(Press-News.org) Philadelphia, PA, Aug 27, 2015 - Having twins accounts for only 1.5% of all births but 25% of preterm births, the leading cause of infant mortality worldwide. Successful strategies for reducing singleton preterm births include prophylactic use of progesterone and cervical cerclage in patients with a prior history of preterm birth. To investigate whether the use of a cervical pessary might reduce premature births of twins, an international team of researchers conducted a large, multicenter, international randomized clinical trial (RCT) of approximately 1200 twin pregnancies. They report in the American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology that placement of a cervical pessary did not reduce spontaneous preterm births or reduce neonatal complications.
The rates of preterm birth (defined as END
Cervical pessary doesn't reduce rate of preterm birth or neonatal complications in twin gestatations
Large international study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology shows that this intervention is not effective
2015-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
To track winter flounder, UNH researchers look to ear bones
2015-08-27
DURHAM, N.H. - Researchers at the University of New Hampshire are turning to an unusual source --otoliths, the inner ear bones of fish -- to identify the nursery grounds of winter flounder, the protected estuaries where the potato chip-sized juveniles grow to adolesence. The research, recently published in the journal Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, could aid the effort to restore plummeting winter flounder populations along the East Coast of the U.S.
In addition to showing the age of a fish, much like the rings in the cross-section of a tree, otoliths ...
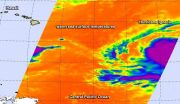
NASA data shows Hurricane Ignacio's very cold cloud tops indicate quick strengthening
2015-08-27
When cloud top temperatures get colder, the uplift in tropical cyclones gets stronger and the thunderstorms that make up the tropical cyclones have more strength. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Ignacio and infrared data revealed cloud top temperatures had cooled from the previous day.
Ignacio strengthened to a hurricane at 11 p.m. EDT on August 26. It became the seventh hurricane of the Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season.
A false-colored infrared image of Hurricane Ignacio was made at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena California, using data ...
HIV particles do not cause AIDS, our own immune cells do
2015-08-27
Researchers from the Gladstone Institutes have revealed that HIV does not cause AIDS by the virus's direct effect on the host's immune cells, but rather through the cells' lethal influence on one another.
HIV can either be spread through free-floating virus that directly infect the host immune cells or an infected cell can pass the virus to an uninfected cell. The second method, cell to cell transmission, is 100 to 1000 times more efficient, and the new study shows that it is only this method that sets off a cellular chain reaction that ends in the newly infected cells ...
Researchers develop framework for value-based pricing of cancer drugs
2015-08-27
At a time when cancer drug prices are rising rapidly, an innovative new study provides the framework for establishing value-based pricing for all new oncology drugs entering the marketplace. Using a highly sophisticated economic model, researchers from Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology used an example of a new lung cancer drug. The study findings will be published August 27, 2015 in JAMA Oncology.
Researchers focused their investigation on a drug called necitumumab, which is awaiting approval from the U.S. Food and Drug ...
21-gene recurrence score and receipt of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer
2015-08-27
Use of the 21-gene recurrence test score was associated with lower chemotherapy use in high-risk patients and greater use of chemotherapy in low-risk patients compared with not using the test among a large group of Medicare beneficiaries, according to an article published online by JAMA Oncology.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend considering chemotherapy in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, node-negative breast cancer for all but the smallest tumors. Several studies have suggested the 21-gene recurrence score assay (testing) is cost-effective ...
Safety of microfocused ultrasound with visualization in darker skin types
2015-08-27
Microfocused ultrasound (MFU) treatment to tighten and lift skin on the face and neck appeared to be safe for patients with darker skin types in a small study that resulted in only a few temporary adverse effects, according to a report published online by JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery.
Normal aging results in changes in the skin and underlying connective tissue. A system that uses MFU together with ultrasound visualization was developed to treat lax, aging skin. Previous clinical trials have shown the system to be a safe and effective noninvasive aesthetic treatment, according ...
