NASA measures rainfall in stronger Tropical Storm Ignacio
2015-08-26
(Press-News.org) The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM mission core satellite measured rainfall as Tropical Depression Twelve was upgraded to Tropical Storm Ignacio.
Tropical Depression 12E strengthened into Tropical Storm Ignacio at 5 p.m. EDT yesterday, August 25. At that time, it became the ninth named tropical storm of the Eastern Pacific hurricane season.
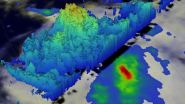
The GPM core observatory satellite saw Ignacio on August 25, 2015 at 2256 UTC. GPM's Dual-Frequency Precipitation Radar (DPR) found rain falling at a rate of over 74 mm (2.9 inches) per hour with storm tops reaching to altitudes of close to 15 km (8.7 miles). GPM is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency.
On August 26, the strongest convection (rising air that form the thunderstorms that make up a tropical cyclone) has been persisting mainly over the western half of the circulation. That means more thunderstorm development on that side of the storm. Recent microwave images show increased banding of thunderstorms.
At 5 a.m. EDT (0900 UTC) on August 26, the center of Tropical Storm Ignacio was located near latitude 12.3 North, longitude 134.1 West. That's about 1,485 miles (2,385 km) east-southeast of Hilo, Hawaii. Ignacio currently poses no threat to land areas.
Ignacio is moving toward the west near 7 mph (11 km/h). This westward motion is expected to continue today with an increase in forward speed. A turn toward the west-northwest is forecast on Thursday.
Maximum sustained winds have increased to near 50 mph (85 kph) and the National Hurricane Center expects Ignacio to become a hurricane by Thursday, August 27. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1001 millibars. For updated forecasts, visit: http://www.nhc.noaa.gov.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-26
Treatments for cystic fibrosis (CF) have added years to the lives of thousands of Americans. But they can be difficult to administer, and most don't fix the underlying cause. Scientists have now found that a small molecule, when tested in yeast, can substitute for a protein and restore a key cellular function related to those missing in people with CF and similar conditions. Their report appears in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
CF is caused by a genetic mutation that affects certain cellular proteins that make up "channels," which act like gates managing ...
2015-08-26
Nobody likes flight delays, but they are a common occurrence: In 2011, about 20 percent of U.S. flights were at least 15 minutes behind schedule. Those delays irritate passengers and, in 2010, added an estimated $6.5 billion to U.S. airlines' operating costs.
Delays tend to hit some airlines harder than others, due to the approach the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) uses to resolve them. This approach places an emphasis on minimizing aggregate system delays, nationwide -- a policy that affects some airlines much more than others at a given time.
But now a study ...
2015-08-26
While exploring the remote coral reefs of Raja Ampat in Indonesia, Dr. James Thomas from the Halmos College of Natural Sciences and Oceanography, Florida, and his colleagues from Naturalis Natural History museum in the Netherlands, stumbled across a small but extraordinary crustacean living inside another reef invertebrate in a commensal association (without causing any harm, nor benefit to its host).
In his amazement to the amphipod's unusual form, Dr. Tomas called it L. eltoni after musician and actor Sir Elton John. The research is available in the open access journal ...
2015-08-26
Female mice exposed in utero, or in the womb, to low levels of arsenic through drinking water displayed signs of early puberty and became obese as adults, according to scientists from the National Institutes of Health. The finding is significant because the exposure level of 10 parts per billion used in the study is the current U.S. Environmental Protection Agency standard, or maximum allowable amount, for arsenic in drinking water. The study, which appeared online August 21 in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives, serves as a good starting point for examining ...
2015-08-26
The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM mission core satellite can measure rainfall from space, and saw heavy rainfall in the Central Pacific's Loke when it was a hurricane.
Hurricane Loke formed southwest of the Hawaiian Islands on August 21, 2015 but Loke has not been a threat to Hawaii because it intensified to hurricane strength while moving well west of Hawaii over the open waters of the Pacific Ocean.
The GPM core observatory satellite measured precipitation within the hurricane as it flew above the most powerful thunderstorms in the hurricane on August 25, ...
2015-08-26
"If I offered you a bruised banana, you probably wouldn't be interested," said Jonathan Deutsch, PhD, director of Drexel University's Center for Hospitality and Sport Management. "But what if I offered you some banana ice cream on a hot summer day? I bet you'd find that a lot more appealing."
It was this simple observation that inspired a new model for recovering would-be wasted - or surplus - food and repurposing it to feed hungry people, generate revenue and even create jobs. The model was recently piloted in West Philadelphia, home to a large population of low-income ...
2015-08-26
Summertime is waning, and that means the end of backyard barbecues is almost upon us. That also means an end to dousing charcoal briquettes with lighter fluid. Reducing the use of lighter fluid might not be a bad thing, as many of those products are made from crude oil and emit potentially harmful compounds when lit. Now, researchers report in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering that they developed a waste-paper-based, environmentally friendly and sustainable alternative.
Igniting fires has been a keystone to human civilization. Ancient communities used plant and ...
2015-08-26
As Tropical Storm Ericka continued moving toward the Lesser Antilles, NASA's Aqua and other satellites were gathering data. Satellite imagery showed strong thunderstorms wrapped around Erika's center.
Infrared data, such as that gathered by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite is used to determine cloud top temperature. The colder the cloud tops, the higher they are in the atmosphere, and they are usually stronger. Cloud tops around Erika's center were near -63F/-53C, indicating strong thunderstorms.
A Tropical Storm ...
2015-08-26
Individuals previously diagnosed with heart disease may be less likely to experience heart failure, heart attacks, or stroke, or to die from these events, if they have higher blood levels of two very closely related proteins, according to a new study led by a UC San Francisco research team.
One of these proteins, known as GDF11, has attracted great interest since 2013, when researchers showed that it could rejuvenate old mice. Based on these findings, scientists have speculated that drugs that increase GDF11 levels might reverse physiological manifestations of aging that ...
2015-08-26
Researchers from the University of Birmingham have shown that drinking 500ml of water at half an hour before eating main meals may help obese adults to lose weight. They believe that the simple intervention could be hugely beneficial, and be easily promoted by healthcare professionals and through public health campaigns.
Obese adult participants were recruited from general practices and monitored over a 12 week period.
Each of the participants, all adults with obesity, were given a weight management consultation, where they were advised on how to adapt their lifestyle ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA measures rainfall in stronger Tropical Storm Ignacio