Suomi-NPP satellite sees formation of Tropical Depression Chan-Hom
2015-06-30
(Press-News.org) NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP Satellite passed over the newborn ninth tropical depression of the Northwestern Pacific Ocean typhoon season on June 30.
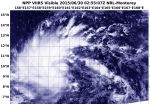
At 02:55 UTC (10:55 p.m. EDT, June 29), the VIIRS or Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard NASA-NOAA's Suomi satellite captured a visible image of the newly developed depression. The VIIRS image revealed bands of thunderstorms wrapping into the low-level center from the north and western quadrants.
VIIRS collects visible and infrared imagery and global observations of land, atmosphere, cryosphere and oceans. VIIRS flies aboard the Suomi NPP satellite, which is managed by both NASA and NOAA.
On Tuesday, June 30, 2015, Tropical Depression Chan-Hom was born. By 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Chan-Hom's maximum sustained winds were near 30 knots (35.5 mph/55.5 kph). Chan-Hom was centered near 9.7 North latitude and 160.0 East longitude, about 204 nautical miles northeast of Pohnpei. Chan-Hom was moving to the west at 3 knots (3.5 mph/5.5 kph).
Chan-Hom is expected to strengthen to tropical storm status and move to the west, then northwest. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Chan-Hom to pass north of Fananu and then strengthen to typhoon status on July 3, while remaining at sea, east of Guam.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-30
CHICAGO -- While studying Yersinia pestis, the bacteria responsible for epidemics of plague such as the Black Death, Wyndham Lathem, Ph.D., assistant professor in microbiology-immunology at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, found a single small genetic change that fundamentally influenced the evolution of the deadly pathogen, and thus the course of human history.
In a paper published in Nature Communications, Lathem and first author Daniel Zimbler, Ph.D., a Feinberg post-doctoral fellow, demonstrated how the acquisition of a single gene caused the ...
2015-06-30
June 30, 2015, NEW YORK -- A new animal study by NYU Langone Medical Center researchers adds to growing evidence that multiple courses of commonly used antibiotics may have a significant impact on children's development.
In the study, to be published online June 30 by the journal Nature Communications, female mice treated with two classes of widely used childhood antibiotics gained more weight and developed larger bones than untreated mice. Both of the antibiotics also disrupted the gut microbiome, the trillions of microbes that inhabit the intestinal tract.
Overall, ...
2015-06-30
Washington, DC - June 30, 2015 - A new report released today from the Institute of Medicine calls for a campaign to promote public education and training opportunities to reduce barriers to the provision of bystander CPR and defibrillation.
Annual rates of CPR and AED use by bystanders remain less than three percent in the United States even though evidence indicates that its use significantly improves cardiac arrest survival. The American Red Cross strongly supports the IOM's recommendation to encourage training through employers, local public health departments, schools ...
2015-06-30
Bethesda, MD (June 30, 2015) -- Both spouses and first-degree relatives of patients with celiac disease are at increased risk of nonceliac autoimmune disease, according to a study in the July issue of Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. This risk represents a mixture of genetic, environmental and ascertainment bias mechanisms.
"The prevalence of celiac disease in first-degree relatives of individuals with celiac is approximately 10 percent. Despite these findings, little is ...
2015-06-30
Bethesda, MD (June 30, 2015) -- Pinaverium offers quick and effective relief of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms, according to clinical trial results published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
Pinaverium bromide (pinaverium), an antispasmodic, is used widely in many countries around the world, including European countries, Canada and Mexico. However, original clinical studies on pinaverium are scarce and there has been no convincing evidence for its effectiveness ...
2015-06-30
Although vitamin A supplementation can have profound health benefits when someone is deficient, new evidence is emerging to show that vitamin A supplementation above and beyond normal levels may have negative health consequences. A new research report published in the July 2015 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology may help to explain why too much vitamin A can be harmful. Too much vitamin A shuts down the body's trained immunity, opening the door to infections to which we would otherwise be immune. This study adds to the arguments that vitamin A supplementation should ...
2015-06-30
WASHINGTON, D.C. - The amount of water required to hydraulically fracture oil and gas wells varies widely across the country, according to the first national-scale analysis and map of hydraulic fracturing water usage detailed in a new study accepted for publication in Water Resources Research, a journal of the American Geophysical Union. The research found that water volumes for hydraulic fracturing averaged within watersheds across the United States range from as little as roughly 9,800 liters (2,600 gallons) to as much as 37 million liters (9.7 million gallons) per well.
In ...
2015-06-30
A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal suggests that a common molecule found in higher animals, including humans, affects brain structure. This molecule may play a significant role in how brain cells communicate, possibly shedding light on the underlying causes of certain brain disorders. The study, involving mice, shows that small changes in how sialic acid attaches to cell surfaces result in damaging effects on brain structure, poor motor skills, hyperactivity, and difficulty in learning.
"Sialic acid is part of the molecular language that ...
2015-06-30
It is well known that muscles need resistance (gravity) to maintain optimal health, and when they do not have this resistance, they deteriorate. A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal, however, suggests that this might not be true for all muscles, offering hope that there may be ways to preserve muscle mass and strength for individuals in low-resistance environments, whether it be the microgravity of space, extended periods in a hospital bed, or a 9-5 job behind a desk.
"Maintaining muscle mass and good muscle repair is key to all areas of ...
2015-06-30
Here's more evidence that fish oil supplementation and antioxidants might be beneficial for at least some people facing Alzheimer's disease: A new report published in the July 2015 issue of The FASEB Journal describes the findings of a very small study in which people with mild clinical impairment, such as those in the very early stages of the disease, saw clearance of the hallmark amyloid-beta protein and reduced inflammation in neurological tissues. Although the findings involved just 12 patients over the course of 4 to 17 months, the findings suggest further clinical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Suomi-NPP satellite sees formation of Tropical Depression Chan-Hom