(Press-News.org) Natural environments are known to promote physical, mental, and spiritual healing. People can attain health benefits by spending time outside, often in remote places to "get away from it all." Now research conducted by a University of Minnesota graduate student with a team in Vancouver, B.C., shows that green and "blue" spaces (environments with running or still water) are especially beneficial for healthy aging in seniors.
Published in the journal Health and Place, the study -Therapeutic landscapes and wellbeing in later life: Impacts of blue and green spaces for older adults--demonstrates that by incorporating smaller features, such as a koi pond or a bench with a view of flowers, public health and urban development strategies can optimize nature as a health resource for older adults. Throughout the research, green and blue spaces promoted feelings of renewal, restoration, and spiritual connectedness. They also provided places for multi-generational social interactions and engagement, including planned activities with friends and families, and impromptu gatherings with neighbors.
"We zoomed in to everyday life for seniors between the ages of 65 and 86. We discovered how a relatively mundane experience, such as hearing the sound of water or a bee buzzing among flowers, can have a tremendous impact on overall health," says Jessica Finlay, a former research assistant on the project and lead author of the paper. Finlay is now a doctoral candidate in geography and gerontology at the University of Minnesota, where she continues to investigate influences of the built environment on health and well-being in later life. "Accessibility to everyday green and blue spaces encourages seniors to simply get out the door. This in turn motivates them to be active physically, spiritually and socially, which can offset chronic illness, disability and isolation."
Importance of everyday contact with nature
While younger generations may use green and blue spaces more to escape and rejuvenate from their busy work life, our participants used nature to be active physically, spiritually, and socially in later life. Many overcame barriers due to chronic illness, disability, and progressing old age to connect regularly with green and blue spaces.
Natural environments enable older adults to uphold daily structure in retirement and provide opportunities for diverse activities outside the home. This is important to quality of later life by decreasing boredom, isolation, and loneliness; as well as boosting one's sense of purpose and accomplishment. Blue space in particular provides opportunities for non-weight bearing physical activity and physiotherapy (e.g. wading, water walking, swimming). Waterfront areas are comforting sites for spiritual connectedness with deceased loved ones, and relaxing places to escape the strains of later life.
"While our research may seem intuitive, it creates conversations on how to build communities that serve people across their entire lifetime. We don't just need a playground for children, we also need sheltered benches for the grandparents to watch them," says Finlay. "This research is more than anecdotal; it gives credence to some small but significant elements of everyday later life. Hopefully it will help urban planners and developers build communities that span a lifetime."
Finlay offers three tips for healthier aging:
1. Focus on your overall wellbeing: mental and social health are just as important as physical health when aging
2. Get out the door regularly, even if it's just to the end of the block and back
3. Prioritize everyday contact with nature - whether it's sitting in a park, listening to a water fountain, or looking at potted plants on a windowsill
The researchers interviewed adults aged 65 - 86 years who lived in Vancouver, B.C. All study participants were considered low-income, came from 8 different self-identified racial and ethnic groups, and experience a range of chronic conditions and experiences of health.
INFORMATION:
Two of NASA's heliophysics missions can now claim planetary science on their list of scientific findings. A group of scientists used the Venus transit - a very rare event where a planet passes between Earth and the sun, appearing to us as a dark dot steadily making its way across the sun's bright face - to make measurements of how the Venusian atmosphere absorbs different kinds of light. This, in turn, gives scientists clues to exactly what elements are layered above Venus's surface. Gathering such information not only teaches us more about this planet so close to our own, ...
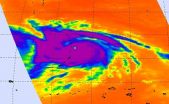
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Supertyphoon Nangka on July 9 and provided a visible and an infrared view of the large storm.
At 0700 UTC (3 a.m. EDT) on July 9 a typhoon warning was in effect for Agrihan, Pagan and Alamagan in the northern Marianas. A tropical storm warning is in effect for Saipan and Tinian. Nangka passed over Alamagan.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite gathered infrared temperature data on Nangka on July 9 at 03:23 UTC (July 8 at 11:23 a.m. EDT). At the same time, the MODIS instrument took a visible ...
