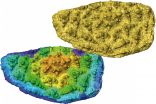
(Press-News.org) A University of Colorado Boulder scientist unexpectedly discovered two lichen species new to science in the same week while conducting research in Boulder Colorado, near the city's eastern limits.
After a day of fieldwork inventorying lichens at White Rocks Open Space, Erin Tripp was walking back to her car when an unfamiliar lichen caught her eye. Later that week, Tripp spotted a second species of lichen that she suspected might also be a new species.
Tripp, curator of botany for the University of Colorado Museum of Natural History and assistant professor of ecology and evolutionary biology, was collaborating with ecologist Lynn Riedel and other staff members at the City of Boulder's Open Space and Mountain Parks (OSMP) program to inventory the lichens along the sandstone cliffs that comprise White Rocks.
Lichens are complex life forms composed of at least two separate organisms, primarily a fungus and an alga that form a symbiotic relationship. They can live on soil, rocks, tree bark, desert sand, animal bones and rusty metal, for example.
"If you want to study Colorado lichens, you come here to the museum's Herbarium on campus, which has one of the most important collections of lichens in the country," said Tripp. "New species are generally found in less accessible parts of the world, rather than within city limits of a sizeable metropolis. Yet, here were these two new species to science within a 10-minute drive of CU-Boulder, which has a very long history of research in lichenology."
The two species Tripp discovered, Candelariella clarkii and Lecidea hoganii, are at present known only from their populations at White Rocks. They are distinctive by their morphology, anatomy and DNA. One has a charismatic yellowish-green color while the other is distinctive by its conspicuously raised fruiting bodies that are tinged pink on the inside.
The Herbarium's extensive botany collection requires devoted efforts by two collections managers who preserve and help curate some 550,000 specimens from around the world, some dating back more than 150 years. As a way of recognizing the staff members' dedication to advancing knowledge of Colorado botany, Tripp named the two new species after Dina Clark and Tim Hogan, collections managers of the Herbarium.
"Tim and Dina work endlessly and have dedicated their careers to building and preserving the collection, as well as extending its resources to others," said Tripp. "When I saw these species in the field, I thought immediately of Dina and Tim, and honoring their careers via eponymy."
Tripp verified that the two lichens were previously unknown to science through extensive study of the Herbarium's collections as well as reading the literature, historical and modern. DNA analyses conducted in Tripp's molecular lab helped to confirm that both were unknown to science. The two new species were formally described in collaboration with colleague James Lendemer of the New York Botanical Garden in the most recent issue of the journal The Bryologist.
Additionally, to facilitate lichen research and conservation by the city of Boulder, Tripp has prepared a field guide of the 57 species of lichens that occur at White Rocks, with high-resolution photos she took in the field. This book is currently under peer review at The University Press of Colorado. She also has authored a paper on the lichen biota at the White Rocks that will be published soon in the journal Western North American Naturalist.
At White Rocks, the unusual geology, its southern exposure and availability of water concentrated in transient springs support diverse vegetation and wildlife and allow other organisms -- such as the newly discovered lichens -- to flourish along the sandstone outcrops. Protected, moist and shady "microhabitats" created by the formation's rock ledges also contribute to the complex ecosystem found along the sandstone cliffs.
The state of Colorado has designated the 100-acre White Rocks site as a State Natural Area because of its high ecological value in providing habitat for uncommon and rare plant and animal species. The open space surrounding White Rocks is home to sensitive wildlife, including bald eagles, northern leopard frogs, northern harriers and the plains top minnow.
"The fact that White Rocks occurs within a sea of development in the Boulder-Longmont-Denver urban triangle makes the preserve that much more special ecologically," said Tripp.
Because of the sensitive ecological features of White Rocks, OSMP only provides public access to the area through staff-guided hikes during the summer.
"Every year, OSMP works with researchers to help us learn more about the lands we manage," said Brian Anacker, OSMP's research and data manger. "Their research provides important information that helps us protect, manage and restore habitat as well as understand how people enjoy a diverse range of recreational experiences on the city's open space."
As if discovering two new species of lichen in this small preserve wasn't enough, Tripp may have discovered two additional species of lichens that are possibly new to science. She is still studying them to confirm her theory.
"The discovery of new species in relatively densely populated regions of North America illustrates the ecological relevance of small patches of native habitat, which are certain to become even more important in the future," said Tripp. "My long-term goal is to expand the study of lichenology in Colorado and eventually produce a total inventory of what we have throughout the state."
INFORMATION:
A study of how people can quickly spot animals by sight is helping uncover the workings of the human brain.
