NASA sees a weakening Hurricane Ignacio moving parallel to Hawaiian Islands
2015-08-31
(Press-News.org) NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Hurricane Ignacio and viewed the storm in infrared light, providing valuable temperature data. Aqua saw a weaker Ignacio moving parallel to the Hawaiian Islands.
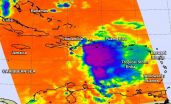
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard Aqua gathers infrared data that shows temperatures. That AIRS data was made into a false-colored infrared image from August 30 at 22:47 UTC (6:47 p.m. EDT) and showed high, cold, strong thunderstorms surrounded the center of Hurricane Ignacio.
AIRS imagery also showed a thick band of thunderstorms spiraling into the northern quadrant of the storm from the east. Coldest cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63F/-53C around the center of the hurricane, somewhat warmer than they were the day before. NASA research has shown that thunderstorms with cloud tops that cold and high in the troposphere have the potential to generate heavy rainfall. As Ignacio weakens, those cloud tops will drop and become less cold. When infrared data shows that cloud tops are warmer, it means the uplift in the storm is weakening.
On August 31, NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) stated that infrared satellite images show that Ignacio continued to steadily weaken...down from a peak intensity that was reached on August 30, with a cloud-filled eye barely discernible.
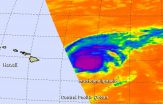
On August 31 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT/5 a.m. HST), the center of Hurricane Ignacio was located near latitude 20.9 north and longitude 150.8 west. That's about 460 miles (735 km) east of Honolulu, and about 335 miles (540 km) east of Hana, Hawaii. The estimated minimum central pressure is 966 millibars.
Maximum sustained winds are near 105 mph (165 kph) and the CPHC expects significant weakening over the next couple of days.
Wednesday. Hurricane force winds extend outward up to 60 miles (95 km) from the center and tropical storm force winds extend outward up to 175 miles (280 km). Because Ignacio remains several hundred miles from land, Hawaii is not experiencing the hurricane-force winds.
Ignacio is moving toward the northwest near 10 mph (17 kph) and this motion Is expected to continue for the next couple of days.
The CPHC forecast calls for Ignacio to track in a general north-northwesterly direction over the next several days, paralleling the Hawaiian Islands to the east, but never making landfall. Ignacio is also forecast to weaken to a tropical storm by September 2 as it continues heading northwest. For updated forecasts, visit NOAA's CPHC website: http://www.prh.noaa.gov/cphc.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-08-31
Researchers link babies' performance on cognitive tasks to later learning progress
Study underscores importance of talking to your baby well before they can talk back
Findings may eventually contribute to reducing "vocabulary gap"
EVANSTON, Ill. --- At 12 months old, your infant's ability to group objects according to the names associated with them -- as opposed to their appearance alone -- offers a glimpse into how his or her vocabulary will develop by the time they are 18 months, Northwestern University researchers have found.
The research, by Brock Ferguson, ...
2015-08-31
This news release is available in Spanish. Marine energy has a great future potential according to the experts, but there is still a long way to go before it can be used on a large scale. Despite the problem of intermittency, wave energy has an advantage over wind energy, for example: it is easier to predict optimum swell than some suitable gusts of wind. That is why knowing how much energy the waves will be bringing within a few hours is as important as having available efficient prototypes to make use of wave power. If this information is known, the energy produced ...
2015-08-31
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 31, 2015 -- People with hostile personality traits who watch more television than their peers may be at a greater risk for injury, potentially because they are more susceptible to the influence of television on violence and risk-taking behaviors, a University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health analysis discovered.
The research, published online in the International Journal of Injury Control and Safety Promotion, suggests that a reduction in television viewing and content rating systems geared not just to age, but also personality traits, ...
2015-08-31
Life on an island isn't always easy. To make the most of the little there is to eat on many Greek islands, the digestive system of Balkan green lizards has evolved considerably compared to family members on the mainland. Surprisingly, many of these insect-eating lizards even have special valves that help to digest plants. These are some of the findings¹ from a study led by Konstantinos Sagonas of the National and Kapodistrian University of Athens in Greece, published in Springer's journal The Science of Nature².
Reptiles can adjust their digestive system and ...
2015-08-31
PITTSBURGH, Aug. 31, 2015 -- The more hours young adults spend watching television each day, the greater the likelihood that they'll have a higher body mass index and bigger waist circumference, a 15-year analysis by the University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health revealed.
The association did not hold in later years, indicating that young adulthood is an important time to intervene and promote less television viewing, according to the research published online in the journal SAGE Open.
"We were quite surprised to find that television viewing was associated ...
2015-08-31
ROCHESTER Minn. -- A team of Mayo Clinic Cancer Center scientists has been awarded a Specialized Program of Research Excellence (SPORE) grant in multiple myeloma from the National Cancer Institute. The Mayo Clinic Cancer Center is one of only three cancer centers to receive a SPORE grant for multiple myeloma cancer research.
MULTIMEDIA ALERT: Video and audio are available for download on the Mayo Clinic News Network.
"With project leaders from Mayo campuses in Arizona, Rochester and Florida, our SPORE team will study the genetic basis for myeloma, develop novel viral ...
2015-08-31
Satellite data from NOAA's GOES-East satellite was made into an animation that showed the demise of former Tropical Storm Erika as it neared eastern Cuba early on August 29.
At NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, NASA/NOAA's GOES Project compiled three days' worth of imagery from NOAA's GOES-East satellite that showed the movement and changes in former Tropical Storm Erika from August 27 to August 29. The animation showed Erika move through the Leeward Islands and into the Eastern Caribbean Sea, as its center passed just south of Puerto Rico, then ...
2015-08-31
London, UK - 30 Aug 2015: Recruitment of leukocytes is a hallmark of stent thrombosis, according to results from the PRESTIGE study presented today at ESC Congress1 and published in European Heart Journal.2 The findings suggest that immune cell mediated thrombotic processes may be a realistic target for novel therapies to prevent stent thrombosis.
"Stent thrombosis (ST) is a life-threatening complication of percutaneous coronary intervention and recent large scale clinical registries reported an incidence of up to 0.4-0.6% per year," said principal investigator Professor ...
2015-08-31
How did the ankylosaur get its tail club? According to research from North Carolina State University and the North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences that traces the evolution of the ankylosaur's distinctive tail, the handle arrived first on the scene, and the knot at the end of the tail followed.
The typical ankylosaur had a wide armored body and a flexible tail. But one group of ankylosaurs - ankylosaurids - also had a tail club that could have served as a useful weapon. These "weaponized" ankylosaurids lived about 66 million years ago, during the Cretaceous period. ...
2015-08-31
LONDON (Aug. 31, 2015) -- Cardiologists failed to identify more than half of basic and about 35 percent of advanced pre-recorded murmurs, but skills improved after a 90 minute training session, according to research presented today at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2015.
Recent breakthroughs in the transcatheter treatment of aortic and mitral valve disorders provide new therapies for patients, but physicians must be able to detect valve problems in a timely manner for patients to see the full benefit of these advances, said Michael Barrett, MD, the lead ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees a weakening Hurricane Ignacio moving parallel to Hawaiian Islands