Pitt team identifies cause of resilience to tinnitus, potential drug therapy
2015-08-27
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 27, 2015 - Researchers have identified in an animal model the molecular mechanisms behind resilience to noise-induced tinnitus and a possible drug therapy that could reduce susceptibility to this chronic and sometimes debilitating condition. The findings by a team from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine were published online in the journal eLife.
Tinnitus is typically induced by exposure to loud noise and causes whistling, clicking, roaring and other phantom sounds. It is estimated that 5 to 15 percent of Americans suffer from tinnitus, said ...
Intensity of desert storms may affect ocean phytoplankton
2015-08-27
Each spring, powerful dust storms in the deserts of Mongolia and northern China send thick clouds of particles into the atmosphere. Eastward winds sweep these particles as far as the Pacific, where dust ultimately settles in the open ocean. This desert dust contains, among other minerals, iron -- an essential nutrient for hundreds of species of phytoplankton that make up the ocean's food base.
Now scientists at MIT, Columbia University, and Florida State University have determined that once iron is deposited in the ocean, it has a very short residence time, spending ...
To get girls more interested in computer science, make classrooms less 'geeky'
2015-08-27
Women lag behind men in the lucrative computer science and technology industries, and one of the possible contributors to this disparity is that they're less likely to enroll in introductory computer science courses.
A new study of 270 high school students shows that three times as many girls were interested in enrolling in a computer science class if the classroom was redesigned to be less "geeky" and more inviting.
The results, by University of Washington researchers, reveal a practical way for teachers to help narrow the gender gap in computer science by helping ...
About 10 percent of mothers experienced depression 2 years after Hurricane Katrina, study shows
2015-08-27
About 10 percent of mothers experienced chronic, persistent depressive symptoms two years after Hurricane Katrina slammed into the Gulf Coast, killing more than 1,800 people, displacing hundreds of thousands and causing widespread damage estimated at more than $100 billion, according to a Georgia State University study.
While most people don't develop persistent depression after a major disaster like that, a small but significant number will, according to a study led by Dr. Betty S. Lai, assistant professor of epidemiology and biostatistics at the School of Public Health ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The hidden breath of cities: Why we need to look closer at public fountains
Rewetting peatlands could unlock more effective carbon removal using biochar
Microplastics discovered in prostate tumors
ACES marks 150 years of the Morrow Plots, our nation's oldest research field
Physicists open door to future, hyper-efficient ‘orbitronic’ devices
$80 million supports research into exceptional longevity
Why the planet doesn’t dry out together: scientists solve a global climate puzzle
Global greening: The Earth’s green wave is shifting
You don't need to be very altruistic to stop an epidemic
Signs on Stone Age objects: Precursor to written language dates back 40,000 years
MIT study reveals climatic fingerprints of wildfires and volcanic eruptions
A shift from the sandlot to the travel team for youth sports
Hair-width LEDs could replace lasers
The hidden infections that refuse to go away: how household practices can stop deadly diseases
Ochsner MD Anderson uses groundbreaking TIL therapy to treat advanced melanoma in adults
A heatshield for ‘never-wet’ surfaces: Rice engineering team repels even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
Skills from being a birder may change—and benefit—your brain
Waterloo researchers turning plastic waste into vinegar
Measuring the expansion of the universe with cosmic fireworks
How horses whinny: Whistling while singing
US newborn hepatitis B virus vaccination rates
When influencers raise a glass, young viewers want to join them
Exposure to alcohol-related social media content and desire to drink among young adults
Access to dialysis facilities in socioeconomically advantaged and disadvantaged communities
Dietary patterns and indicators of cognitive function
New study shows dry powder inhalers can improve patient outcomes and lower environmental impact
Plant hormone therapy could improve global food security
A new Johns Hopkins Medicine study finds sex and menopause-based differences in presentation of early Lyme disease
Students run ‘bee hotels’ across Canada - DNA reveals who’s checking in
SwRI grows capacity to support manufacture of antidotes to combat nerve agent, pesticide exposure in the U.S.
[Press-News.org] Cervical pessary doesn't reduce rate of preterm birth or neonatal complications in twin gestatationsLarge international study in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology shows that this intervention is not effective