iron or 'iron overload' can be very damaging to cells and tissues, and is implicated in numerous diseases, including AMD.
'The reason that cells die due to iron ...
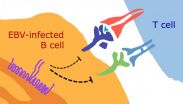
About 90% of adults worldwide are infected with Epstein-Barr virus, or EBV. The virus infects B cells (the white blood cells that make antibodies) and can contribute to B-cell-derived cancers, but in most people it remains dormant--a state scientists refer to as "latent infection"--for the rest of their lives. A study published on June 11th in PLOS Pathogens sheds new light on why the infected person's immune system cannot eliminate EBV, or the associated cancer risk.
Interested in the immune response against EBV, Andreas Moosmann, from the Helmholtz-Zentrum in Munich, ...
It's difficult enough to see things in the dark, but what if you also had to hover in mid-air while tracking a flower moving in the wind? That's the challenge the hummingbird-sized hawkmoth (Manduca sexta) must overcome while feeding on the nectar of its favorite flowers.
Using high-speed infrared cameras and 3-D-printed robotic flowers, scientists have now learned how this insect juggles these complex sensing and control challenges - all while adjusting to changing light conditions. The work shows that the creatures can slow their brains to improve vision under low-light ...
ANN ARBOR--Variations in the amount of oxygen in Earth's atmosphere significantly altered global climate throughout the planet's history. Efforts to reconstruct past climates must include this previously overlooked factor, a new University of Michigan-led study concludes.
Oxygen currently comprises about 21 percent of Earth's atmosphere by volume but has varied between 10 percent and 35 percent over the past 541 million years.
In periods when oxygen levels declined, the resulting drop in atmospheric density led to increased surface evaporation, which in turn led to ...