(Press-News.org) PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Old dogs can teach humans new things about evolution. In Nature Communications a new study of North American dog fossils as old as 40 million years suggests that the evolutionary path of whole groups of predators can be a direct consequence of climate change.
"It's reinforcing the idea that predators may be as directly sensitive to climate and habitat as herbivores," said Christine Janis, professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at Brown University, who worked with lead author Borja Figueirido, a former Brown Fulbright postdoctoral researcher who is now a professor at the Universidad de Málaga in Spain. "Although this seems logical, it hadn't been demonstrated before."
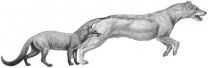
The climate in North America's heartland back around 40 million years ago was warm and wooded. Dogs are native to North America. The species of the time, fossils show, were small animals that would have looked more like mongooses than any dogs alive today and were well-adapted to that habitat. Their forelimbs were not specialized for running, retaining the flexibility to grapple with whatever meal unwittingly walked by.
But beginning just a few million years later, the global climate began cooling considerably and in North America the Rocky Mountains had reached a threshold of growth that made the continental interior much drier. The forests slowly gave way to open grasslands.
Pups of the plains
Did this transition affect the evolution of carnivores? To find out, Figueirido and the research team, including Jack Tseng of the American Museum of Natural History in New York, examined the elbows and teeth of 32 species of dogs spanning the period from ca. 40 million years ago to 2 million years ago. They saw clear patterns in those bones at the museum: At the same time that climate change was opening up the vegetation, dogs were evolving from ambushers to pursuit-pounce predators like modern coyotes or foxes -- and ultimately to those dogged, follow-a-caribou-for-a-whole-day pursuers like wolves in the high latitudes.
"The elbow is a really good proxy for what carnivores are doing with their forelimbs, which tells their entire locomotion repertoire," Janis said.
The telltale change in those elbows has to do with the structure of the base where the humerus articulates with the forearm, changing from one where the front paws could swivel (palms can be inward or down) for grabbing and wrestling prey to one with an always downward-facing structure specialized for endurance running. Modern cats still rely on ambush rather than the chase (cheetahs are the exception) and have the forelimbs to match, Janis said, but canines signed up for lengthier pursuits.
In addition, the dogs' teeth trended toward greater durability, Figueirido's team found, consistent perhaps with the need to chow down on prey that had been rolled around in the grit of the savannah, rather than a damp, leafy forest floor.
Not an 'arms race' of limbs
The study, with some of Janis' prior research, suggests that predators do not merely evolve as an "arms race" response to their prey. They don't develop forelimbs for speedy running just because the deer and the antelope run faster. While the herbivores of this time were evolving longer legs, the predator evolution evident in this study tracked in time directly with the climate-related changes to habitat rather than to the anatomy of their prey species.
After all, it wasn't advantageous to operate as a pursuit-and-pounce predator until there was room to run.
"There's no point in doing a dash and a pounce in a forest," Janis quipped. "They'll smack into a tree."
If predators evolved with climate change over the last 40 million years, the authors argue, then they likely will have to continue in response to the human-created climate change underway now. The new results could help predict the effects we are setting in motion.
"Now we're looking into the future at anthropogenic changes," Janis said.
INFORMATION:
In addition to Figueirido and Janis, the paper's other authors are A. Mártin-Serra of Málaga and Z.J. Tseng of the American Museum of National History.
Most of the debate around e-cigarettes has focused on the developed world, but the devices are becoming more widely available in some low- and middle-income countries, where there is even greater potential for impact on public health, say two Stanford University School of Medicine researchers.
"People don't think e-cigarettes will reach the developing world. But they are already being produced in developing countries, and they are cheap. People know they are available," said Andrew Chang, MD, a resident in internal medicine who focuses on global health.
Chang and Michele ...
Among high school students in Los Angeles, those who had ever used electronic cigarettes were more likely to report initiation of smokable ("combustible") tobacco (such as cigarettes, cigars, and hookah) use over the next year compared with nonusers, according to a study in the August 18 issue of JAMA.
