INFORMATION:
The research was funded initially by a Rapid Response Grant from the National Science Foundation, and continued for three years through support from the Deerbook Charitable Trust and Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
The Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution is a private, non-profit organization on Cape Cod, Mass., dedicated to marine research, engineering, and higher education. Established in 1930 on a recommendation from the National Academy of Sciences, its primary mission is to understand the ocean and its interaction with the Earth as a whole, and to communicate a basic understanding of the ocean's role in the changing global environment. For more information, please visit http://www.whoi.edu.
Examining the fate of Fukushima contaminants
A fraction of buried, ocean sediment uncovered by typhoons, carried offshore by currents
2015-08-18
(Press-News.org) An international research team reports results of a three-year study of sediment samples collected offshore from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in a new paper published August 18, 2015, in the American Chemical Society's journal, Environmental Science and Technology.
The research aids in understanding what happens to Fukushima contaminants after they are buried on the seafloor off coastal Japan.
Led by Ken Buesseler, a senior scientist and marine chemist at the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), the team found that a small fraction of contaminated seafloor sediments off Fukushima are moved offshore by typhoons that resuspend radioactive particles in the water, which then travel laterally with southeasterly currents into the Pacific Ocean.
"Cesium is one of the dominant radionuclides that was released in unprecedented amounts with contaminated water from Japan's Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant following the March 11, 2011, earthquake and tsunami," says Buesseler. "A little over 99 percent of it moved with the water offshore, but a very small fraction--less than one percent--ended up on the sea floor as buried sediment."
"We've been looking at the fate of that buried sediment on the continental shelf and tracking how much of that contaminated sediment gets offshore through re-suspension from the ocean bottom," he adds.
The research team, which included colleagues from the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology and the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, analyzed three years' worth of data collected from time-series sediment traps.
Researchers deployed the pre-programmed, funnel-shaped instruments 115 kilometers (approximately 70 miles) southeast of the nuclear power plant at depths of 500 meters (1,640 feet) and 1,000 meters (3,280 feet). The two traps began collecting samples on July 19, 2011--130 days after the March 11th earthquake and tsunami--and were recovered and reset annually.
After analyzing the data, researchers found radiocesium from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident in the sediment samples along with a high fraction of clay material, which is characteristic of shelf and slope sediments suggesting a near shore source.
"This was a bit of a surprise because when we think of sediment in the ocean, we think of it as sinking vertically, originating from someplace above. But what this study clearly shows is that the only place that the material in our sediment traps could have come from was the continental shelf and slope buried nearshore. We know this because the coastal sediments from the shelf have a unique Fukushima radioactive and mineral signal," says Buesseler.
The data also revealed that peak movements of the sediments with radiocesium coincided with passing typhoons which likely triggered the resuspension of coastal sediments. Radiocesium was still detected in sediment samples from July 2014.
"The total transport is small, though it is readily detectable. One percent or less of the contaminated sediment that's moving offshore every year means things aren't going to change very fast," Buesseler says. "What's buried is going to stay buried for decades to come. And that's what may be contributing to elevated levels of cesium in fish--particularly bottom-dwelling fish off Japan."
While there were hundreds of di?erent radionuclides released from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant during the disaster, after the initial decay of contaminants with half lives (the time it takes for one half of a given amount of radionuclide to decay) less than days to weeks, much of the attention has remained focused on cesium-137 and-134-- two of the more abundant contaminants. Cesium-134 has a half-life of a little over two years, and so any found in the ocean could come only from the reactors at Fukushima. Cesium-137 has a half-life of roughly 30 years and is also known to have entered the Pacific as a result of aboveground nuclear weapons tests in the 1950s and '60s, providing a benchmark against which to measure any additional releases from the reactors.
In October, Buesseler and the research team will return to Japan to redeploy more sediment traps. The continued study will help estimate how long it takes to decrease the level of radiocesium in seafloor sediments near the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Just 1 in 10 are referred for cardiac rehab after treatment for heart failure
2015-08-18
Only 1 in 10 heart failure patients is referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program after being hospitalized, despite strong evidence that such exercise programs improve quality of life and reduce the likelihood of future hospitalizations.
The findings, from a UCLA-led study, appear in the August 25 Journal of the American College of Cardiology. Researchers drew the data from a national database of more than 100,000 people with heart failure who were discharged from hospitals between 2005 and 2014 and were eligible for cardiac rehabilitation programs.
"Although we expected ...
Breakthrough optics pave way for new class of intriguing technologies
2015-08-18
A new class of fascinating technologies -- including optics in computing, telecommunications links and switches, and virtually any other optical component -- could be created simply by configuring a mesh of light-controlling devices known as interferometers. This is similar to the way electronic semiconductors can fashion the wide array of digital technologies we have at our disposal today.
