(Press-News.org) WORCESTER, MA -- Researchers at the University of Massachusetts Medical School have found that Google Glass, a head-mounted streaming audio/video device, may be used to effectively extend bed-side toxicology consults to distant health care facilities such as community and rural hospitals to diagnose and manage poisoned patients. Published in the Journal of Medical Toxicology, the study also showed preliminary data that suggests the hands-free device helps physicians in diagnosing specific poisonings and can enhance patient care.
"In the present era of value-based care, a toxicology service using hands-free devices, such as Google Glass, could conceivably expand its coverage area and enhance patient care, while potentially decreasing overall treatment costs," said Peter R. Chai, MD, toxicology fellow at UMass Medical School. "Our work shows that the data transmitted by Google Glass can be used to supplement traditional telephone consults, validate bedside physical exams, and diagnose and manage patients."
Traditional telemedicine devices usually consist of large desktop or laptop computers affixed to a big cart that has to be rolled from exam room to exam room. This limits both access and functionality in a busy emergency room setting.
"Glass is positioned perfectly as an emergency medicine telemedical device. Its small, hands free and portable, so you can bring it right to the bedside and have a real-time specialist with you when you need one," said Dr. Chai.
Advances in wireless infrastructure, the miniaturization of hardware and the advent of wearable devices such as Google Glass allow a new generation of technologies that can assist physicians and improve health care delivery to be deployed in clinical settings. Through the device, physicians can stream video of an exam, take and enlarge photos and consult with remote specialists.
In the study, emergency medicine residents at UMass Memorial Medical Center performed 18 toxicology consults with Google Glass. ER physicians wearing Google Glass evaluated the patients at bedside while a secure video feed was sent to the toxicology supervising consultant. The supervising consultant then guided the resident through text messages displayed on the Glass. Consultants also obtained static photos of medication bottles, electrocardiograms (EKG) and other pertinent information at the discretion of the supervisor. This was done in addition to the standard verbal consult available to residents.
As a result of using Google Glass, consulting toxicologists reported being more confident in diagnosing specific toxidromes. Additional data collected showed that the use of Google Glass also changed management of patient care in more than half of the cases seen. Specifically, six of those patients received antidotes they otherwise would not have. Overall, 89 percent of the cases seen with Glass were considered successful by the consulting toxicologist.
"Placing an expert at the virtual bedside of the patient has huge advantages," said Chai. "It brings a specialist to patients that might not otherwise have access to that kind of expertise. Because Google Glass is relatively unobtrusive to patients, can be operated hands free and is extremely portable, it has a distinct advantage over traditional telemedicine platforms."
Having shown that Google Glass is a feasible option for toxicology consults in the emergency room setting, Chai said the next step will be to determine the role Google Glass can play in the remote care of poisoned patients.
To safeguard patient information, each device was equipped with a third-party HIPPA-complaint platform called Pristine Eyesight. Information passing through Google Glass was encrypted for security and privacy.
INFORMATION:
About the University of Massachusetts Medical School
The University of Massachusetts Medical School, one of the fastest growing academic health centers in the country, has built a reputation as a world-class research institution, consistently producing noteworthy advances in clinical and basic research. The Medical School attracts more than $240 million in research funding annually, 80 percent of which comes from federal funding sources. The mission of the Medical School is to advance the health and well-being of the people of the commonwealth and the world through pioneering education, research, public service and health care delivery with its clinical partner, UMass Memorial Health Care. For more information, visit http://www.umassmed.edu.
Health care organizations have been implementing health information technology at increasing rates in an effort to engage patients and caregivers improve patient satisfaction, and favorably impact outcomes. A new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital (BWH) finds that a novel web-based, patient-centered toolkit (PCTK) used by patients and/or their healthcare proxys in the hospital setting helped them to engage in understanding and developing their plan of care, and has the potential to improve communication with providers. The results of the study are ...
Australian scientists have discovered many tropical, mountaintop plants won't survive global warming, even under the best-case climate scenario.
