(Press-News.org) Since 1987, when a surgeon at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters developed a minimally-invasive surgery to correct sunken chest, the procedure has been adopted world-wide as a standard of care and continually refined to increase its effectiveness and safety, according to a paper published in the December issue of the Annals of Surgery.
Coming more than two decades after the procedure was developed by surgeon Donald Nuss, the article summarizes the cases of 1,215 patients who had the Nuss Procedure at Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters and focuses on technical modifications which have increased both the success rate and the safety of the surgery.
"Any time new surgical techniques are developed, it is essential to review outcomes and share refinements, so that others can benefit from our experience," CHKD surgeon Robert Kelly, one of the authors.
Often described as sunken or funnel chest, pectus excavatum appears as an indentation of the chest toward the spine. It is the most common deformity of the chest wall, occurs in one in every 1,000 children and can range from mild to severe.
In years past, pectus excavatum was considered to be primarily a cosmetic concern, but an increasing body of research performed at CHKD and elsewhere documents that patients with uncorrected pectus excavatum often suffer shortness of breath and exercise intolerance.
Before the development of the Nuss procedure, correction of pectus excavatum required radical, open chest surgery. In the Nuss Procedure, surgeons insert a curved medal bar through the chest cavity and under the sternum, popping the depression out. The bar is anchored to the ribs and remains in place for 2-3 years while the chest hardens into the proper position.
Although the Nuss Procedure is performed around the world, CHKD has emerged as the world's primary site of surgical training, research and treatment of pectus excavatum and a related condition called pectus carinatum, or pigeon chest, in which the cartilage protrudes outward.
In reviewing the pectus excavatum surgeries performed since 1987, authors determined that 95.8 percent of patients who had the surgery had a "good to excellent anatomic result."
During that time, and especially in the last decade, new instruments were developed with input from CHKD surgeons, according to the article. These include:
a stronger and more streamlined bar
an instrument specially designed to improve substernal tunnel creation
a stabilizer to prevent bar displacement
titanium bars for patients with metal allergies
New surgical techniques were also developed to minimize risk when dissecting between the heart and the sternum in an extremely deep defect. These include:
dissecting two tunnels, one higher than the deepest part of the depression, and using the first tunnel to elevate the lowest part of the defect before the bar is inserted
use of a chest suction cup to elevate the sternum
introduction of a high resolution thorascopic camera into the chest as the procedure is performed
The paper details a radical revision of CHKD's post-operative pain management and post operative therapies such as deep breathing exercises patients should perform.
Dr. Kelly believes that it's important to include the full range of surgical modifications to benefit centers around the world whose surgeons routinely perform the Nuss procedure.
"The minimally invasive repair of pectus excavatum has become a standard of care," he said. "What we're demonstrating in this paper is that the procedure can be performed both safely and effectively."
INFORMATION: END
Despite the common clinical practice among surgeons to discontinue their patients' anti-platelet therapy prior to surgery, a recent study of patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy (CEA) indicated that this practice may be unnecessary. The study will be published in the December issue of the Annals of Vascular Surgery.
The use of clopidogrel (Plavix, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Sanofi-Aventis), an antiplatelet agent prescribed for patients with acute myocardial infarction (severe heart attack), recent stroke or peripheral arterial disease, continues to rise with U.S. sales ...
Whatever its final incarnation, the recently enacted landmark Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act will expand Medicaid eligibility and is expected by 2013 to provide coverage, including mental health care, to an estimated 4.1 million children currently uninsured.
That's a good thing. But what will the quality of care be, especially for vulnerable children with special health care needs? Poor, according to a new report in the current online edition of the Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry.
In cooperation with LA Care, one of ...
SAN ANTONIO, TEX. (December 9, 2010)––Nearly one-fifth of all metastatic breast cancer patients develop brain metastases and have significantly shorter overall survival than patients who do not have brain involvement. One way to improve the affected patients' survival might be to prevent the brain metastases from arising in the first place. With that in mind, researchers have been working on a predictive model that accurately identifies these high risk patients. Now, Veeraiah Siripurapu, M.D., and colleagues from Fox Chase Cancer Center have verified several factors––including ...
Despite their initial focus on national economic competitiveness, the nanotechnology research initiatives now funded by more than 60 countries have become increasingly collaborative, with nearly a quarter of all papers co-authored by researchers across borders.
Researchers from the two leading producers of nanotechnology papers – China and the United States – have become each nation's most frequent international co-authors. Though Chinese and U.S. researchers now publish roughly the same number of nanotechnology papers, the U.S. retains a lead in the quality of publications ...
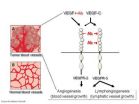
A novel strategy of blocking the growth of blood vessels with antibodies should result in improved treatment of cancerous tumors.
The growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature is called angiogenesis. In adults, angiogenesis occurs only during wound healing and menstrual cycling, but is abundant and harmful in cancerous tumors and the old-age eye disease frequently leading to blindness called age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Without the formation of new blood vessels, tumors cannot grow beyond a small size due to lack of oxygen and nutrients. Inhibition ...
(Washington) – The American College of Physicians (ACP) today commended Congress for taking bipartisan action to preserve access for patients enrolled in Medicare and TriCare by stabilizing physician payments through 2011. The College noted, though, that the incoming 112th Congress will need to enact legislation to provide longer-term stability in payments and lead to repeal of the Sustainable Growth Rate (SGR) formula.
The legislation, passed unanimously by the Senate yesterday and passed by an overwhelming majority in the House of Representatives today, will avert ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich.---A wave of reptile extinctions on the Greek islands over the past 15,000 years may offer a preview of the way plants and animals will respond as the world rapidly warms due to human-caused climate change, according to a University of Michigan ecologist and his colleagues.
The Greek island extinctions also highlight the critical importance of preserving habitat corridors that will enable plants and animals to migrate in response to climate change, thereby maximizing their chances of survival.
As the climate warmed at the tail end of the last ice age, ...
CINCINNATI—Researchers at the University of Cincinnati (UC) and Massachusetts General Hospital have found that warfarin, a known anticoagulation (blood-thinning) drug, may not be as beneficial to some patients with atrial fibrillation as previously thought.
These findings were published online this week ahead of print in the journal Circulation: Cardiovascular Quality and Outcomes.
Warfarin is commonly prescribed to prevent blood clotting, particularly for patients with atrial fibrillation—a type of abnormal heart rhythm.
Mark Eckman, MD, professor of medicine at ...
Alzheimer and heart attacks have been found to share common genetic basis. The research leads the way to the first genetic test on developing the risk of the diseases even at a young age. According to Federico Licastro, an immunologist at the University of Bologna who coordinated the study published in the scientific journal, Journal of Alzheimer's Disease, a test is now ready. "They are already selling it in America", he says, citing the case of a private firm in New Mexico (USA) that collaborated on the study. "But the tests could easily be also conducted wherever, using ...
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) –– Remarkable progress in understanding how stem cell biology works has been reported by a team of leading scientists, directed by experts at UC Santa Barbara. Their research has been published in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
Stem cell biology is making waves around the world with great hope for the eventual repair of parts of the body. While many scientists see these breakthroughs as viable, there are hurdles that must be overcome, including the worrisome potential for introducing cancer when making a repair to an organ.
Significant interdisciplinary ...