NASA's GPM sees Hurricane Jimena's eroding eyewall
2015-09-03
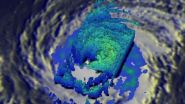
(Press-News.org) Hurricane Jimena, a once powerful Category 4 storm with maximum sustained winds estimated at 140 mph by the National Hurricane Center, has continued to weaken well east of Hawaii. The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core satellite analyzed rainfall rates and saw the eyewall was eroding.
The eyewall of a hurricane contains a storm's most damaging winds and intense rainfall. It consists of a vertical wall of powerful thunderstorms circling a hurricane's open eye.
GPM is a joint mission between NASA and the Japanese space agency JAXA. GPM captured data on Jimena on Thursday, September 3, 2015 at 10:01 UTC (6:01 a.m. PDT). At the time Jimena, which began to recurve to the northwest yesterday, steering it away from the Hawaiian Islands, was located about 750 east of Hilo, Hawaii and was moving slowly towards the northwest at 3 mph with maximum sustained winds estimated at 110 mph by the central Pacific Hurricane Center. GPM shows that Jimena's eyewall continued to erode away on the southern side. Most of the rain bands south of the center have also greatly diminished.
Jimena is forecast to continue to weaken and take a more north-northwest track over the next few days. NOAA's Central Pacific Hurricane Center noted that large swells from Jimena will produce hazardous surf along east facing shores of the main Hawaiian Islands. Surf produced by these swells will build and continue through the weekend of September 5 and 6.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-09-03
The world is facing an extinction crisis as more and more forests are converted into farmland. But does it help when farms share the land with birds and other animals?
The short answer is "no," according to new evidence based on the diversity of bird species reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 3. If the goal is to preserve more bird species, representing a greater span of evolutionary history, then it's better to farm more intensively in some areas while leaving more blocks of land entirely alone. In other words, land-sparing wins out over ...
2015-09-03
High levels of saturated fat in the blood could make an individual more prone to inflammation and tissue damage, a new study suggests.
Received wisdom on the health risks of eating saturated fat has been called into question recently. This new research supports the view that excessive consumption of saturated fat can be bad for us.
Scientists from Imperial College London studied mice that have an unusually high level of saturated fat circulating in their blood. The research, published today (3 September 2015) in Cell Reports shows that the presence of saturated fats ...
2015-09-03
Giving cancer patients aspirin at the same time as immunotherapy could dramatically boost the effectiveness of the treatment, according to new research published in the journal Cell today (Thursday).
Francis Crick Institute researchers, funded by Cancer Research UK, have shown that skin, breast and bowel cancer cells often produce large amounts of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This molecule dampens down the immune system's normal response to attack faulty cells, which helps cancer to hide. It is a trick that allows the tumour to thrive and may explain why some immunotherapy ...
2015-09-03
LAWRENCE - Men might want to ditch the pickup lines and polish their punchlines in their quest to attract women, new research at the University of Kansas suggests.
Jeffrey Hall, associate professor of communication studies, found that when two strangers meet, the more times a man tries to be funny and the more a woman laughs at those attempts, the more likely it is for the woman to be interested in dating. However, an even better indicator of romantic connection is if the two are spotted laughing together.
Those findings were among the discoveries Hall made in his search ...
2015-09-03
Coral Gables, Fla. (September 1, 2015) - Cognitive flexibility is the ability to shift our thoughts and adapt our behavior to the changing environment. In other words, it's one's ability to disengage from a previous task and respond effectively to a new one. It's a faculty that most of us take for granted, yet an essential skill to navigate life.
In a new paper published in the journal Trends in Neurosciences, University of Miami (UM) College of Arts & Sciences researchers clarify many of the concepts surrounding cognitive flexibility and propose a model of its underlying ...
2015-09-03
Researchers involved in an international collaboration across six institutions, including the University of Copenhagen and the National Aquarium of Denmark (Den Blå Planet), have successfully identified the exact composition of sea snake venom, which makes the future development of synthetic antivenoms more realistic. Currently, sea snake anitvenom costs nearly USD 2000, yet these new findings could result in a future production of synthetic antivenoms for as little as USD 10-100.
Venomous snakebites represent a major health concern in many tropical and subtropical ...
2015-09-03
Sea level rise poses one of the biggest threats to human systems in a globally warming world, potentially causing trillions of dollars' worth of damages to flooded cities around the world. As surface temperatures rise, ice sheets are melting at record rates and sea levels are rising.
But there may be some good news amid the worry. Sea levels may not rise as high as assumed.
To predict sea level changes, scientists look to Earth's distant past, when climate conditions were similar to today, and investigate how the planet's ice sheets responded then to warmer temperatures ...
2015-09-03
High blood sugar is a defining characteristic of Type 2 diabetes and the cause of many of the condition's complications, including kidney failure, heart disease, and blindness. Most diabetes medications aim to maintain normal blood sugar (glucose) levels and prevent high blood sugar by controlling insulin.
A new University of Iowa study shows that another biological checkpoint, known as the Mitochondrial Pyruvate Carrier (MPC), is critical for controlling glucose production in the liver and could potentially be a new target for drugs to treat diabetes.
The study, led ...
2015-09-03
LAWRENCE -- Researchers at the University of Kansas working with an international team at the Large Hadron Collider have produced quark-gluon plasma -- a state of matter thought to have existed right at the birth of the universe -- with fewer particles than previously thought possible.
The material was discovered by colliding protons with lead nuclei at high energy inside the supercollider's Compact Muon Solenoid detector. Physicists have dubbed the resulting plasma the "littlest liquid."
"Before the CMS experimental results, it had been thought the medium created in ...
2015-09-03
DARIEN, IL - A new study shows that high school students lose sleep on school nights following the change to daylight saving time that occurs in March. The loss of sleep during the school week was associated with a decline in vigilance and cognitive function, which raises safety concerns for teen drivers.
Results show that the average objectively measured sleep duration on the weeknights after the spring time change declined to 7 hours, 19 minutes, which reflects a mean loss of 32 minutes per night compared with the school week prior to the implementation of daylight ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA's GPM sees Hurricane Jimena's eroding eyewall