INFORMATION:
Getting a picture of the molecules in a cell in just minutes
2015-08-27
(Press-News.org) Understanding exactly what is taking place inside a single cell is no easy task. For DNA, amplification techniques are available to make the task possible, but for other substances such as proteins and small molecules, scientists generally have to rely on statistics generated from many different cells measured together. Unfortunately, this means they cannot look at what is happening in each individual cell.
Now, thanks to seven years of work done at the RIKEN Quantitative Biology Center and Hiroshima University, scientists can take a peek into a single plant cell and--within minutes--get a view of the small molecules, including metabolites, hormones, nutrients, and lipids, inside it.
In this method, published in Nature Protocols, the contents of the single target cell are directly sucked up by a metal coated glass capillary called a "nanospray tip" under a stereo microscope and the contents are directly fed into the inlet of a mass spectrometer. Within minutes, the mass spectrometer detects hundreds or thousands of molecular peaks, and these peaks can then be matched to databases to determine which metabolites are present in the plant cell under the specific conditions it faced at the time the contents were removed.
This method promises not only to speed up the ability to understand how molecules are distributed in cells in time and space, but also to change how research is done in agricultural science. According to corresponding author Tsutomu Masujima, who leads RIKEN'S Single Cell Project, "Using this method we can compare the molecular peaks of cells which are in different stages of growth, different locations, or responding to different circumstances using statistical analyses of the mass spectrometry data. If, for example, we find that certain metabolites are increased in a specific strain, it implies that the enzyme or protein of this specific metabolic pathway may be the key to the specificity of this strain. It might also help us to identify new pathways that are important."
For the moment, the team is focusing on plant cells, but they are preparing a protocol for animal cells--which is much more difficult since the cells are smaller and softer--together with high content screening applications.
Given the potential of the new method, the authors have decided to publish the protocols to the global research community.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mammary gland is shaped by adaptive immune system during development
2015-08-27
In experiments with mouse tissue, UC San Francisco researchers have discovered that the adaptive immune system, generally associated with fighting bacterial and viral infections, plays an active role in guiding the normal development of mammary glands, the only organs--in female humans as well as mice--that develop predominately after birth, beginning at puberty.
The scientists say the findings have implications not only for understanding normal organ development, but also for cancer and tissue-regeneration research, as well as in the highly active field of cancer immunotherapy, ...
Cervical pessary doesn't reduce rate of preterm birth or neonatal complications in twin gestatations
2015-08-27
Philadelphia, PA, Aug 27, 2015 - Having twins accounts for only 1.5% of all births but 25% of preterm births, the leading cause of infant mortality worldwide. Successful strategies for reducing singleton preterm births include prophylactic use of progesterone and cervical cerclage in patients with a prior history of preterm birth. To investigate whether the use of a cervical pessary might reduce premature births of twins, an international team of researchers conducted a large, multicenter, international randomized clinical trial (RCT) of approximately 1200 twin pregnancies. ...
To track winter flounder, UNH researchers look to ear bones
2015-08-27
DURHAM, N.H. - Researchers at the University of New Hampshire are turning to an unusual source --otoliths, the inner ear bones of fish -- to identify the nursery grounds of winter flounder, the protected estuaries where the potato chip-sized juveniles grow to adolesence. The research, recently published in the journal Transactions of the American Fisheries Society, could aid the effort to restore plummeting winter flounder populations along the East Coast of the U.S.
In addition to showing the age of a fish, much like the rings in the cross-section of a tree, otoliths ...
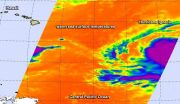
NASA data shows Hurricane Ignacio's very cold cloud tops indicate quick strengthening
2015-08-27
When cloud top temperatures get colder, the uplift in tropical cyclones gets stronger and the thunderstorms that make up the tropical cyclones have more strength. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Ignacio and infrared data revealed cloud top temperatures had cooled from the previous day.
Ignacio strengthened to a hurricane at 11 p.m. EDT on August 26. It became the seventh hurricane of the Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season.
A false-colored infrared image of Hurricane Ignacio was made at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena California, using data ...
HIV particles do not cause AIDS, our own immune cells do
2015-08-27
Researchers from the Gladstone Institutes have revealed that HIV does not cause AIDS by the virus's direct effect on the host's immune cells, but rather through the cells' lethal influence on one another.
HIV can either be spread through free-floating virus that directly infect the host immune cells or an infected cell can pass the virus to an uninfected cell. The second method, cell to cell transmission, is 100 to 1000 times more efficient, and the new study shows that it is only this method that sets off a cellular chain reaction that ends in the newly infected cells ...
Researchers develop framework for value-based pricing of cancer drugs
2015-08-27
At a time when cancer drug prices are rising rapidly, an innovative new study provides the framework for establishing value-based pricing for all new oncology drugs entering the marketplace. Using a highly sophisticated economic model, researchers from Winship Cancer Institute of Emory University and Georgia Institute of Technology used an example of a new lung cancer drug. The study findings will be published August 27, 2015 in JAMA Oncology.
Researchers focused their investigation on a drug called necitumumab, which is awaiting approval from the U.S. Food and Drug ...
21-gene recurrence score and receipt of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer
2015-08-27
Use of the 21-gene recurrence test score was associated with lower chemotherapy use in high-risk patients and greater use of chemotherapy in low-risk patients compared with not using the test among a large group of Medicare beneficiaries, according to an article published online by JAMA Oncology.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines recommend considering chemotherapy in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, node-negative breast cancer for all but the smallest tumors. Several studies have suggested the 21-gene recurrence score assay (testing) is cost-effective ...
Safety of microfocused ultrasound with visualization in darker skin types
2015-08-27
Microfocused ultrasound (MFU) treatment to tighten and lift skin on the face and neck appeared to be safe for patients with darker skin types in a small study that resulted in only a few temporary adverse effects, according to a report published online by JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery.
Normal aging results in changes in the skin and underlying connective tissue. A system that uses MFU together with ultrasound visualization was developed to treat lax, aging skin. Previous clinical trials have shown the system to be a safe and effective noninvasive aesthetic treatment, according ...
Pitt team identifies cause of resilience to tinnitus, potential drug therapy
2015-08-27
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 27, 2015 - Researchers have identified in an animal model the molecular mechanisms behind resilience to noise-induced tinnitus and a possible drug therapy that could reduce susceptibility to this chronic and sometimes debilitating condition. The findings by a team from the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine were published online in the journal eLife.
Tinnitus is typically induced by exposure to loud noise and causes whistling, clicking, roaring and other phantom sounds. It is estimated that 5 to 15 percent of Americans suffer from tinnitus, said ...
Intensity of desert storms may affect ocean phytoplankton
2015-08-27
Each spring, powerful dust storms in the deserts of Mongolia and northern China send thick clouds of particles into the atmosphere. Eastward winds sweep these particles as far as the Pacific, where dust ultimately settles in the open ocean. This desert dust contains, among other minerals, iron -- an essential nutrient for hundreds of species of phytoplankton that make up the ocean's food base.
Now scientists at MIT, Columbia University, and Florida State University have determined that once iron is deposited in the ocean, it has a very short residence time, spending ...