(Press-News.org) Background: According to Sturgis, the incidence of HPV-positive oropharyngeal carcinoma has increased dramatically in recent years. Although patients with HPV-positive disease have a better prognosis than those with HPV-negative disease, researchers are still seeking a better understanding of what group of patients is more likely to respond to treatment.
How the Study Was Conducted: Sturgis and colleagues used blood samples from 209 patients with previously untreated oropharyngeal carcinoma, including 96 who had confirmed HPV-positive disease, and screened the samples for HPV16 antibodies E1, E4-7, L1, L2, and the N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of E2. Samples were taken as part of the initial patient workup, six weeks after the end of treatment, and at six-month intervals up to three years.
Results: Patients who were positive for any of the E antibodies tested had improved overall and progression-free survival compared with those negative for the antibodies. The five-year overall survival estimate for patients positive for E antibodies was 87.4 percent compared with 42.2 percent for patients negative for E antibodies. The five-year progression-free survival estimate was 82.9 percent for antibody-positive patients compared with 46.1 percent for antibody-negative patients.
Patients with HPV-positive disease who were also positive for the NE2, E1, or E6 antibodies had an 80 percent reduced risk for death and a 70 percent reduced risk for disease progression.
No survival advantage was noted for the L antibodies tested in the study.
E proteins of HPV are antigens that play a role in HPV-mediated carcinogenesis, and L proteins are involved in the development of the virus shell, which are lost once the HPV DNA is integrated into human DNA, Sturgis explained.
Author Comment: In an interview, Sturgis said, ""We found that patients who were serologically positive to the E proteins of HPV16 had a better prognosis than those patients who were seronegative to these antigens. This seemed particularly true of patients who had tumors that we could confirm were HPV-positive.
"If this testing became commercially available it could not only be used as a means of identifying people who are at risk for oropharyngeal and other HPV cancers, but may also allow identification of HPV-related oropharyngeal cancer patients at greater or lower risk for cancer recurrence and death. These data further suggest that if we can modify patient immunity and increase a patient's E antibody response, we might be able to affect cancer outcomes," Sturgis added. "Clinical trials are now testing whether vaccines that can stimulate these antibodies have clinical utility in HPV-related cancers."
INFORMATION:
Main Finding(s): The presence of certain human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 antibodies in the blood was associated with improved rates of survival among patients with HPV-related oropharyngeal carcinoma.
Journal in Which the Study was Published: Clinical Cancer Research, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research
Author: Erich M. Sturgis, MD, MPH, professor in the Department of Head and Neck Surgery at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
To interview Erich Sturgis, contact Ron Gilmore at rlgilmore1@mdanderson.org or 713-745-1898. For other inquiries, contact Lauren Riley at lauren.riley@aacr.org or 215-446-7155.
Funding & Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Arizona State University institutional funds, the National Cancer Institute Early Detection Research Network, and the Stiefel Oropharyngeal Research Fund. Sturgis declares no conflicts of interest.
Follow us: Cancer Research Catalyst http://blog.aacr.org; Twitter @AACR; and Facebook http://www.facebook.com/aacr.org
About the American Association for Cancer Research
Founded in 1907, the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) is the world's oldest and largest professional organization dedicated to advancing cancer research and its mission to prevent and cure cancer. AACR membership includes more than 35,000 laboratory, translational, and clinical researchers; population scientists; other health care professionals; and cancer advocates residing in 101 countries. The AACR marshals the full spectrum of expertise of the cancer community to accelerate progress in the prevention, biology, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer by annually convening more than 25 conferences and educational workshops, the largest of which is the AACR Annual Meeting with almost 19,300 attendees. In addition, the AACR publishes eight prestigious, peer-reviewed scientific journals and a magazine for cancer survivors, patients, and their caregivers. The AACR funds meritorious research directly as well as in cooperation with numerous cancer organizations. As the Scientific Partner of Stand Up To Cancer, the AACR provides expert peer review, grants administration, and scientific oversight of team science and individual investigator grants in cancer research that have the potential for near-term patient benefit. The AACR actively communicates with legislators and other policymakers about the value of cancer research and related biomedical science in saving lives from cancer. For more information about the AACR, visit http://www.AACR.org.
