(Press-News.org) A team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) developing a bioinorganic hybrid approach to artificial photosynthesis have achieved another milestone. Having generated quite a buzz with their hybrid system of semiconducting nanowires and bacteria that used electrons to synthesize carbon dioxide into acetate, the team has now developed a hybrid system that produces renewable molecular hydrogen and uses it to synthesize carbon dioxide into methane, the primary constituent of natural gas.
"This study represents another key breakthrough in solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency and artificial photosynthesis," says Peidong Yang, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and one of the leaders of this study. "By generating renewable hydrogen and feeding it to microbes for the production of methane, we can now expect an electrical-to-chemical efficiency of better than 50 percent and a solar-to-chemical energy conversion efficiency of 10-percent if our system is coupled with state-of-art solar panel and electrolyzer."
Yang, who also holds appointments with UC Berkeley and the Kavli Energy NanoScience Institute (Kavli-ENSI) at Berkeley, is one of three corresponding authors of a paper describing this research in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The paper is titled "A hybrid bioinorganic approach to solar-to-chemical conversion." The other corresponding authors are Michelle Chang and Christopher Chang. Both also hold joint appointments with Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley. In addition, Chris Chang is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator. (See below for a full list of the paper's authors.)
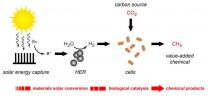
Photosynthesis is the process by which nature harvests the energy in sunlight and uses it to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. Carbohyrates are biomolecules that store the chemical energy used by living cells. In the original hybrid artificial photosynthesis system developed by the Berkeley Lab team, an array of silicon and titanium oxide nanowires collected solar energy and delivered electrons to microbes which used them to reduce carbon dioxide into a variety of value-added chemical products. In the new system, solar energy is used to split the water molecule into molecular oxygen and hydrogen. The hydrogen is then transported to microbes that use it to reduce carbon dioxide into one specific chemical product, methane.
"In our latest work, we've demonstrated two key advances," says Chris Chang. "First, our use of renewable hydrogen for carbon dioxide fixation opens up the possibility of using hydrogen that comes from any sustainable energy source, including wind, hydrothermal and nuclear. Second, having demonstrated one promising organism for using renewable hydrogen, we can now, through synthetic biology, expand to other organisms and other value-added chemical products."
The concept in the two studies is essentially the same - a membrane of semiconductor nanowires that can harness solar energy is populated with bacterium that can feed off this energy and use it to produce a targeted carbon-based chemical. In the new study, the membrane consisted of indium phosphide photocathodes and titanium dioxide photoanodes. Whereas in the first study, the team worked with Sporomusa ovata, an anaerobic bacterium that readily accepts electrons from the surrounding environment to reduce carbon dioxide, in the new study the team populated the membrane with Methanosarcina barkeri, an anaerobic archaeon that reduces carbon dioxide using hydrogen rather than electrons.
"Using hydrogen as the energy carrier rather than electrons makes for a much more efficient process as molecular hydrogen, through its chemical bonds, has a much higherdensity for storing and transporting energy," says Michelle Chang.
In the newest membrane reported by the Berkeley team, solar energy is absorbed and used to generate hydrogen from water via the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The HER is catalyzed by
earth-abundant nickel sulfide nanoparticles that operate effectively under biologically compatible conditions. Hydrogen produced in the HER is directly utilized by the Methanosarcina barkeri archaeons in the membrane to produce methane.
"We selected methane as an initial target owing to the ease of product separation, the potential for integration into existing infrastructures for the delivery and use of natural gas, and the fact that direct conversion of carbon dioxide to methane with synthetic catalysts has proven to be a formidable challenge," says Chris Chang. "Since we still get the majority of our methane from natural gas, a fossil fuel, often from fracking, the ability to generate methane from a renewable hydrogen source is another important advance."
Adds Yang, "While we were inspired by the process of natural photosynthesis and continue to learn from it, by adding nanotechnology to help improve the efficiency of natural systems we are showing that sometimes we can do even better than nature."
INFORMATION:
In addition to the corresponding authors, other co-authors of the PNAS paper describing this research were Eva Nichols, Joseph Gallagher, Chong Liu, Yude Su, Joaquin Resasco, Yi Yu and Yujie Sung.
This research was primarily funded by the DOE Office of Science.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit http://www.lbl.gov.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov/.
