(Press-News.org) July 24, 2015 - Patient satisfaction ratings after surgery for spinal degenerative disease--especially in terms of reduced pain and disability--are a good indicator of the procedure's effectiveness, reports a study in the August issue of Neurosurgery, official journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons. The journal is published by Wolters Kluwer.
"Patient satisfaction with outcome may accurately represent the effectiveness of surgical spine care in terms of one-year improvement in pain and disability," according to the new research by Dr. Clinton J. Devin of Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, and colleagues. But more research is needed to clarify the impact of insurance status and initial severity scores on the outcomes of surgery for degenerative spine disease.
Reduced Pain and Disability Predict Satisfaction after Spine Surgery
The researchers analyzed one-year follow-up data on 1,645 patients undergoing surgery for degenerative disease of the upper (cervical) and lower (lumbar) spine. Before and one year after surgery, the patients were evaluated using standard rating scales for disability and neck, back, arm and leg pain.
Based on a spinal surgery satisfaction scale, 83 percent of patient said they were satisfied with the outcomes of surgery one year later. The researchers wanted to see whether any of the factors evaluated before surgery could predict whether patients would be satisfied or dissatisfied with their outcomes.
After adjustment for a wide array of patient-specific factors, several specific predictors were identified. Patients who didn't have at least a 15 percent improvement on a standard disability rating scale--considered to be the "minimal clinically important difference"--were four times more likely to be dissatisfied with their surgical outcomes.
Patients who didn't achieve minimal clinically important differences in pain scores were about three times more likely to be dissatisfied with the results of surgery. Patients who were on Medicaid or uninsured also had lower satisfaction rates, as did those with higher initial pain and disability scores.
Patients with depression or anxiety before surgery were less likely to achieve clinically meaningful improvement, and had lower satisfaction rates. However, after adjustment for initial pain and disability scores, these mental health factors were not significant predictors.
Patient satisfaction scores are increasingly used as measures of the quality of medical care--and as a determinant of reimbursement for care provided. "Identifying modifiable factors that improve satisfaction is of utmost importance," according to Dr. Devin and coauthors.
The new study shows that patient satisfaction ratings after surgery for spinal degenerative disease line up well with the level of improvement in pain and disability achieved. The researchers write, "Surgical ineffectiveness was a strong independent predictor of dissatisfaction."
But the results also show a significant impact of initial pain and disability, suggesting that patients with more severe spinal degenerative disease are less likely to be satisfied with the results of surgery. Insurance status also seems to have an impact--Medicaid recipients or uninsured patients may have lower satisfaction rates even if they do improve clinically.
The study may provide tools to help identify individuals at risk of dissatisfaction and to improve the delivery of spine care, Dr. Devin and coauthors believe. They conclude, "Individualizing the patient preoperative counseling on the basis of these patient-specific factors can improve patient satisfaction with outcomes."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Patient-Specific Factors Associated With Dissatisfaction After Elective Surgery for Degenerative Spine Diseases."
Article: "Patient-Specific Factors Associated With Dissatisfaction After Elective Surgery for Degenerative Spine Diseases" (doi: 10.1227/NEU.0000000000000768)
About Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery, the Official Journal of the Congress of Neurological Surgeons, is your most complete window to the contemporary field of neurosurgery. Members of the Congress and non-member subscribers receive 3,000 pages per year packed with the very latest science, technology, and medicine, not to mention full-text online access to the world's most complete, up-to-the-minute neurosurgery resource. For professionals aware of the rapid pace of developments in the field, Neurosurgery is nothing short of indispensable.
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer is a global leader in professional information services. Professionals in the areas of legal, business, tax, accounting, finance, audit, risk, compliance and healthcare rely on Wolters Kluwer's market leading information-enabled tools and software solutions to manage their business efficiently, deliver results to their clients, and succeed in an ever more dynamic world.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2014 annual revenues of €3.7 billion. The group serves customers in over 170 countries, and employs over 19,000 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands. Wolters Kluwer shares are listed on NYSE Euronext Amsterdam (WKL) and are included in the AEX and Euronext 100 indices. Wolters Kluwer has a sponsored Level 1 American Depositary Receipt program. The ADRs are traded on the over-the-counter market in the U.S. (WTKWY).
For more information about our products and organization, visit http://www.wolterskluwer.com, follow @WKHealth or @Wolters_Kluwer on Twitter, like us on Facebook, follow us on LinkedIn, or follow WoltersKluwerComms on YouTube.
