(Press-News.org) Rice University researchers have moved a step closer to creating robust, three-dimensional microbatteries that would charge faster and hold other advantages over conventional lithium-ion batteries. They could power new generations of remote sensors, display screens, smart cards, flexible electronics and biomedical devices.
The batteries employ vertical arrays of nickel-tin nanowires perfectly encased in PMMA, a widely used polymer best known as Plexiglas. The Rice laboratory of Pulickel Ajayan found a way to reliably coat single nanowires with a smooth layer of a PMMA-based gel electrolyte that insulates the wires from the counter electrode while allowing ions to pass through.
The work was reported this week in the online edition of the journal Nano Letters.
"In a battery, you have two electrodes separated by a thick barrier," said Ajayan, professor in mechanical engineering and materials science and of chemistry. "The challenge is to bring everything into close proximity so this electrochemistry becomes much more efficient."
Ajayan and his team feel they've done that by growing forests of coated nanowires -- millions of them on a fingernail-sized chip -- for scalable microdevices with greater surface area than conventional thin-film batteries. "You can't simply scale the thickness of a thin-film battery, because the lithium ion kinetics would become sluggish," Ajayan said.
"We wanted to figure out how the proposed 3-D designs of batteries can be built from the nanoscale up," said Sanketh Gowda, a graduate student in Ajayan's lab. "By increasing the height of the nanowires, we can increase the amount of energy stored while keeping the lithium ion diffusion distance constant."
The researchers, led by Gowda and postdoctoral researcher Arava Leela Mohana Reddy, worked for more than a year to refine the process.
"To be fair, the 3-D concept has been around for a while," Reddy said. "The breakthrough here is the ability to put a conformal coat of PMMA on a nanowire over long distances. Even a small break in the coating would destroy it." He said the same approach is being tested on nanowire systems with higher capacities.
The process builds upon the lab's previous research to build coaxial nanowire cables that was reported in Nano Letters last year. In the new work, the researchers grew 10-micron-long nanowires via electrodeposition in the pores of an anodized alumina template. They then widened the pores with a simple chemical etching technique and drop-coated PMMA onto the array to give the nanowires an even casing from top to bottom. A chemical wash removed the template.
They have built one-centimeter square microbatteries that hold more energy and that charge faster than planar batteries of the same electrode length. "By going to 3-D, we're able to deliver more energy in the same footprint," Gowda said.
They feel the PMMA coating will increase the number of times a battery can be charged by stabilizing conditions between the nanowires and liquid electrolyte, which tend to break down over time.
The team is also studying how cycling affects nanowires that, like silicon electrodes, expand and contract as lithium ions come and go. Electron microscope images of nanowires taken after many charge/discharge cycles showed no breaks in the PMMA casing -- not even pinholes. This led the researchers to believe the coating withstands the volume expansion in the electrode, which could increase the batteries' lifespans.
INFORMATION:
Co-authors are Rice graduate student Xiaobo Zhan; former Rice postdoctoral researcher Manikoth Shaijumon, now an assistant professor at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Thiruvananthapuram, India; and former Rice research scientist Lijie Ci, now a senior research and development manager at Samsung Cheil Industries.
The Hartley Family Foundation and Rice University funded the research.
Read the abstract at http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl102919m
Download artwork at http://www.media.rice.edu/images/media/2010RiceNews/1207_artwork.tif
CAPTION:
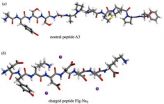
A nanostructured lithium ion battery developed at Rice University may charge faster and last longer than Li ion batteries in current use. Nanowires with a PMMA polymer coating, seen in a transmission electron microscope image at right, solve a long-standing problem of forming ultrathin electrolyte layers around nanostructured electrode materials. (Credit: Ajayan Lab/Rice University)
Located in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked one of America's best teaching and research universities. Known for its "unconventional wisdom," Rice is distinguished by its: size -- 3,279 undergraduates and 2,277 graduate students; selectivity -- 12 applicants for each place in the freshman class; resources -- an undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio of 5-to-1; sixth largest endowment per student among American private research universities; residential college system, which builds communities that are both close-knit and diverse; and collaborative culture, which crosses disciplines, integrates teaching and research, and intermingles undergraduate and graduate work.
Children exposed to Jalan Sesama, an Indonesian version of the children's television show Sesame Street, had improved educational skills and healthy development, according to a study by researchers at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health. Over a 14-week period, the children who had the greatest exposure to Jalan Sesama improved significantly in literacy, mathematics, early cognitive skills, safety knowledge and social awareness, compared to those with no or low exposure to the program. The study is available online in advance of publication in the International ...
