(Press-News.org) New research led by the University of Southampton is paving the way to protect the endangered European eel as they migrate through rivers to the ocean.
The European eel, a fish of high cultural, commercial and conservation concern, has suffered a dramatic decline over recent decades, with the number of juvenile fish returning to rivers down by over 90 per cent.
While several explanations (including overfishing, pollution and climate change) have been proposed for the cause of this demise, one of the key factors is river infrastructure, such as hydropower stations, that can injure or kill the long bodied adult fish as they migrate to the ocean and eventually to the Sargasso Sea where they spawn.
Because of their long bodies, eels that enter turbine intakes are likely be struck by the rotating blades, causing physical injury and high rates of mortality.
An international collaboration between fish biologists and engineers, led by researchers at the University of Southampton and involving the Environment Agency and the University of Padua in Italy, has now demonstrated the potential to use accelerating water gradients, common at many types of river infrastructure, to influence eel behaviour and produce an avoidance response.
In field experiments, Dr Adam Piper, from the University's International Centre for Ecohydraulics Research (ICER), used acoustic telemetry to track the paths of 40 tagged eels as they approached a hydropower intake site where the speed of water flows were manipulated.
The results of the research, published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B, demonstrated that eels exhibited stronger avoidance when the acceleration of water velocity was greater.
Initially, the eels aligned with streamlines near the channel banks and approached the intake semi-passively. Under normal water velocity, when the eels encountered the constricted flows of the intake, exploratory 'search' behaviour was common prior to coming into physical contact with structures. However, under high water velocity gradients, the eels swam in the opposite direction to escape rapidly back upstream.
Dr Paul Kemp from ICER and the project leader, said: "This interdisciplinary research provides hope that behavioural deterrents may be developed to divert eels away from hazardous routes during their downstream migration."
INFORMATION:
This news release is available in Japanese.
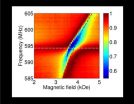
Researchers at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University (OIST) have identified a system that could store quantum information for longer times, which is critical for the future of quantum computing. This study was recently published in Physical Review Letters.
Quantum computing -- which aims to use particles on the atomic scale to make calculations and store the results -- has the potential to solve some key problems much faster than current computers.
To make quantum computing a reality, ...
(NEW YORK CITY - July 1, 2015) A novel synthetic hormone that makes certain skin cells produce more melanin significantly increases pain-free sun exposure in people with erythropoietic protoporphyria, a rare, genetic disorder resulting in excruciating pain within minutes of sun exposure. Two Phase III trials, conducted in Europe and in the United States by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and six other U.S. sites, showed that the duration of pain-free time in the sun and quality of life were significantly improved by treatment with afamelanotide, ...
Pregnancy and motherhood are both wonderful and worrisome times - could public health campaigns and social stereotypes be contributing to anxiety for mothers? Researchers from Monash University have identified links between perinatal anxiety and social and health messages that women are exposed to during the perinatal period, the period immediately before and after birth.
In a paper recently published in Women's Studies International Forum, Dr Heather Rowe and Professor Jane Fisher from the Jean Hailes Research Unit within the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine ...
Unwanted, intrusive visual memories are a core feature of stress- and trauma-related clinical disorders such as posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), but they can also crop up in everyday life. New research shows that even once intrusive memories have been laid down, playing a visually-demanding computer game after reactivating the memories may reduce their occurrence over time.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"This work is the first to our knowledge to show that a 'simple cognitive blockade' ...
Spider-like cells inside the brain, spinal cord and eye hunt for invaders, capturing and then devouring them. These cells, called microglia, often play a beneficial role by helping to clear trash and protect the central nervous system against infection. But a new study by researchers at the National Eye Institute (NEI) shows that they also accelerate damage wrought by blinding eye disorders, such as retinitis pigmentosa. NEI is part of the National Institutes of Health.
"These findings are important because they suggest that microglia may provide a target for entirely ...
A new method for calculating the exact time of death, even after as much as 10 days, has been developed by a group of researchers at the University of Salzburg.
Currently, there are no reliable ways to determine the time since death after approximately 36 hours. Initial results suggest that this method can be applied in forensics to estimate the time elapsed since death in humans.
By observing how muscle proteins and enzymes degrade in pigs, scientists at the University of Salzburg have developed a new way of estimating time since death that functions up to at least ...
When remembering something from our past, we often vividly re-experience the whole episode in which it occurred. New UCL research funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust has now revealed how this might happen in the brain.
The study, published in Nature Communications, shows that when someone tries to remember one aspect of an event, such as who they met yesterday, the representation of the entire event can be reactivated in the brain, including incidental information such as where they were and what they did.
"When we recall a previous life event, ...
Classical Brownian motion theory was established over one hundred year ago, describing the stochastic collision behaviors between surrounding molecules. Recently, researchers from Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences discovered that the self-powered liquid metal motors in millimeter scale demonstrated similar Brownian like motion behaviors in alkaline solution. And the force comes from the hydrogen gas stream generated at the interface between liquid metal motor and its contacting substrate bottom.
Ever since the irregular motions ...
A group of the world's top doctors and scientists working in cardiology and preventive medicine have issued a call to action to tackle the global problem of deaths from non-communicable diseases (NCDs), such as heart problems, diabetes and cancer, through healthy lifestyle initiatives.
They say that identifying the enormous burden caused by NCDs is not enough and it is time for "all hands on deck" to pursue strategies both within and outside traditional healthcare systems that will succeed in promoting healthier lifestyles in order to prevent or delay health conditions ...
Sophia Antipolis, 02 July 2015: Patients are experiencing significant delays in access to approved cardiovascular devices due to bureaucratic inefficiencies, reveals a Devices White Paper from the Cardiovascular Round Table (CRT) published today in European Heart Journal.1
There is a clear correlation between declining death rates from cardiovascular disease and the introduction of innovative techniques and devices.1
The CRT is an independent forum established by the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and comprised of cardiologists and representatives of the pharmaceutical, ...