Background: Pietras said that although prognosis for breast cancer is relatively good when detected in its early stages, metastatic disease is the cause of 90 percent of all cancer-related deaths. Therefore, learning more about the metastatic process and finding new cures to inhibit disease spread is at the center of clinical attention.
He explained that in order for a tumor to spread, a cancer cell must detach and traverse the vascular wall to escape into the blood stream, exit the vasculature to enter the metastatic site, and colonize the new tissue. The fact that ...
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: Women with endometriosis are at an increased risk of miscarriage and ectopic pregnancy, according to results of a huge nationwide study presented today. Moreover, women with a history of endometriosis whose pregnancies progressed beyond 24 weeks were found to be at a higher than average risk of complications, including haemorrhage (ante- and postpartum) and preterm birth.
"These results indicate that endometriosis predisposes women to an increased risk of early pregnancy loss and later pregnancy complications," said the study's first author Dr Lucky ...
Medical guidance on how to care for elderly people with dementia following a hip fracture is 'sadly lacking' according to researchers at the University of East Anglia.
Almost half of all people who suffer hip fractures also have dementia. But a Cochrane Review published today reveals there is no conclusive evidence on how to care for this particularly vulnerable group.
The review, which was funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), highlights an urgent need for better research into what strategies improve post-operative care - both within hospital ...
More than 60,000 Australians are estimated to have reduced or discontinued their use of prescribed cholesterol-lowering statin medications following the airing of a two-part series critical of statins by ABC TV's science program, Catalyst, a University of Sydney study reveals in the latest Medical Journal of Australia.
The analysis of the Pharmaceutical Benefits Scheme medication records of 191,000 people revealed that there was an immediate impact after Catalyst was aired in October 2013, with 14,000 fewer people dispensed statins per week than expected.
"In the eight ...
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Ms Arbjerg Højen said: "Young VTE patients are scared of having another VTE and of dying. We treat these patients in our Thrombosis Research Unit and have seen how anxious and mentally unwell they can be, even a long time after the VTE occurs. They are troubled and have a hard ...
Rome, Italy, 13 June 2015: The results of an interventional trial presented today at the European League Against Rheumatism Annual Congress (EULAR 2015) showed that use of the disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug hydroxychloroquine for 24 weeks did not diminish mild-moderate pain from primary hand osteoarthritis (OA). Furthermore, treatment did not improve overall physical, social and emotional wellbeing. These findings suggest that hydroxychloroquine should no longer be routinely prescribed for patients with this form of arthritis.
OA is the most common type of arthritis, ...
Rome, Italy, 13 June 2015: The results of a study presented today at the European League Against Rheumatism Annual Congress (EULAR 2015) showed that, in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, a good clinical response to maintenance treatment with a tumour necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) was maintained even when the dose was reduced by one-third.
Reducing the TNFi dose by two-thirds resulted in more flares (exacerbations of symptoms and signs) but these subsided when the higher dose of TNFi was restarted, and did not adversely affect subsequent progression of any disability. ...
Time may heal all wounds, but in the case of stroke survivors, the key to better recovery is to spend more time in an intensive physical therapy program, according to a University of Florida Health study.
After a stroke, the brain and body can start recovering immediately and can show improvement up to six months afterward, said UF Health researcher Janis Daly, Ph.D. But this study focused on people who had persistent disability even a year or more after completing standard care. The study found that extensive physical therapy helped them recover motor function, even ...
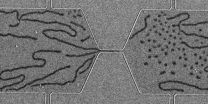
New ideas are bubbling up for more efficient computer memory.
Researchers at UCLA and the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory announced today a new method for creating magnetic skyrmion bubbles at room temperature. The bubbles, a physics phenomenon thought to be an option for more energy-efficient and compact electronics, can be created with simple equipment and common materials.
Skyrmions, discovered just a few years ago, are tiny islands of magnetism that form in certain materials. If you wrapped one up into a sphere, its magnetic fields would ...
African-American adults -- particularly women -- are much more likely to know or be related to someone behind bars than whites, according to the first national estimates of Americans' ties to prisoners.
The research, led by Hedwig Lee, University of Washington associate professor of sociology, reveals the racial inequality wrought by the U.S. prison boom, with potentially harmful consequences to families and communities left lacking social supports for raising children and managing households.
In an article published May 20 in the Du Bois Review: Social Science Research ...