Personalized banner ads are a double-edged sword
2015-07-23
(Press-News.org) Sometimes consumers might appreciate a pop-up ad that reflects the merchandise they were recently browsing online, and sometimes they just might decide to spike it and thereafter avoid the seller that placed the ad. Retailers can learn about this behavior in the September 2015 issue of the Journal of Retailing.
In "The Importance of Trust for Personalized Online Advertising," Marketing Professors Alexander Bleier, of Boston College's Carroll School of Management, and Maik Eisenbeiss, of the University of Bremen, show how trust in a particular vendor affects the degree to which consumers will accept or reject a personalized banner ad.
The authors used field data and also designed a series of lab experiments to elicit such responses, using personalized ads that showed the consumer varying levels of information based on the consumer's browsing history at a particular online store. They wondered where people would draw the line at having the items they had looked at reflected back at them.
"For the more trusted retailer in our field study, we find banner click-through rates to increase by 27 percent," the authors write. Generally, they found that consumers preferred personalized ads that showed one of the items they had looked at, rather than all of them. Privacy concerns and discomfort with intrusiveness triggered the customers' negative responses, especially vis-à-vis retailers that had not established trust with the consumer through positive prior experience.
In order to avoid triggering a negative response to personalized ads, the authors suggest ways retailers can enhance and gauge customers' trust in them before diving into the practice.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-07-23
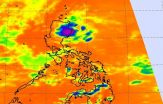
When Tropical Depression 12W formed on the northeastern tip of the Philippines in the Luzon Region, NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on the newborn storm.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Depression 12W. AIRS data showed some cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63F/-53C on July 23 at 5:17 UTC (1:17 a.m. EDT). Cloud top temperatures that cold have been shown to generate heavy rainfall.
Tropical Depression 12W (TD12W) formed at 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT) on July 23 ...
2015-07-23
Fairfax, Va., July 22, 2015 - The American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) is concerned about proposed additional payment cuts to radiation therapy detailed in the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services' (CMS) proposed Medicare Physician Fee Schedule (MPFS), released July 8, 2015, which will take effect on January 1, 2016. Freestanding centers estimate that the combined impact of the Medicare proposals would result in a five to seven percent reduction in payment for radiation oncology services at community-based centers, although the cuts will vary and could ...
2015-07-23
Tropical Storm Felicia was born early on July 23 in the Eastern Pacific Ocean, over 400 miles southwest of Baja California's southern tip. NOAA's GOES-West satellite provided an infrared image of the newborn storm.
Previously known as tropical low pressure area "System 99E," the storm finally developed after days of remaining unorganized. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Felicia on July 23, 2015 at 15:45 UTC (11:45 a.m. EDT). Satellite imagery shows that a curved band of thunderstorms are wrapping around the southern quadrant of the storm.
The ...
2015-07-23
Researchers in the Division of Hematology, Oncology and Blood & Marrow Transplantation at Children's Hospital Los Angeles have shown greatly improved outcomes in using stem cell transplantation to treat patients with a serious but very rare form of chronic blood cancer called juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML).
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) involves the transplantation of stem cells from a donor, which may be derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood or umbilical cord blood. The recipient's immune system is usually destroyed with radiation ...
2015-07-23
Researchers from Scripps Institution of Oceanography at UC San Diego have accurately mapped out the movement of the devastating 7.8-magnitude Nepal earthquake that killed over 9,000 and injured over 23,000 people. Scientists have determined that the earthquake was a rupture consisting of three different stages. The study could help a rapidly growing region understand its future seismic risks.
The Himalayan region is particularly prone to earthquakes and this study will serve as an important benchmark for understanding where future earthquakes may occur, especially ...
2015-07-23
SEDE BOQER, Israel...July 23, 2015 - Ben-Gurion University of the Negev (BGU) and University of Western Australia researchers have developed a new process to develop few-layer graphene for use in energy storage and other material applications that is faster, potentially scalable and surmounts some of the current graphene production limitations.
Graphene is a thin atomic layer of graphite (used in pencils) with numerous properties that could be valuable in a variety of applications, including medicine, electronics and energy. Discovered only 11 years ago, graphene is one ...
2015-07-23
The physical symptoms of weakness and fatigue from multiple sclerosis (MS) can rock a person's confidence and ability to engage in what he or she feels is important, from being a good parent and friend to taking up a hobby, according to Matthew Plow, assistant professor from Case Western Reserve University's Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing.
To help people with MS maintain autonomy and independence, a team of researchers set out to determine what factors prevented individuals from undertaking and enjoying the activities they believe are most important to live fulfilling ...
2015-07-23
Researchers at the University of Birmingham have made a breakthrough in understanding how mutated genes in leukaemia reprogram blood stem cells and send them spiralling out of control.
The findings help to explain the early development of leukaemia, representing the essential first step to developing new treatments for patients based on these findings.
A study, published in Cell Reports by Professors Peter Cockerill and Constanze Bonifer, investigated the role of one specific mutation in the FLT3 gene found in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML).
AML is diagnosed in ...
2015-07-23
Researchers add a new twist to the more than century old biological principles of Mendelian inheritance - describing a small group of cells in pregnant mothers that promote genetic fitness and multi-generational reproductive health.
Scientists at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center report their findings online July 23 in Cell. The study suggests a scientific basis for developing new therapies to promote reproductive health and prevent pregnancy complications like prematurity and stillbirth, according to Sing Sing Way, MD, PhD, senior author and pediatrician ...
2015-07-23
When does aging really begin? Two Northwestern University scientists now have a molecular clue. In a study of the transparent roundworm C. elegans, they found that adult cells abruptly begin their downhill slide when an animal reaches reproductive maturity.
A genetic switch starts the aging process by turning off cell stress responses that protect the cell by keeping important proteins folded and functional. The switch is thrown by germline stem cells in early adulthood, after the animal starts to reproduce, ensuring its line will live on.
While the studies were conducted ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Personalized banner ads are a double-edged sword