Waterford, Ireland, August 24, 2015 - Ongoing European Research Council-funded research at Waterford Institute of Technology's (WIT) Macular Pigment Research Group (MPRG) is investigating the potential link between cognitive function and levels of a vital eye pigment linked to diet. The study suggests that measuring macular pigment offers potential as a biomarker of cognitive health. The results of this study are highlighted to a global audience through the prestigious international medical journal, the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
The Waterford clinical trial research, ...
Tahiti is a popular tourist destination, but one unwanted visitor has decided to make its home there: the brown widow spider (Latrodectus geometricus). A paper published in the Journal of Medical Entomology has reported the discovery of the spider for the first time on Tahiti and also on four of the Cook Islands.
The brown widow is a known invasive species. It has been found in South America, Central America, North America, the Caribbean islands, and a host of Pacific islands. It was first found in French Polynesia in 2006, when it was discovered on the island of Moorea. ...
WASHINGTON (Aug. 25, 2015)--In the most comprehensive study to date, researchers at the George Washington University have identified a potential link between microbes (viruses, bacteria and fungi) in the throat and schizophrenia. This link may offer a way to identify causes and develop treatments of the disease and lead to new diagnostic tests.
"The oropharynx of schizophrenics seems to harbor different proportions of oral bacteria than healthy individuals," said Eduardo Castro-Nallar, a Ph.D. candidate at GW's Computational Biology Institute (CBI) and lead author of ...
Tampa, Fla. (Aug. 25, 2015) - Fresh water--connecting and sustaining all aspects of life on Earth, including food and energy--is in great danger. Moreover, scientists are worried not only about fresh water; they worry that we are not worried enough about fresh water, especially in light of growing concern over recent events, such as the prolonged California drought. The current Special Issue Section of Technology and Innovation - Journal of the National Academy of Inventors has a special section devoted to fresh water and the challenges it faces from us and from the changing ...
Tampa, Fla. (Aug. 25, 2015) - Wasting fresh water is a real concern. A recent study conducted with homeowners in central Florida found that, on average, 64 percent of the drinking water used by homes went to irrigation. In the summer months, this percentage increased to 88 percent. As the population increases, conservation of fresh water becomes increasingly important.
The Special Issue Section of the current Technology and Innovation - Journal of the National Academy of Inventors focuses on challenges to fresh water from environmental changes and from the human population.
Florida ...
A 24-hour news cycle, viral videos and tweets about football players' run-ins with the law can make it seem like criminal activity is an epidemic in the National Football League.
But a new UT Dallas study refutes that impression. The research found that the overall arrest rate for the general population was nearly twice as high as the rate for NFL players from 2000 to 2013.
"There's a perception that the NFL has this huge crime problem and that it's longstanding. That's what everybody believes," said one of the study's authors, Dr. Alex Piquero,Ashbel Smith Professor ...
CHICAGO -- Most people who meet a new acquaintance, or merely pass someone on the street, need only a glance to categorize that person as a particular race. But, sociologist Asia Friedman wondered, what can we learn about that automatic visual processing from people who are unable to see?
Friedman, an assistant professor of sociology at the University of Delaware, set out to explore that question by interviewing 25 individuals who are blind. She will present her findings in a study at the 110th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association (ASA).
"The visual ...
CHICAGO -- Romantic opportunities appear to influence women's sexual identities -- but not men's, suggests a new study that will be presented at the 110th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association (ASA).
"This indicates that women's sexuality may be more flexible and adaptive than men's," said study author Elizabeth Aura McClintock, an assistant professor of sociology at the University of Notre Dame.
McClintock's study relies on data from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health (Add Health) and considers its first (1994-1995), ...
This news release is available in German.
A chimpanzee population in Uganda has been found to be three times larger than previously estimated, according to research published in the open access journal BMC Ecology. The study suggests that chimpanzees may adapt to degraded habitats better than expected, but also highlights the importance of new and more focused conservation strategies.
The protected Budongo and Bugoma Forest Reserves together compose approximately one quarter of the estimated total chimpanzee population in Uganda. The unprotected area between ...
Men whose image of themselves falls short of the traditional masculine gender norms, and who feel that others think this about them too, may be more prone to violence than men who feel comfortable in their own skin, suggests research published online in the journal Injury Prevention.
How men perceive traditional male gender norms and masculinity can affect their behaviour. In general, 'macho,' highly masculine men are more likely to engage in stereotypical male behaviours, such as risk taking, substance misuse, and acts of aggression, say the researchers.
But they wanted ...