Flickr and a citizen science website help in recording a sawfly species range expansion
2015-09-08
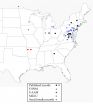
(Press-News.org) Social network Flickr and citizen science website BugGuide have helped scientists to expand the known range of a rarely collected parasitic woodwasp, native to the eastern United States. Partially thanks to the two online photograph platforms, now the species' distribution now stretches hundreds of miles west of previous records. Previously known from only 50 specimens mainly from the Northeast, now the species was discovered in the Ozark Mountains by researchers from the University of Arkansas. Their study is published it in the open access journal Biodiversity Data Journal.
Spurred on by the find, Michael Skvarla, a Ph.D. candidate at the university, contacted retired sawfly expert David Smith who alerted him to a hundred unpublished specimens housed in the United States National Entomology Collection at the Smithsonian, many of which were collected as bycatch in surveys that targeted invasive species like emerald ash borer and Asian longhorned beetle. Additional specimens from Iowa, Minnesota, and Manitoba, which also represent significant western range expansions, were found after users posted photos of the species on the social network Flickr and the citizen science website BugGuide.
"We used two resources - photos on social media and bycatch from large trapping surveys - which are often underutilized and I was really happy we could work both of them into the paper," said Skvarla, the lead author. "This work highlights their utility, as well as the importance of maintaining biological collections like the U.S. National Collection and continuing to collect in undersampled regions like the Ozark Mountains."
Parasitic woodwasps attack the immature stages of longhorned beetles, jewel beetles, and other woodwasps which bore into wood and have long fascinated entomologists because of this parasitoid nature, which is unique among woodwasps, and rarity in collections. The Arkansas specimens, which belong to the species Orussus minutus and motivated the initial research into the group, were collected as part of a larger survey of the insect fauna around the Buffalo National River.
INFORMATION:
Original Source:
Skvarla, M.J., Tripodi, A., Szalanski, A., Dowling, A.P.G. 2015. New records of Orussus minutus Middlekauff, 1983 (Hymenoptera: Orussidae) represent a significant western range expansion. Biodiversity Data Journal, 3: e35793. doi: 10.3897/BDJ.3.e5793
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-09-08
[Basel, Switzerland - 8 September 2015] The Drugs for Neglected Diseases initiative (DNDi) has announced today at the 9th European Congress on Tropical Medicine and International Health (ECTMIH) in Basel, Switzerland, the successful completion of Phase I human clinical trials for SCYX-7158 (AN5568), the first oral drug candidate specifically developed from the earliest drug discovery stage to combat human African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness, a deadly parasitic disease transmitted by the tsetse fly.
The Phase I study, conducted in France, assessed the safety, ...
2015-09-08
Edible dormice (Glis glis) spend about eight months on average in hibernation. Wildlife biologists from the Research Institute of Wildlife Ecology of the Vetmeduni Vienna have shown for the first time that these animals can hibernate for up to 11.4 months. "This may be a world record," says Claudia Bieber, co-author of the study. "Dormice in our climate zone don't just spend the winter months underground, they sometimes begin hibernating in summer."
The animals do not hibernate for so long every year, but only in years when beech trees produce few beechnuts. Successful ...
2015-09-08
In the new study 'Building trust: Heart rate synchrony and arousal during joint action increased by public goods game' (Journal of Physiology and Behavior) PhD and assistant professor Panagiotis Mitkidis and colleagues from the Interacting Minds Centre at Aarhus University studied the link between heart rate and trust. They had 37 pairs of participants do a cooperative task involving building LEGO cars. The control group only did the LEGO task, while a second group played an investment game in between the building sessions. The game, known as the 'Public Goods Game', had ...
2015-09-08
Select patients age 90 years and older with aortic stenosis (AS) can benefit from a relatively new, minimally invasive surgery for aortic valve replacement, according to an article in the September 2015 issue of the Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
Key points
Both transfemoral and transapical approaches to TAVR appear to be safe and effective for treatment of aortic stenosis in select patients age 90 years and older.
By 6 months post-surgery, most quality-of-life measures had stabilized at a level considerably better than baseline, meaning patients quality of life was ...
2015-09-08
Lueneburg. A recent study on the psychology of trademarks shows that they are perceived by the same psychological mechanisms as those, which enable the recognition of faces. The survey, whose result is particularly interesting for the advertising industry and brand management, originated at the Institute for Experimental Business Psychology at Leuphana University of Lueneburg.
For their investigation, Leuphana researchers Rainer Hoeger and Anne Lange compared the reactions of viewers to 16 well-known brands, such as Coca Cola, Rolex, Porsche or Apple and 18 computer-generated ...
2015-09-08
Trained volunteers are as good as professional astronomers at finding jets shooting from massive black holes and matching them to their host galaxies, research suggests.
Scientists working on citizen science project Radio Galaxy Zoo developed an online tutorial to teach volunteers how to spot black holes and other objects that emit large amounts of energy through radio waves.
Through the project, volunteers are given telescope images taken in both the radio and infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum and asked to compare the pictures and match the "radio source" ...
2015-09-08
A rare, deadly form of skin cancer known as desmoplasmic melanoma (DM) may possess the highest burden of gene mutations of any cancer, suggesting that immunotherapy may be a promising approach for treatment, according to an international team led by UC San Francisco scientists. One of these mutations, never before observed in any cancer, may shield nascent DM tumors from destruction by the immune system and allow further mutations to develop.
"The focus of our lab has been to show that there's not just one 'melanoma' but many different types," said senior author Boris ...
2015-09-08
In the course of billions of years continents break up, drift apart, and are pushed back together again. The cores of continents are, however, geologically extremely stable and have survived up to 3.8 billions of years. These cores that are called cratons are the oldest known geological features of our planet. It was assumed that the cratons are stable because of their especially solid structure due to relatively low temperatures compared to the surrounding mantle. A team of German-American scientists now discovered that these cratons that were assumed to be "as solid as ...
2015-09-08
A novel research tool developed by researchers from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London has identified a link between the negative symptoms experienced by people with schizophrenia and adverse clinical outcomes.
Negative symptoms can include poor motivation, poor eye contact and a reduction in speech and activity. As a result, people with schizophrenia often appear emotionless, flat and apathetic. These contrast with positive symptoms - psychotic behaviours not seen in healthy people, such as delusions or hallucinations.
Published ...
2015-09-08
This news release is available in German. The scientific world was astonished when, in 2011, Chinese researchers claimed to have found evidence suggesting that minute fragments of plant genetic material - so-called microRNA molecules - of rice ingested from food could play a role in regulating physiological processes in the human body. If this is indeed true, it might even be possible to deliberately modify human physiological functions via this route, for instance by incorporating microRNAs into novel functional foods. As a strategy, this holds considerable potential. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Flickr and a citizen science website help in recording a sawfly species range expansion


