(Press-News.org) Chicago, August 5, 2015--A new national survey conducted by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research reveals a disparity among blacks' and whites' perception of violence against civilians by police. Nearly three-quarters of black respondents consider violence against civilians by police officers to be an extremely or very serious problem, compared to less than 20 percent of whites. However, the poll also finds agreement across racial groups on many of the causes of police violence, as well as further consensus that changes in policies and procedures could be effective in reducing tensions between minorities and police and in limiting violence against civilians.
The nationwide poll was collected July 17 to 19, 2015, using the AmeriSpeak Omnibus, the probability-based panel of NORC at the University of Chicago. Online and telephone interviews using landlines and cell phones were conducted with 1,223 adults, including 311 blacks who were sampled at a higher rate than their proportion of the population for reasons of analysis.
"This survey indicates that while there is a deep divide among Americans on these issues, there are key points of agreement as well," said Trevor Tompson, director of The AP-NORC Center. "There is widespread agreement that race relations in the United States are in a sorry state, and blacks and whites agree that changes in policies and procedures could be effective in reducing tensions between minorities and police and in limiting violence against civilians."
Some of the poll's key findings include:
Many Americans, regardless of race, say that violence against police is also an extremely or very serious problem in the United States. And half of all Americans, regardless of race, say fear caused by the physical danger that police officers face is a major contributor to aggression against civilians.
An overwhelming majority of blacks say that, generally, the police are too quick to use deadly force and that they are more likely to use it against a black person. Most whites say police officers typically use deadly force only when necessary and that race is not a factor in decisions to use force.
Blacks and whites are sharply divided on whether police officers who injure or kill civilians are treated too leniently by prosecutors and on how much that contributes to the use of force against members of the public.
Half of black Americans report being treated unfairly by police because of their race, and their views of law enforcement are shaped by this experience.
Minorities are more concerned about crime and more skeptical about law enforcement's efforts to control it.
Blacks and whites agree that changes in policies and procedures, such as community policing programs and police body cameras, could be effective in reducing tensions between minorities and police and in limiting violence against civilians.
There is widespread agreement that race relations in the United States are in a bad state, but racial division exists on whether this contributes to police violence.
INFORMATION:
About AmeriSpeak Omnibus
AmeriSpeak Omnibus is a once-a-month, multi-client survey using a probability sample of at least 1,000 nationally representative adults age 18 and older. Respondents are interviewed online and by phone from NORC's AmeriSpeak panel--the most scientifically rigorous multi-client household panel in the United States. AmeriSpeak households are selected randomly from NORC's National Sample Frame, the industry leader in sample coverage. The National Frame is representative of over 99 percent of U.S. households and includes additional coverage of hard-to-survey population segments, such as rural and low-income households, that are underrepresented in other sample frames. More information about AmeriSpeak is available at AmeriSpeak.NORC.org.
About the Survey
Respondents were interviewed online and by phone from NORC's AmeriSpeak panel. The overall margin of sampling error is +/- 4.2 percentage points at the 95 percent confidence level, including the design effect. The margin of sampling error may be higher for subgroups; it is +/- 9.1 percentage points for the oversample of blacks. A full description of the study methodology can be found at http://www.apnorc.org.
About The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research
The AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research taps into the power of social science research and the highest-quality journalism to bring key information to people across the nation and throughout the world.
http://www.apnorc.org
The Associated Press is the essential global news network, delivering fast, unbiased news from every corner of the world to all media platforms and formats. Founded in 1846, AP today is the most trusted source of independent news and information. On any given day, more than half the world's population sees news from AP.
http://www.ap.org
NORC at the University of Chicago is an independent research institution that delivers reliable data and rigorous analysis to guide critical programmatic, business, and policy decisions. Since 1941, NORC has conducted groundbreaking studies, created and applied innovative methods and tools, and advanced principles of scientific integrity and collaboration. Today, government, corporate, and nonprofit clients around the world partner with NORC to transform increasingly complex information into useful knowledge.
http://www.norc.org
The two organizations have established The AP-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research to conduct, analyze, and distribute social science research in the public interest on newsworthy topics, and to use the power of journalism to tell the stories that research reveals.
Contact: For more information, contact Eric Young for NORC at young-eric@norc.org or (703) 217-6814 (cell); Ray Boyer for NORC at boyer-ray@norc.org or (312) 330-6433; or Paul Colford for AP at pcolford@ap.org or info@apnorc.org.