Combustible tobacco, which has well-known health consequences, has long been the most common nicotine-delivering product used. Electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), which are devices that deliver inhaled aerosol usually containing nicotine, are becoming increasingly popular, ...
Among overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes, daily injection of the diabetes drug liraglutide with a modified insulin pen device, in addition to diet and exercise, resulted in greater weight loss over 56 weeks compared with placebo, according to a study in the August 18 issue of JAMA.
Obesity is a chronic disease and a significant global health challenge. Weight loss is recommended for patients with type 2 diabetes. Moderate weight loss (5 percent-10 percent) can improve glycemic control and other cardiometabolic risk factors and disorders. Weight loss is ...
Among patients with active cancer and acute symptomatic venous thromboembolism (VTE; blood clots in the deep veins), the use of the low molecular-weight heparin tinzaparin daily for 6 months compared with warfarin did not significantly reduce recurrent VTE and was not associated with reductions in overall death or major bleeding, but was associated with a lower rate of clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding, according to a study in the August 18 issue of JAMA.
Venous thromboembolism is a major cause of illness and death in patients with cancer. Treatment with low-molecular-weight ...
Scientists from the University of Sheffield have discovered MRI scanners, normally used to produce images, can steer cell-based, tumour busting therapies to specific target sites in the body.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners have been used since the 1980s to take detailed images inside the body - helping doctors to make a medical diagnosis and investigate the staging of a disease.
An international team of researchers, led by Dr Munitta Muthana from the University of Sheffield's Department of Oncology, have now found MRI scanners can non-invasively steer cells, ...
Women giving birth after undergoing fertility treatment face an increased risk of depression compared to women ending up not having a child following fertility treatment, according to new research from the University of Copenhagen. According to the researchers, this has key implications for fertility treatment in future.
Danish researchers are among the first worldwide to study the risk of developing a clinical depression for women undergoing fertility treatment. The new study shows that women who give birth after receiving fertility treatment are five times more likely ...
Tropical Depression 11E came to an end early today, Tuesday, August 18 when the National Hurricane Center noted that the storm degenerated into a remnant low pressure area. NOAA's GOES-West satellite caught an infrared image of the fizzling system.
At 5 a.m. EDT (2 a.m. PDT/0900 UTC) the National Hurricane Center (NHC) issued the final bulletin on Post-Tropical depression 11E. At that time, the center of Post-Tropical cyclone 11E was located near latitude 24.9 North and longitude 125.6 West. It had fizzled about 1,000 miles (1,610 km) west of the southern tip of Baja ...
Researchers from Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have used computed microtomography (micro-CT) to identify to the species level an exceptionally wellpreserved fossil arthropod from the famous Chengjiang Lagerstätte in China.
Modern imaging methods make it possible to perform detailed, non-invasive studies on the internal structures of irreplaceable fossil specimens. Researchers led by Dr. Yu Liu of LMU's Department of Biology II now demonstrate the power of this approach by using computed microtomography (micro-CT) to investigate a specimen recovered ...
Researchers from the University of Southampton have demonstrated for the first time a new laser cooling method, based upon the interference of matter waves, that could be used to cool molecules.
Our ability to produce samples of ultra-cold atoms has revolutionised experimental atomic physics, giving us devices from atomic clocks (the core of GPS) and enabling a range of quantum devices, including the possibility of a quantum computer.
However, the current technique of cooling atoms down from room temperature to the ultra-cold regime using optical molasses (the preferential ...
Methylmercury, a toxic form of mercury that is readily absorbed from the gastro-intestinal tract and can cause in a variety of health issues, poses a significant threat to marine animals at the top of the food web. A new study confirms that Artic species of these animals have higher concentrations of methylmercury in their tissues compared with animals lower in the food web; however, it also shows similar trends in selenium, which could help play a protective role against the toxic effects of mercury.
"Methylmercury concentrations increased through the food web at greater ...