Studying the gastric cancers of 15 Southeast Asian patients, researchers at The Jackson Laboratory, the Genome Institute of Singapore and other institutions identified five recurrent fusion genes, one of which appears to lead to cellular changes involved in acute gastritis and cancer.
Worldwide, close to a million cases of gastric cancers are diagnosed each year, and some of the world's highest incidence rates are in Asia (particularly in Korea, Japan and China).
The researchers, led by JAX Professor Yijun Ruan, Ph.D., and Axel M. Hillmer, Ph.D., of GIS, published ...
LOS ANGELES (July 9, 2015) - After generating new brain tumor models, Cedars-Sinai scientists in the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute identified the role of a family of genes underlying tumor growth in a wide spectrum of high grade brain tumors.
"With these new genetic findings, our group of researchers plan to develop targeted therapeutics that we hope will one day be used treat patients with high grade brain tumors and increase their survival," said Joshua Breunig, PhD, a research scientist in the Brain Program at the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors ...
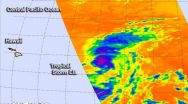
Tropical Storm Ela was born in the western-most part of the Eastern Pacific Ocean but has become the Central Pacific's first named storm. NASA's Aqua satellite took a look at the storm that's already battling wind shear to survive.
After developing as a depression on July 8, Tropical Depression 4E crossed over the 140 degree West longitude line that separates the Eastern Pacific from the Central Pacific Ocean region. The depression strengthened into a tropical storm early on July 9, taking a name from the Eastern Pacific tropical cyclone list and being renamed Ela.
When ...
Traumatic spinal cord injuries are increasing with the population, and incidence is higher in older individuals, according to a Vanderbilt study that was published in the June 9 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association.
The study, which analyzed data from 63,109 patients with acute traumatic spinal cord injury from 1993 to 2012, will help target specific populations for preventive measures, said lead author Nitin B. Jain, M.D., M.S.P.H, associate professor of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.
"We find that spinal cord injury as a result of falls is ...
MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (7/9/2015) -- Draining tropical peatlands for oil palm plantations may result in nearly twice as much carbon loss as official estimates, according to a new study by researchers from the University of Minnesota Institute on the Environment and the Union of Concerned Scientists in the journal Environmental Research Letters.
Peatlands -- waterlogged, organic soils -- have developed over thousands of years as carbon storage systems. In Southeast Asia, peat swamp forests cover about 250,000 square kilometers, a land area about the size of Michigan. In ...
Scientists at the University of East Anglia in collaboration with the University Pompeu Fabra in Barcelona have found a way to separate the medical benefits of cannabis from its unwanted side effects.
The research comes from the team that discovered how the main psychoactive ingredient in cannabis, known as THC, reduces tumour growth in cancer patients.
Their latest findings, published today in the journal PLOS Biology, reveal how the cognitive effects of THC are triggered by a pathway which is separate from some of its other effects.
That pathway involves both a ...
Neutralizing antibodies (Nabs) are immune proteins that recognize, bind to, and trigger the elimination of virus before it can establish a chronic infection. How to elicit a potent Nab response capable of protecting against different HIV subtypes and against different modes of infection is critical to the development of an AIDS vaccine. Two studies published on July 9th in PLOS Pathogens provide results on Nabs that could help guide vaccine design. One shows what type of Nab "repertoire" can be generated following superinfection, and the second one examines the efficacy ...
SALT LAKE CITY, July 9, 2015 - More than a quarter of the rain and snow that falls on continents reaches the oceans as runoff. Now a new study helps show where the rest goes: two-thirds of the remaining water is released by plants, more than a quarter lands on leaves and evaporates and what's left evaporates from soil and from lakes, rivers and streams.
"The question is, when rain falls on the landscape, where does it go?" says University of Utah geochemist Gabe Bowen, senior author of the study published today in the journal Science. "The water on the continents sustains ...