(Press-News.org) Rich, creamy, nutritious and now cancer fighting. New research reveals that molecules derived from avocados could be effective in treating a form of cancer.
Professor Paul Spagnuolo from the University of Waterloo has discovered a lipid in avocados that combats acute myeloid leukemia (AML) by targeting the root of the disease - leukemia stem cells. Worldwide, there are few drug treatments available to patients that target leukemia stem cells.
AML is a devastating disease and proves fatal within five years for 90 per cent of seniors over age 65. Spagnuolo's new avocado-derived drug could one day significantly increase life expectancy and quality of life for AML patients.
"The stem cell is really the cell that drives the disease," said Professor Spagnuolo, in Waterloo's School of Pharmacy. "The stem cell is largely responsible for the disease developing and it's the reason why so many patients with leukemia relapse. We've performed many rounds of testing to determine how this new drug works at a molecular level and confirmed that it targets stem cells selectively, leaving healthy cells unharmed."
Spagnuolo's research is published today in Cancer Research, a top-ten oncology journal. Through partnership with the Centre for Commercialization of Regenerative Medicine (CCRM) he has also filed a patent application for the use of the compound, named avocatin B, to treat AML.
"It's an exciting time for our lab. With the help of CCRM we are now pursuing commercial partnership that would take avocatin B into clinical trials," said Professor Spagnuolo. "Not only does avocatin B eliminate the source of AML, but its targeted, selective effects make it less toxic to the body, too."
The drug is still years away from becoming approved for use in oncology clinics, but Spagnuolo is already performing experiments to prepare the drug for a Phase I clinical trial. This is the first round of trials where people diagnosed with AML could have access to the drug.
Professor Spagnuolo is among only a handful of researchers worldwide, applying the pharmaceutical industry's rigorous drug discovery research processes to food-derived compounds, called nutraceuticals.
There are multiple potential applications for Avocatin B beyond oncology, and the drug is just one of several promising compounds that Spagnuolo and his team have isolated from a library of nutraceuticals. Most labs would use food or plant extracts, but Spagnuolo prefers the precision of using nutraceuticals with defined structures.
"Extracts are less refined. The contents of an extract can vary from plant to plant and year to year, depending on lots of factors - on the soil, the location, the amount of sunlight, the rain," said Spagnuolo. "Evaluating a nutraceutical as a potential clinical drug requires in-depth evaluation at the molecular level. This approach provides a clearer understanding of how the nutraceutical works, and it means we can reproduce the effects more accurately and consistently. This is critical to safely translating our lab work into a reliable drug that could be used in oncology clinics."
INFORMATION:
The University of Waterloo and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society of Canada fund Professor Spagnuolo's research on avocatin B. CCRM is a not-for-profit, public-private consortium that supports the development of technologies that accelerate the commercialization of stem cell- and biomaterials-based technologies and therapies.
The world's first study into the brain anatomy of a marine reptile that lived at the same time as the dinosaurs sheds light on how the reptilian brain adapted to life in the oceans.
The fossils of ichthyosaurs, which lived 150 to 200 million years ago, are often very well preserved, but they are commonly flattened. Now investigators have used computed tomography to create a 3-D scan of the animal's skull, revealing internal details of the palate and braincase that usually cannot be seen. A reconstruction of the brain shows the importance of vision for the predator, which ...
In a new study, older women who lived in places with higher air pollution had significantly reduced white matter in the brain. For the study, a research team took brain MRIs of 1403 women who were 71 to 89 years old and used residential histories and air monitoring data to estimate their exposure to air pollution in the previous 6 to 7 years.
The findings suggest that ambient particulate air pollutants may have a deleterious effect on brain aging.
"Investigating the impact of air pollution on the human brain is a new area of environmental neurosciences. Our study provides ...
The prevalence of smoking among undergraduate nursing and physiotherapy students in Spain decreased from 29.3% in 2003 to 18.2% in 2013. Many of the students remained unaware of the link between smoking and diseases such as bladder cancer or the negative health effects of second-hand smoke, which points to a significant deficiency in undergraduate training.
The majority of nursing and physiotherapy students recognized that healthcare professionals were role models in society, noted Dr. Beatriz Ordás, lead author of the Journal of Advanced Nursing study.
INFORMATION: ...
Following a decade of steady growth, use of bisphosphonates--medications that are effective for treating osteoporosis--declined in the United States by more than 50% from 2008 to 2012.
The sudden drop seemed to occur after media reports highlighted safety concerns, such as the development of certain fractures that occurred rarely in long-term users, despite the fact that the US Food and Drug Administration and the American Society of Bone and Mineral Research did not recommend any specific safety restrictions on bisphosphonates. The findings are published in the Journal ...
A new study shows that shorter telomeres--which are the protective caps at the end of a cell's chromosomes--are linked with worse survival in a progressive respiratory disease called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). In patients with IPF, excessive scar tissue forms in the lungs.
The average telomere length of IPF patients was significantly shorter than that of healthy individuals. Also, the telomere length of patients with IPF who died from their disease during the study was shorter than that of patients who survived.
The Respirology results support the theory that ...
A new global review reveals that elder abuse--which includes psychological, physical, and sexual abuse; neglect; and financial exploitation--is common among community-dwelling older adults and is especially prevalent among minority older adults. Older adults with cognitive and physical impairments or psychosocial distress are also at increased risk of elder abuse.
In North and South American epidemiological studies, the prevalence of elder abuse ranged from about 10% among cognitively intact older adults to 47% in older adults with dementia. In Europe, the prevalence ...
One of the body's own tools for preventing wound infections may actually interfere with wound healing, according to new research from Boston Children's Hospital. In a study published online in Nature Medicine, scientists from the hospital's Program in Cellular and Molecular Medicine (PCMM) found they could speed up wound healing in diabetic mice by keeping immune cells called neutrophils from producing bacteria-trapping neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs).
The study, led by PCMM senior investigator Denisa Wagner, Ph.D., and postdoctoral fellow Siu Ling Wong, Ph.D., ...
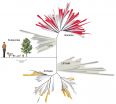
University of California, Berkeley, scientists have identified more than 35 new groups of bacteria, clarifying a mysterious branch of the tree of life that has been hazy because these microbes can't be reared and studied in the lab.
The new groups make up more than 15 percent of all known groups or phyla of bacteria, the scientists say, and include the smallest life forms on Earth, microbes a mere 400 nanometers across. The number of new bacterial phyla is equal to all the known animal phyla on Earth.
The scientists, who recently also identified nine new groups of microbes ...
Researchers estimate that 48.5 percent of the nearly 346,000 deaths from 12 cancers among adults 35 and older in 2011 were attributable to cigarette smoking, according to an article published online by JAMA Internal Medicine.
Researcher Rebecca L. Siegel, M.P.H., of the American Cancer Society, Atlanta, and coauthors provide an updated estimate because they note smoking patterns and the magnitude of the association between smoking and cancer death have changed in the past decade. While smoking prevalence decreased from 23.2 percent in 2000 to 18.1 percent in 2012, some ...
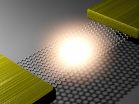
New York, June 15 -- Led by Young Duck Kim, a postdoctoral research scientist in James Hone's group at Columbia Engineering, a team of scientists from Columbia, Seoul National University (SNU), and Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) reported today that they have demonstrated -- for the first time -- an on-chip visible light source using graphene, an atomically thin and perfectly crystalline form of carbon, as a filament. They attached small strips of graphene to metal electrodes, suspended the strips above the substrate, and passed a current through ...