Scientists examined why volunteers who were shown hundreds of pictures - some with animals and some without - were able to detect animals in as little as one-tenth of a second.
They found that one of the first parts of the brain to process visual information - the primary visual cortex - can control this fast response, rather than more complex parts of the brain being required, as previously thought.
The findings suggest that when people look at a scene for ...
South African and Argentinian palaeontologists have discovered a new 200 million year old dinosaur from South Africa, and named it Sefapanosaurus, from the Sesotho word "sefapano".
The researchers from South Africa's University of Cape Town (UCT) and the University of the Witwatersrand (Wits University), and from the Argentinian Museo de La Plata and Museo Paleontológico Egidio Feruglio made the announcement in the scientific journal, Zoological Journal of the Linnaean Society. The paper, titled: A new basal sauropodiform from South Africa and the phylogenetic relationships ...
Boulder, Colo. -- The 26 December 2004 Mw ~9.2 Indian Ocean earthquake (also known as the Sumatra-Andaman or Aceh-Andaman earthquake), which generated massive, destructive tsunamis, especially along the Aceh coast of northern Sumatra, Indonesia, clearly demonstrated the need for a better understanding of how frequently subduction zone earthquakes and tsunamis occur. Toward that end, Harvey M. Kelsey of Humboldt State University and colleagues present a study of earthquake history in the area.
Using subsidence stratigraphy, the team traced the different modes of coastal ...
The tooth plate of just some millimeters in size had been in a box for more than 40 years, without being recognized after the discovery and preparation of the fish it belonged to. Palaeontologists from Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Netherlands and the University of Bristol, United Kingdom, studied the fossil using high energy X-rays at the Swiss Light Source at the Paul Scherrer Institut in Switzerland, revealing the structure and development of teeth and bones. Their findings are published today in Biology Letters.
Teeth are important in our daily life, they are crucial ...
A digital map of the ageing brain could aid the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease and other neurodegenerative disorders in older people, a study suggests.
The atlas created using images from MRI scans of older people could aid diagnosis by comparing the patients' scans with a detailed map of the healthy ageing brain.
Most existing MRI atlases are based on the brains of young and middle-aged people, which don't reflect the normal changes that take place in the brain as we age, the team says.
Researchers at the University of Edinburgh constructed a detailed atlas of ...
Various diagnostic imaging techniques are currently used for clinical imaging/disease diagnosis. The accuracy of diagnosis is mainly based on the type of energy used (such as X-ray, sound waves, photons and positrons) to derive the visual information, as well as the degree of spatial resolution (mesoscopic or microscopic) and the level of information that can be obtained (physiological, anatomical or molecular). Based on potential health hazards imposed by type of energy used, clinical imaging modalities can be broadly categorized as ionizing and non-ionizing modalities. ...
Milan, Italy - 24 June 2015: Uninterrupted treatment with novel oral anticoagulants (NOACs) during catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation (AF) is safe, reveals research presented today at EHRA EUROPACE - CARDIOSTIM 2015 by Dr Carsten Wunderlich, senior consultant in the Department of Invasive Electrophysiology, Heart Centre Dresden, Germany.1 Continuation of NOAC therapy was not associated with periprocedural bleeding or thromboembolic complications.
The joint meeting of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and Cardiostim ...
TORONTO, ON - Adults who were exposed to childhood adversity, including witnessing parental domestic violence, childhood physical and sexual abuse have higher odds of experiencing migraine headaches in adulthood, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Toronto.
"We found the more types of violence the individual had been exposed to during their childhood, the greater the odds of migraine. For those who reported all three types of adversities--parental domestic violence, childhood physical and sexual abuse--the odds of migraine were a little over ...
Scientists have demonstrated for the first time the ability to rapidly, reliably and simultaneously identify the 'handedness' of different molecules in a mixture.
The research, led by chemists at The University of Nottingham and the VU University Amsterdam, and published in the academic journal Nature Communications, could offer a new technique to easily distinguish whether a molecule is present in a left- or right-handed form.
The breakthrough could be important in developing effective molecules for use in a wide range of industries -- everything from the development ...
Piscataway, N.J. -- A form of 'virtual-reality' therapy may help people with alcohol dependence reduce their craving for alcohol, a new study suggests.
The findings, published in the July issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, come from a small study of just 10 patients. But researchers said they are optimistic about the potential for virtual reality as a therapy for alcohol use disorders.
'This technology is already popular in the fields of psychology and psychiatry,' said senior researcher Doug Hyun Han, M.D., Ph.D., of Chung-Ang University Hospital ...