Disney Research has created LinkEdit, interactive software for predictably changing the shape or motion of planar linkages used in such objects as kinetic sculptures, folding furniture and mechanical toys.
The LinkEdit software enables users to make desired changes in a linkage, such as altering its size or shape, while preserving other features, such as the walking gait of a linkage for a mechanical leg. The researchers demonstrated this capability by making alterations to the Jansen linkage, the building block to the famous walking sculptures created by artist Theo ...
Forehead wrinkles that rapidly deepen and crow's feet that appear suddenly around the eyes might distress the average person, but the ability to quickly and realistically incorporate such details in a facial reconstruction is the key feature of a new performance capture method developed at Disney Research.
The method, which requires only a single video camera such as a webcam, is the first to both operate in real-time and to capture facial features in high resolution, including such details as wrinkles.
"This could open up a variety of new applications, from casual ...
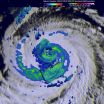
Heavy rain, towering thunderstorms, and a large area are things that NASA satellites observed as Typhoon Soudelor moves toward Taiwan on August 5, 2015.
NASA's Terra satellite passed over Soudelor on August 5, 2015 at 01:45 UTC and the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) instrument captured a visible image of the large storm in the Philippine Sea. The eye appeared to be cloud-filled as bands of thunderstorms spiraled into the center of the storm.
The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission core observatory, a satellite managed by both NASA and ...
A team of astronomers led by Caltech has discovered a giant swirling disk of gas 10 billion light-years away--a galaxy-in-the-making that is actively being fed cool primordial gas tracing back to the Big Bang. Using the Caltech-designed and -built Cosmic Web Imager (CWI) at Palomar Observatory, the researchers were able to image the protogalaxy and found that it is connected to a filament of the intergalactic medium, the cosmic web made of diffuse gas that crisscrosses between galaxies and extends throughout the universe.
The finding provides the strongest observational ...
Washington, DC, August 5, 2015 -- Potentially harmful bacteria can survive on endoscopes used to examine the interior of the digestive tract, despite a multi-step cleaning and disinfecting process, according to a study published in the August issue of the American Journal of Infection Control, the official publication of the Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC).
Though endoscopes were cleaned in accordance with multi-society guidelines, viable microbes and residual contamination remained on surfaces after each stage of cleaning, ...
Dan's Wild Wild Science Journal
New paper shows global climate model errors are significantly less than thought
Scientists have matched the output of climate models to the way the Earth's temperature record is constructed in a new study in Geophysical Research Letters. Dan Satterfield explores how climate models are doing an even better job at predicting the Earth's temperature than was thought.
Eos.org
On the rebound: Modeling Earth's ever-changing shape
A new modeling tool easily computes the elastic response of changes in loading on Earth's surface to high resolution. ...
While undergoing laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy induced weight loss and improvements in obesity-related disorders, long-term followup shows significant weight regain and a decrease in remission rates of diabetes and, to a lesser extent, other obesity-related disorders over time, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Obesity was recognized as a global epidemic by the World Health Organization 15 years ago and rates of obesity have since been increasing. Obesity is currently considered a severe health hazard and a risk factor for diabetes mellitus, hypertension, ...
In a small study, women who had Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery reached certain blood alcohol concentrations in half the number of drinks compared to women who didn't have the surgery, and reported a greater feeling of drunkenness, according to a study published online by JAMA Surgery.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) is the most common bariatric surgical procedure performed in the world. Although RYGB surgery causes a marked reduction in food intake and induces remission of food addiction, it is associated with an increased risk of developing alcohol use disorders. It ...
Telephone-based cognitive behavioral therapy was better at reducing worry, generalized anxiety disorder symptoms and depressive symptoms in older adults who live in rural areas, where access to mental health treatment may be limited, according to an article published online by JAMA Psychiatry.
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common anxiety disorders in older adults and is associated with poor quality of life, increased health care utilization and impaired memory. Medications and psychotherapy are the primary treatments. Many older adults prefer psychotherapy ...
To lose weight, boost energy or soothe nerves, many consumers turn to dietary supplements. But some of these products contain undeclared substances. To protect consumers from taking something without their knowledge, scientists have developed a technique to determine what secret ingredients could be lurking in these supplements. They report their approach, which helped them find the active Viagra ingredient and other synthetic designer compounds in various products, in ACS' Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry.
Dietary supplements can appear to be a healthful option ...