A KAIST research team develops the first flexible phase-change random access memory
2015-06-15
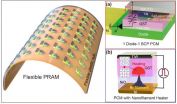
(Press-News.org) Daejeon, Republic of Korea, Jun 15, 2015 -- Phase change random access memory (PRAM) is one of the strongest candidates for next-generation nonvolatile memory for flexible and wearable electronics. In order to be used as a core memory for flexible devices, the most important issue is reducing high operating current. The effective solution is to decrease cell size in sub-micron region as in commercialized conventional PRAM. However, the scaling to nano-dimension on flexible substrates is extremely difficult due to soft nature and photolithographic limits on plastics, thus practical flexible PRAM has not been realized yet.
Recently, a team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed the first flexible PRAM enabled by self-assembled block copolymer (BCP) silica nanostructures with an ultralow current operation (below one quarter of conventional PRAM without BCP) on plastic substrates. BCP is the mixture of two different polymer materials, which can easily create self-ordered arrays of sub-20 nm features through simple spin-coating and plasma treatments. BCP silica nanostructures successfully lowered the contact area by localizing the volume change of phase-change materials and thus resulted in significant power reduction. Furthermore, the ultrathin silicon-based diodes were integrated with phase-change memories (PCM) to suppress the inter-cell interference, which demonstrated random access capability for flexible and wearable electronics. Their work was published in the March issue of ACS Nano: "Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Another way to achieve ultralow-powered PRAM is to utilize self-structured conductive filaments (CF) instead of the resistor-type conventional heater. The self-structured CF nanoheater originated from unipolar memristor can generate strong heat toward phase-change materials due to high current density through the nanofilament. This ground-breaking methodology shows that sub-10 nm filament heater, without using expensive and non-compatible nanolithography, achieved nanoscale switching volume of phase change materials, resulted in the PCM writing current of below 20 uA, the lowest value among top-down PCM devices. This achievement was published in the June online issue of ACS Nano "Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition." In addition, due to self-structured low-power technology compatible to plastics, the research team has recently succeeded in fabricating a flexible PRAM on wearable substrates.
Professor Lee said, "The demonstration of low power PRAM on plastics is one of the most important issues for next-generation wearable and flexible non-volatile memory. Our innovative and simple methodology represents the strong potential for commercializing flexible PRAM."
In addition, he wrote a review paper regarding the nanotechnology-based electronic devices in the June online issue of Advanced Materials entitled "Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-15
From the adventures of Lara Croft in Tomb Raider to the apocalyptic drama of Fallout - new research from the University of Warwick has revealed the secret to how some of the world's most iconic video games were created.
Professor David Stark says it is because the creative teams behind these ground-breaking titles had the ideal mix of career backgrounds and working relationships.
He claims his research offers a fresh insight into the factors which
stimulate innovation - theories that can also apply away from the video gaming industry.
The 'Big Data' analysis looked ...
2015-06-15
Humans are unlikely to be the only animal capable of self-awareness, a new study has shown.
Conducted by University of Warwick researchers, the study found that humans and other animals capable of mentally simulating environments require at least a primitive sense of self. The finding suggests that any animal that can simulate environments must have a form of self-awareness.
Often viewed as one of man's defining characteristics, the study strongly suggests that self-awareness is not unique to mankind and is instead likely to be common among animals.
The researchers, ...
2015-06-15
Scientists from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed a new technique to more precisely analyze bacterial populations, to reveal epigenetic mechanisms that can drive virulence. The new methods hold the promise of a potent new tool to offset the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance by bacterial pathogens. The research was published today in the journal Nature Communications, and conducted in collaboration with New York University Langone Medical Center and Brigham and Women's Hospital of Harvard Medical School.
The information content of the ...
2015-06-15
Scientists at Helmholtz Zentrum München have now discovered how Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) conceals itself in human cells. A main culprit for its bad visibility by the immune system is the viral protein LMP2A. As published in the scientific journal PLOS Pathogens, the protein helps EBV-infected cells hide from T cells. This camouflage through the LMP2A protein may play a major role in the causation of cancer by EBV.
„We suspected that a viral protein was behind EBV's camouflage in cancerous cells", says Dr. Andreas Moosmann from the Research Unit Gene Vectors ...
2015-06-15
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- After this year's legalization of powdered alcohol, some states have already banned it -- a move that the majority of the public supports, according to a new University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health.
Adults across the country share the same top concern about the new alcohol-on-the-go product: potential misuse among underage youth.
Packaged in travel-friendly pouches, powdered alcohol will be available in flavors of distilled spirits like vodka and rum and also mixed drinks. One packet of powdered alcohol ...
2015-06-15
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: In October last year the Gothenburg, Sweden, group of Mats Bra?nnstro?m announced the world's first live birth following the transplantation of a donated uterus.(1) In an editorial accompanying the report, The Lancet listed this remarkable achievement as comparable to only three other landmarks in the history of reproductive medicine: "the arrival of in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) in the late 1970s; the development of intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) in the early 1990s; the first ovarian transplant a decade ago; and [now] the first live birth ...
2015-06-15
Lisbon, 15 June 2015: The academic performance of children conceived by assisted reproduction techniques (ART) is no better or worse than that of spontaneously conceived children when assessed at the ninth grade of their school education.(1) Similarly, ART singletons and ART twins also had comparable test scores, suggesting, say the investigators, that "the higher obstetric risk" identified in ART pregnancies - and particularly in twins - "is not associated with poorer academic performance in adolescence".(2)
"These findings are very important for infertile patients," ...
2015-06-15
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Professor Gafarov said: "Mortality from cardiovascular diseases accounts for nearly 50% of the total mortality among the population. Nearly 80% of deaths from cardiovascular disease are due to myocardial infarction (heart attack) and stroke. It means that today we are talking about ...
2015-06-15
"It is my coronary artery and my coronary artery calcification and I am facing a real risk and challenge," said one patient.
EuroHeartCare is the official annual meeting of the Council on Cardiovascular Nursing and Allied Professions (CCNAP) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). The 2015 meeting is held 14 to 15 June in Dubrovnik, Croatia, in collaboration with the Croatian Association of Cardiology Nurses.
Ms Mols said: "Patients with non-obstructive coronary artery disease and hyperlipidaemia (high blood lipids) urgently need to improve their lifestyles and ...
2015-06-15
The American Thoracic Society has released a policy statement with recommendations for clinicians and the general public on achieving good quality sleep and getting an adequate quantity of sleep.
"Sleep plays a vital role in human health, yet there is a lack of sufficient guidance on promoting good sleep health," said Sutapa Mukherjee, MBBS, PhD, chair of the committee that produced the statement. "In this statement, with an eye towards improving public health, we address the importance of good quality sleep with a focus on sleep health in adults and children; the effects ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A KAIST research team develops the first flexible phase-change random access memory