COLLEGE STATION, Dec. 9, 2010 – Changes in clouds will amplify the warming of the planet due to human activities, according to a breakthrough study by a Texas A&M University researcher.
Andrew Dessler, a professor in the Department of Atmospheric Sciences, says that warming due to increases in greenhouse gases will cause clouds to trap more heat, which will lead to additional warming. This process is known as the "cloud feedback" and is predicted to be responsible for a significant portion of the warming over the next century.
Dessler used measurements from the Clouds ...
WASHINGTON — A new National Research Council report finds no scientific basis that more stringent testing of meat purchased through the government's ground beef purchase program and distributed to various federal food and nutrition programs -- including the National School Lunch Program -- would lead to safer meat.
The U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Marketing Service (AMS) buys ground beef from suppliers who must meet mandatory process, quality, traceback, and handling controls as well as comply with strict limitations on the amounts of bacteria in the ...
Columbus, Ohio – A University of Akron researcher is leveraging advanced modeling and simulation techniques to more precisely understand how organic materials bond to inorganic materials, a natural phenomenon that if harnessed, could lead to the design of composite materials and devices for such applications as bone replacement, sensing systems, efficient energy generation and treatment of diseases.
Hendrik Heinz, Ph.D., an assistant professor of polymer engineering at UA, is accessing the systems of the Ohio Supercomputer Center (OSC) to study the process of biomineralization, ...
Menlo Park, Calif. – December 9, 2010 – Scientists from Pacific Biosciences of California, Inc. (NASDAQ: PACB) and Harvard Medical School have successfully employed single molecule, real-time (SMRT™) DNA sequencing technology to rapidly characterize the pathogen responsible for the recent deadly cholera epidemic in Haiti. Published Thursday in the New England Journal of Medicine, the results provide the first whole genome sequence analysis and most detailed genetic profile to date of the Haitian Vibrio cholerae outbreak strain.
The multi-strain sequencing and bioinformatic ...
Fungi are a major cause of plant diseases and are responsible for large-scale harvest failure in crops like maize and other cereals all over the world. Together with scientists from the Helmholtz Zentrum in Munich, Regine Kahmann, from the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Marburg, and Jan Schirawski, who is now based at the University of Göttingen, analysed the genetic make-up of Sporisorium reilianum, an important maize parasite. Based on a comparison with the genome of a related fungal species, they succeeded in identifying new genes that play an important ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio – A preliminary look at an ice field atop the highest mountain in the eastern European Alps suggests that the glacier may hold records of ancient climate extending back as much as a thousand years.
Researchers warn, however, that the record may soon be lost as global warming takes its toll on these high-altitude sites, according to a new study in the Journal of Glaciology.
The glacier, Alto dell'Ortles, is the highest large ice body in the eastern Alps, reaching an altitude of 12,812 feet (3,905 meters) above sea level. It is small, though, measuring ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — The risk of esophageal cancer among patients who suffer from gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is not as high as many may think, according to new research from University of Michigan gastroenterologists.
GERD is considered a relative risk for developing esophageal adenocarcinoma, but the absolute risk is not known, says Joel Rubenstein, M.D., M.Sc., an investigator with the Department of Veterans Affairs Center for Clinical Management Research in Ann Arbor and Assistant Professor in the University of Michigan's Department of Internal Medicine.
"Since ...
New clinical strains of cholera appear to have evolved a distinctly different mechanism to cause the same disease according to research published in the current issue of the online journal mBio®.
Vibrio cholerae is the causative agent for the diarrheal disease cholera. While there are more than 200 different serogroups only the O1 and the O139 strains have been known to cause epidemic and pandemic outbreaks of disease, using a toxin-coregulated pilus (TCP) and cholera toxin (CT), which other strains lack.
"While non-O1, non-O139 strains have caused sporadic disease ...
A light-weight bike that costs around £1000 may not get you to work any quicker than a similar, yet heavier and cheaper model, finds research in the Christmas issue published on bmj.com today.
A keen cyclist since childhood, the author Dr Jeremy Groves, owns two bikes. One a second hand 13.5 kg steel framed bike bought for £50 and the other a brand new 9.5 kg carbon framed bike that cost £1000.
When Dr Groves, a consultant in anaesthesia and intensive care at Chesterfield Royal Hospital, realised his new bike took 43 minutes to get him to work rather than the 44 minutes ...