James Cook University and Australian Tropical Herbarium researchers say their climate change modelling of mountaintop plants in the tropics has produced an "alarming" finding.
They found many of the species they studied will likely not be able to survive in their current locations past 2080 as their high-altitude climate changes.
The Wet Tropics World Heritage Area in Queensland, Australia is predicted to almost completely ...
A James Cook University study shows fish retreating to deeper water to escape the heat, a finding that throws light on what to expect if predictions of ocean warming come to pass.
JCU scientists tagged 60 redthroat emperor fish at Heron Island in the southern Great Barrier Reef. The fish were equipped with transmitters that identified them individually and signaled their depth to an array of receivers around the island.
The experiment monitored fish for up to a year and found the fish were less likely to be found on the reef slope on warmer days. Scientists think ...
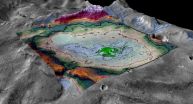
Mars turned cold and dry long ago, but researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have discovered evidence of an ancient lake that likely represents some of the last potentially habitable surface water ever to exist on the Red Planet.
The study, published Thursday in the journal Geology, examined an 18-square-mile chloride salt deposit (roughly the size of the city of Boulder) in the planet's Meridiani region near the Mars Opportunity rover's landing site. As seen on Earth in locations such as Utah's Bonneville Salt Flats, large-scale salt deposits are considered ...
Ruxolitinib (trade name: Jakavi) has been approved since March 2015 for the treatment of adults with polycythaemia vera, a rare disease of the bone marrow. It can be used when the drug hydroxyurea is ineffective or not tolerated. The German Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG) examined in a dossier assessment whether this drug offers an added benefit over the appropriate comparator therapy.
According to the findings, ruxolitinib offers better relief of individual symptoms and improves quality of life. Dyspnoea and muscle cramps are more frequent, ...
Brussels, [7 August 2015] - An unresolved inflammatory response is likely to be involved from the early stages of disease development. Controlling inflammation is crucial to human health and a key future preventative and therapeutic target. In a recent ILSI Europe's article published in the British Journal of Nutrition, a coalition of experts explain how nutrition influences inflammatory processes and help reduce chronic diseases risk.
Inflammation is a normal component of host defence, but elevated unresolved chronic inflammation is a core perturbation in a range of ...
Simon Fraser University scientist Jonathan Moore has authored new research suggesting that a proposed controversial terminal to load fossil fuels in the Skeena River estuary has more far-reaching risks than previously recognized.
In a letter newly published in the journal Science Moore and First Nations leaders and fisheries biologists from throughout the Skeena watershed refer to the new data, which is on the Moore Lab site.
Moore is a Faculty of Science and a Faculty of Environment professor of ecology and conservation of freshwaters and the Liber Ero Chair of Coastal ...
HOUSTON, August 6, 2015 - This week marks the 50th anniversary of the Voting Rights Act. This week also marks a watershed ruling by a federal appeals court striking down the controversial Texas voter ID law as violating that landmark civil rights act.
A new study conducted by the University of Houston Hobby Center for Public Policy and Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy examines the impact of the contested Texas law in U.S. Congressional District 23 (CD-23).
The study suggests that the most significant impact of the Texas voter photo ID law on voter ...
Psychologists from Cardiff University have developed the first self-assessment test designed to help clinicians diagnose autism in adults.
Published in the Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders the test measures the extent to which adults are affected by repetitive behaviours - one of the criteria used to diagnose autism.
These behaviours include common habits and routines, such as lining up objects or arranging them in patterns, fiddling obsessively with objects, or insisting that aspects of a daily routine remain exactly the same.
Researchers say that the ...
A web-based programme to encourage more frequent handwashing reduces the risk of catching and passing on respiratory tract infections to other household members, a randomised trial of more than 16000 UK households published in The Lancet has found. Users of the programme, called PRIMIT [1], also reported fewer gastrointestinal infections, a lower demand for consultations with their doctors, and fewer antibiotic prescriptions.
"Our findings suggest that a simple, cheap internet programme to encourage handwashing can reduce the risk of infection by around 14%. Because most ...