Optical technologies have the potential to greatly reduce the power consumption of computers, speed telecommunications, and enhance the sensitivity of chemical and biological sensors. ...
Pediatric training essential to improving out-of-hospital emergency care for children
2015-08-18
A national survey of more than 750 emergency medical services providers conducted by researchers at Oregon Health & Science University identified airway management skills, personal anxiety and limited pediatric care proficiency among key factors that may contribute to pediatric safety events for children in out-of-hospital emergent care situations. The study, published online today in The Journal of Pediatrics, supports the American Academy of Pediatrics' recommendation for pediatric physician involvement in EMS training, medical oversight and policy development.
"Pediatric ...
Massacres, torture and mutilation: Extreme violence in neolithic conflicts
2015-08-18
Violent conflicts in Neolithic Europe were held more brutally than has been known so far. This emerges from a recent anthropological analysis of the roughly 7000-year-old mass grave of Schöneck-Kilianstädten by researcher of the Universities of Basel and Mainz. The findings, published in the journal PNAS, show that victims were murdered and deliberately mutilated.
It was during the time when Europeans first began to farm. To what degree conflicts and wars featured in the early Neolithic (5600 to 4900 B.C.), and especially in the so-called Linear Pottery culture ...
Key genetic event underlying fin-to-limb evolution
2015-08-18
A study of catsharks reveals how alterations in the expression and function of certain genes in limb buds underlie the evolution of fish fins to limbs. The findings are reported by researchers from Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG, Barcelona) and their collaborators in the journal eLife and give new insight into how fish evolved to live on land in the form of early tetrapods.
The first four-legged, land-living creatures - known as early tetrapods - evolved from fish, following the transformation of fins into limbs. This ...
Patient satisfaction is a poor surrogate for quality of care in brain surgery
2015-08-18
Patient satisfaction is a very poor proxy for quality of care comparisons in elective cranial neurosurgery. Because deaths are rare events in elective cranial neurosurgery, reporting of surgeon or even department-specific mortality figures cannot differentiate a high or low level of the quality of care.
The current focus on patient safety in health care has led to public quality-of-care comparisons between health care facilities and even between individual health care professionals. In the United States, a new reimbursement method based on patient satisfaction ratings ...
Challenge to classic theory of 'organic' solar cells could improve efficiency
2015-08-18
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - New research findings contradict a fundamental assumption about the functioning of "organic" solar cells made of low-cost plastics, suggesting a new strategy for creating inexpensive solar technology.
Commercialization of organic solar cells has been hindered by inefficiencies, but the findings point toward a potential path to create a new class of solar technology able to compete with standard silicon cells.
"These solar cells could provide a huge cost advantage over silicon," said Muhammad Ashraful Alam, Purdue University's Jai N. Gupta Professor ...
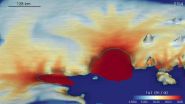
Most comprehensive projections for West Antarctica's future revealed
2015-08-18
A new international study is the first to use a high-resolution, large-scale computer model to estimate how much ice the West Antarctic Ice Sheet could lose over the next couple of centuries, and how much that could add to sea-level rise. The results paint a clearer picture of West Antarctica's future than was previously possible. The study is published today (18 August) in The Cryosphere, an open access journal of the European Geosciences Union (EGU).
"The IPCC's [Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change] 4th and 5th Assessment Reports both note that the acceleration ...
Possible test for liver cancer using technology for analysing rocks and minerals
2015-08-18
A group of clinicians and geochemists are working to develop a test for the most common form of primary liver cancer, HCC (Hepatocellular Carcinoma). HCC kills over 600,000 people worldwide every year. It usually develops from chronic liver disease such as hepatitis or cirrhosis, but there is no good biochemical test to indicate when the cancer develops, meaning that even for patients most at risk, it is nearly impossible to know when a cancer may develop until symptoms appear. Now a multi-national group of scientists are developing a new test for HCC, based on methods ...
How having racially diverse friends can help you on the job
2015-08-18
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Employees with a racially diverse group of friends outside of work may actually perform better at their jobs, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that workers who had more different-race friends in their personal lives than their co-workers also tended to have a more racially diverse network of friends on the job. This broader network was linked to employees who did more tasks beyond their job responsibilities and who, under certain circumstances, had more trust in their supervisors.
"Your friends outside of work actually have this connection to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
[Press-News.org] Examining the fate of Fukushima contaminantsA fraction of buried, ocean sediment uncovered by typhoons, carried offshore by currents