Flu remedies help combat E. coli bacteria
2015-08-25
(Press-News.org) This news release is available in German.
Trillions of bacteria populate the human gut - which makes them more common than any other cells in our body. The composition of this bacterial population is very variable and influenced by our diet. Diseases, but also antibiotic treatments can induce significant shifts in this equilibrium. If entire bacterial groups suddenly multiply heavily, critical situations occur. They damage the intestinal tissue and cause inflammations. How such shifts are triggered largely remained a mystery. Physiologists from the University of Zurich have now discovered why the intestinal bacterium Escherichia coli (E. coli) multiplies heavily and has an inflammatory effect.
A carbohydrate causes E. coli to multiply
In their normal state, E. coli are harmless and only make up around 0.1 percent of the intestinal flora. If present in large amounts, however, they can cause diarrhea or a serious intestinal inflammation. The Zurich study reveals that an overproduction of E. coli can be attributed to the availability of the carbohydrate sialic acid, which is found in large amounts in the proteins of the intestinal mucosa. To actually be able to utilize the sialic acid, the bacteria enlist the aid of the enzyme sialidase, which is released by other intestinal bacteria. "It's striking that E. coli doesn't produce this kind of enzyme itself," explains Thierry Hennet, a professor from the Institute of Physiology at the University of Zurich.
Hennet and his colleagues succeeded in demonstrating the complex chain of events involved in a severe inflammation triggered by E. coli: An injury to the intestinal mucosa initially causes the increased multiplication of a non-pathogenic bacteria, which emits sialidase. This increased enzyme production releases sialic acid, which facilitates an overproduction of E. coli and can thus cause intestinal inflammation.
Sialidase inhibitors combat intestinal inflammations
The researchers also discovered that the intake of a sialidase inhibitor prevents the excessive formation of E. coli and was thus able to alleviate the disease symptoms. Interestingly, such sialidase inhibitors were already developed against the influenza virus. "Derivatives of known flu agents such as Tamiflu and Relenza could therefore also be used for inflammatory intestinal diseases, which opens up new therapeutic possibilities," says Hennet.
INFORMATION:
Literature:
Yen-Lin Huang, Christophe Chassard, Martin Hausmann, Mark von Itzstein, Thierry Hennet. Sialic acid catabolism drives intestinal inflammation and microbial dysbiosis in mice. Nature Communications. August 25, 2015. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9141
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-25
This news release is available in German.
Root bacteria are known to form symbiotic relationships with plants by improving the plants' supply of nutrients. Yet as scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Ecology in Jena, Germany, found recently, the bacteria actually play a much more profound role. During field experiments in Utah, in the western USA, researchers discovered that the right mixture of soil microbiota directly influences the survival of Nicotiana attenuata, a species of wild tobacco. Plants that had been unable to establish a protective ...
2015-08-25
University of Manchester scientists have bridged a gap between two separate pieces of small intestine kept alive outside the body, in an advance which could have implications for surgery in human adults and babies.
It is not currently possible to study the intestine in embryos when inside the body, which holds back advances in treatment for conditions causing damage in infants. However, new techniques used by the researchers in this study have allowed organs to be kept alive and grown on supports which allow the absorption of nutrients.
A video is available here
or ...
2015-08-25
In an era where popular culture is increasingly recognized for its impact on lay understanding of health and medicine, few scholars have looked at television's powerful role in the creation of patient expectations, especially regarding pregnancy and birth.
As part of a larger research project funded by a National Science Foundation Dissertation Improvement Grant, Danielle Bessett, University of Cincinnati assistant professor of sociology in the McMicken College of Arts and Sciences examined how women understand their television viewing practices regarding pregnancy and ...
2015-08-25
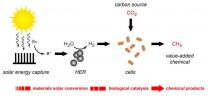
A team of researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) developing a bioinorganic hybrid approach to artificial photosynthesis have achieved another milestone. Having generated quite a buzz with their hybrid system of semiconducting nanowires and bacteria that used electrons to synthesize carbon dioxide into acetate, the team has now developed a hybrid system that produces renewable molecular hydrogen and uses it to synthesize carbon dioxide into methane, the primary constituent of natural gas.
"This study represents ...
2015-08-25
Waterford, Ireland, August 24, 2015 - Ongoing European Research Council-funded research at Waterford Institute of Technology's (WIT) Macular Pigment Research Group (MPRG) is investigating the potential link between cognitive function and levels of a vital eye pigment linked to diet. The study suggests that measuring macular pigment offers potential as a biomarker of cognitive health. The results of this study are highlighted to a global audience through the prestigious international medical journal, the Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.
The Waterford clinical trial research, ...
2015-08-25
Tahiti is a popular tourist destination, but one unwanted visitor has decided to make its home there: the brown widow spider (Latrodectus geometricus). A paper published in the Journal of Medical Entomology has reported the discovery of the spider for the first time on Tahiti and also on four of the Cook Islands.
The brown widow is a known invasive species. It has been found in South America, Central America, North America, the Caribbean islands, and a host of Pacific islands. It was first found in French Polynesia in 2006, when it was discovered on the island of Moorea. ...
2015-08-25
WASHINGTON (Aug. 25, 2015)--In the most comprehensive study to date, researchers at the George Washington University have identified a potential link between microbes (viruses, bacteria and fungi) in the throat and schizophrenia. This link may offer a way to identify causes and develop treatments of the disease and lead to new diagnostic tests.
"The oropharynx of schizophrenics seems to harbor different proportions of oral bacteria than healthy individuals," said Eduardo Castro-Nallar, a Ph.D. candidate at GW's Computational Biology Institute (CBI) and lead author of ...
2015-08-25
Tampa, Fla. (Aug. 25, 2015) - Fresh water--connecting and sustaining all aspects of life on Earth, including food and energy--is in great danger. Moreover, scientists are worried not only about fresh water; they worry that we are not worried enough about fresh water, especially in light of growing concern over recent events, such as the prolonged California drought. The current Special Issue Section of Technology and Innovation - Journal of the National Academy of Inventors has a special section devoted to fresh water and the challenges it faces from us and from the changing ...
2015-08-25
Tampa, Fla. (Aug. 25, 2015) - Wasting fresh water is a real concern. A recent study conducted with homeowners in central Florida found that, on average, 64 percent of the drinking water used by homes went to irrigation. In the summer months, this percentage increased to 88 percent. As the population increases, conservation of fresh water becomes increasingly important.
The Special Issue Section of the current Technology and Innovation - Journal of the National Academy of Inventors focuses on challenges to fresh water from environmental changes and from the human population.
Florida ...
2015-08-25
A 24-hour news cycle, viral videos and tweets about football players' run-ins with the law can make it seem like criminal activity is an epidemic in the National Football League.
But a new UT Dallas study refutes that impression. The research found that the overall arrest rate for the general population was nearly twice as high as the rate for NFL players from 2000 to 2013.
"There's a perception that the NFL has this huge crime problem and that it's longstanding. That's what everybody believes," said one of the study's authors, Dr. Alex Piquero,Ashbel Smith Professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Flu remedies help combat E. coli bacteria