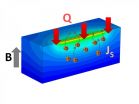
It doesn't happen often that a young scientist makes a significant and unexpected discovery, but postdoctoral researcher Stephen Wu of the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory just did exactly that. What he found--that you don't need a magnetic material to create spin current from insulators--has important implications for the field of spintronics and the development of high-speed, low-power electronics that use electron spin rather than charge to carry information.
Wu's work upends prevailing ideas of how to generate a current of spins. "This is a ...
Needham, MA.-JBJS Case Connector, an online case report journal published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, has issued a "Watch" regarding potential risks with anchor-based all-inside meniscal repairs. While all-inside techniques have many advantages, including shorter surgical time and reduced risk of damage to neurovascular tissues, potential drawbacks include risks of local soft-tissue irritation and implant migration or breakage.
In particular, the "Watch" offers important tips for successfully using FAST-FIX meniscal-repair devices produced by Smith & Nephew. ...
Nailing the diagnosis of a psychiatric disorder may not be important in prescribing effective treatment, according to Mark Zimmerman, M.D., a clinical researcher at Rhode Island Hospital. His opinion editorial was published online today in the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
"During the past 35 years, we have witnessed a revolution in the treatment of psychiatric disorders," said Zimmerman, director of outpatient psychiatry and the partial hospital program at Rhode Island Hospital and director of the Rhode Island Methods to Improve Diagnostic Assessment and Services ...
A new Animal Conservation study shows that sports stadium lighting can alter patterns of bat species activity and feeding, which may in turn have cascading effects on other organisms and the ecosystem as a whole.
Using a novel field experiment, Dr. M. Corrie Schoeman demonstrates that urban exploiter bats are more likely to hunt insects attracted to bright light pollution sources such as stadiums than urban avoider bats. (Exploiter organisms can take advantage of food or resources supplied by humans, while avoider organisms have either a history of conflict with humans ...
In a recent year-long study, 40% of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experienced falls, with more than 75% of these falling multiple times.
Factors linked with an increased risk of falling included smoking, having other illnesses, taking multiple medications, having a fear of falling, and falling in the past.
"The findings could be useful for developing preventative strategies," said Dr. Cristino Oliveira, lead author of the Respirology study.
INFORMATION:
...
A computerized attention-control training program significantly reduced combat veterans' preoccupation with - or avoidance of -- threat and attendant PTSD symptoms. By contrast, another type of computerized training, called attention bias modification - which has proven helpful in treating anxiety disorders - did not reduce PTSD symptoms. NIMH and Israeli researchers conducted parallel trials in which the two treatments were tested in US and Israeli combat veterans.
Daniel Pine, M.D., of the NIMH Emotion and Development Branch, Yair Bar-Haim, Ph.D., School of Psychological ...
Boston, MA -- More than 70% of pollen and honey samples collected from foraging bees in Massachusetts contain at least one neonicotinoid, a class of pesticide that has been implicated in Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD), in which adult bees abandon their hives during winter, according to a new study from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
The study will be published online July 23, 2015 in the Journal of Environmental Chemistry.
"Data from this study clearly demonstrated the ubiquity of neonicotinoids in pollen and honey samples that bees are exposed to during ...
The over 50s who are 'successful agers'--healthy, active, sociable, and well off--are more at risk of harmful drinking than their less successful peers, concludes research published in the online journal BMJ Open.
Harmful drinking is a "middle class phenomenon" which may be a hidden health and social problem in otherwise successful older people, warn the researchers, who call for explicit guidelines on alcohol consumption for this group.
They base their findings on more than 9000 responses to the two most recent waves (2008-9 and 2010-11) of the English Longitudinal ...
Two new studies, both published in The Lancet, suggest that two different classes of drugs, aromatase inhibitors (AIs) and bisphosphonates, can each improve survival prospects for postmenopausal women with early breast cancer. Moreover, the researchers suggest that the two types of drug can be used together, increasing the benefits while also decreasing some side-effects.
Most women are post-menopausal when they develop breast cancer, and breast cancer is usually found early, when surgery can remove all detectable disease, but might leave dangerous undetected micrometastases ...
A class of hormonal drugs called aromatase inhibitors substantially reduce the risk of death in postmenopausal women with the most common type of breast cancer, a major study of more than 30,000 women shows.
The research underlines the importance of aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer - and shows they reduce risk of death by significantly more than the older hormonal treatment tamoxifen.
The study, published in The Lancet today (Friday), is relevant to postmenopausal women with ER-positive breast cancer, which accounts ...