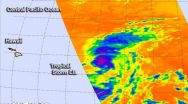
Tropical Storm Ela becomes the Central Pacific's first named storm
2015-07-09
(Press-News.org) Tropical Storm Ela was born in the western-most part of the Eastern Pacific Ocean but has become the Central Pacific's first named storm. NASA's Aqua satellite took a look at the storm that's already battling wind shear to survive.
After developing as a depression on July 8, Tropical Depression 4E crossed over the 140 degree West longitude line that separates the Eastern Pacific from the Central Pacific Ocean region. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm early on July 9, taking a name from the Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone list and being renamed Ela.
When NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Ela on July 8 at 22:29 UTC (6:29 p.m. EDT), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument measured the temperatures of the storm's cloud tops using infrared light. That infrared data showed that wind shear from the southwest was pushing all the strongest thunderstorms with the coldest cloud tops to the northeast of the center. The AIRS data showed those thunderstorms in the northeastern quadrant had temperatures as cold as -63F/-52C. Storms that high in the troposphere, the lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere, have the potential to drop heavy rain. Since Ela is far from land areas the rainfall occurred at sea.
On July 9, NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) noted that the latest satellite imagery showed "that persistent southwesterly shear has shunted the mid-level center of the cyclone well northeast of the surface center. However, data from a U.S. Air Force Hurricane Hunter aircraft indicate surface winds near 35 knots in the northeast quadrant. "
On July 9 at 5 a.m. HST (1500 UTC/11 a.m. EDT) the center of Tropical Storm Ela was located near latitude 20.2 north and longitude 146.1 west. That puts Ela's center about 585 miles (940 km) east of Hilo, Hawaii, and about 765 miles (1,230 km) east of Honolulu, Hawaii.
Ela is moving toward the northwest near 13 mph (20 kph) and this motion is expected to continue through tonight. A turn toward the west and a slight decrease in forward speed is forecast for Friday, July 10 and Saturday, July 11. Maximum sustained winds are near 40 mph (65 kph) with higher gusts. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1003 millibars.
The outlook for Ela seems bleak because the wind shear is expected to persist on its track to the west. Ela is forecast to succumb to the shear and gradually weaken today, July 9 and July 10. Ela is expected to eventually dissipate north of Hawaii.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-09
Traumatic spinal cord injuries are increasing with the population, and incidence is higher in older individuals, according to a Vanderbilt study that was published in the June 9 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The study, which analyzed data from 63,109 patients with acute traumatic spinal cord injury from 1993 to 2012, will help target specific populations for preventive measures, said lead author Nitin B. Jain, M.D., M.S.P.H, associate professor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
"We find that spinal cord injury as a result of falls is ...
2015-07-09
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (7/9/2015) -- Draining tropical peatlands for oil palm plantations may result in nearly twice as much carbon loss as official estimates, according to a new study by researchers from the University of Minnesota Institute on the Environment and the Union of Concerned Scientists in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Peatlands -- waterlogged, organic soils -- have developed over thousands of years as carbon storage systems. In Southeast Asia, peat swamp forests cover about 250,000 square kilometers, a land area about the size of Michigan. In ...
2015-07-09
Scientists at the University of East Anglia in collaboration with the University Pompeu Fabra in Barcelona have found a way to separate the medical benefits of cannabis from its unwanted side effects.
The research comes from the team that discovered how the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, known as THC, reduces tumour growth in cancer patients.
Their latest findings, published today in the journal PLOS Biology, reveal how the cognitive effects of THC are triggered by a pathway which is separate from some of its other effects.
That pathway involves both a ...
2015-07-09
Neutralizing antibodies (Nabs) are immune proteins that recognize, bind to, and trigger the elimination of virus before it can establish a chronic infection. How to elicit a potent Nab response capable of protecting against different HIV subtypes and against different modes of infection is critical to the development of an AIDS vaccine. Two studies published on July 9th in PLOS Pathogens provide results on Nabs that could help guide vaccine design. One shows what type of Nab "repertoire" can be generated following superinfection, and the second one examines the efficacy ...
2015-07-09
SALT LAKE CITY, July 9, 2015 - More than a quarter of the rain and snow that falls on continents reaches the oceans as runoff. Now a new study helps show where the rest goes: two-thirds of the remaining water is released by plants, more than a quarter lands on leaves and evaporates and what's left evaporates from soil and from lakes, rivers and streams.
"The question is, when rain falls on the landscape, where does it go?" says University of Utah geochemist Gabe Bowen, senior author of the study published today in the journal Science. "The water on the continents sustains ...
2015-07-09
Global warming is putting the squeeze on bumblebees. In the most comprehensive study ever conducted of the impacts of climate change on critical pollinators, scientists have discovered that global warming is rapidly shrinking the area where these bees are found in both North America and Europe.
Researchers examined more than 420,000 historical and current records of many species of bumblebees--and confirm that bumblebees are in steep decline at a continental scale because of climate change. The new research is reported in the journal Science.
ECONOMIC THREATS
This ...
2015-07-09
The discovery of a fiber-reinforced, concrete-like rock formed in the depths of a dormant supervolcano could help explain the unusual ground swelling that led to the evacuation of an Italian port city and inspire durable building materials in the future, Stanford scientists say.
The "natural concrete" at the Campi Flegrei volcano is similar to Roman concrete, a legendary compound invented by the Romans and used to construct the Pantheon, the Coliseum, and ancient shipping ports throughout the Mediterranean.
"This implies the existence of a natural process in the subsurface ...
2015-07-09
Researchers from the University of Calgary and University of Ottawa have made an astonishing find when it comes to the habitat range of bumble bees, and the results are troubling.
Findings to be published in the Journal Science, demonstrate that climate change is having a significant impact on bumblebee species in North America and Europe.
Bumblebees are losing vital habitat in the southern regions of North America and Europe, which is cause for concern but another pressing issue is that bumblebee species generally haven't expanded north," explains Paul Galpern, Assistant ...
2015-07-09
TORONTO, July 9, 2015 - Bumblebees are rapidly declining in both North America and Europe, and a new study points to climate change as the major factor. The study, a comprehensive analysis of how climate change impacts these critical pollinators, was published in Science today.
The research shows that bumblebees are losing large amounts of the southern portion of their ranges, but unlike other species which are compensating by moving further north as the climate warms, bumblebees are not heading north. Their range areas are compressing with rapid warming and this is causing ...
2015-07-09
This news release is available in Japanese.
A suite of energy-saving traits, including underactive thyroid glands, allows giant panda bears to survive almost exclusively on bamboo, according to a new study. Yonggang Nie and colleagues report the first measurements of daily energy expenditure (DEE) in these bears, which do not have stomachs designed for such low-nutrient, high-cellulose plants. The researchers studied five captive pandas and three wild ones, discovering that the animal's DEE was just about 38% of the average for a terrestrial mammal with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tropical Storm Ela becomes the Central Pacific's first named storm