INFORMATION:
Microfabricated elastic diamonds improve material's electronic properties
2021-01-02
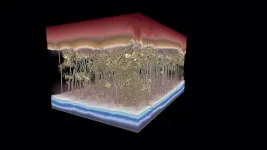
(Press-News.org) Overcoming a key obstacle in achieving diamond-based electronic and optoelectronic devices, researchers have presented a new way to fabricate micrometer-sized diamonds that can elastically stretch. Elastic diamonds could pave the way for advanced electronics, including semiconductors and quantum information technologies. In addition to being the hardest materials in nature, diamonds have exceptional electronic and photonic properties, featuring both ultrahigh thermal and electric conductivity. Not only would diamond-based electronics dissipate heat more quickly, reducing the need for cooling, they can handle high voltages and do so with greater efficiency than most other materials. Because of a diamond's rigid crystalline structure, practical use of the material in electronic devices has remained a limiting challenge. Subjecting diamond to large amounts of strain, which should alter the material's electronic properties, is one way to potentially overcome these obstacles. However, precisely controlling the strain across amounts of diamond needed for device applications has yet to be fully achieved. Here, Chaoqun Dang and colleagues present an approach for engineering diamond that exhibits uniform elastic strain. In a series of experiments, Dang et al. show how their microfabricated, micrometer-sized, single-crystalline diamond plates can elastically stretch - upwards of 10% - along several different crystallographic directions at room temperature. They could recover their length and shape, following these experiments. What's more, the authors show that this highly controllable elasticity can fundamentally change the diamond's electronic properties, including a near 2 electron volt bandgap reduction.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study points the way to boost immunotherapy against breast cancer, other solid tumors
2021-01-02
CHAPEL HILL, NC--Boosting immune system T cells to effectively attack solid tumors, such as breast cancers, can be done by adding a small molecule to a treatment procedure called chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cell therapy, according to a study by researchers at the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center. The boost helps recruit more immune cells into battle at the tumor site. The findings are published in the Journal of Experimental Medicine.
CAR-T immunotherapy, in which T cells are modified in the laboratory to express chimeric antigen receptors, CARs, that in turn target surface proteins ...
Desalination breakthrough could lead to cheaper water filtration
2021-01-02
Producing clean water at a lower cost could be on the horizon after researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and Penn State solved a complex problem that has baffled scientists for decades, until now.
Desalination membranes remove salt and other chemicals from water, a process critical to the health of society, cleaning billions of gallons of water for agriculture, energy production and drinking. The idea seems simple -- push salty water through and clean water comes out the other side -- but it contains complex intricacies that scientists ...
Stretching diamond for next-generation microelectronics
2021-01-02
Diamond is the hardest material in nature. But out of many expectations, it also has great potential as an excellent electronic material. A joint research team led by City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has demonstrated for the first time the large, uniform tensile elastic straining of microfabricated diamond arrays through the nanomechanical approach. Their findings have shown the potential of strained diamonds as prime candidates for advanced functional devices in microelectronics, photonics, and quantum information technologies.
The research was co-led by Dr Lu Yang, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering (MNE) at CityU and ...
Researchers measure, model desalination membranes to maximize flow, clean more water
2021-01-02
AMES, Iowa - Nature has figured out how to make great membranes.
Biological membranes let the right stuff into cells while keeping the wrong stuff out. And, as researchers noted in a paper just published by the journal Science, they are remarkable and ideal for their job.
But they're not necessarily ideal for high-volume, industrial jobs such as pushing saltwater through a membrane to remove salt and make fresh water for drinking, irrigating crops, watering livestock or creating energy.
Can we learn from those high-performing biological membranes? Can we ...
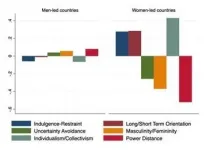
Countries led by women haven't fared significantly better in the COVID-19 pandemic
2021-01-02
Countries led by women have not fared significantly better in the COVID-19 pandemic than those led by men- it may be just our Western media bias that makes us think they have!
INFORMATION:
Article Title: "Gender in the time of COVID-19: Evaluating national leadership and COVID-19 fatalities"
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0244531
...
Transfusions with higher red blood cell levels do not improve preterm baby outcomes
2021-01-02
Very low birthweight infants are at a high risk for anemia and often need blood transfusions to survive. Some doctors use a higher level and some use a lower level of red blood cells to order a transfusion. A National Institutes of Health-funded study suggests that providing a higher threshold of red cells within clinically accepted limits (i.e., using a higher level of red blood cells when ordering a transfusion) offers no advantage in survival or reduction in neurological impairment over a lower threshold.
This large, multi-center randomized clinical trial was conducted ...
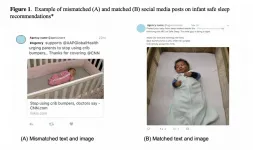
Study: in social media safety messages, the pictures should match the words
2021-01-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio -- When using social media to nudge people toward safe and healthy behaviors, it's critical to make sure the words match the pictures, according to a new study.
After looking at social media posts, parents of young children were better able to recall safety messages such as how to put a baby safely to sleep when the images in the posts aligned with the messages in the text, the researchers found.
The study appears in the Journal of Health Communication.
"Many times, scientists and safety experts aren't involved in decisions about social media for health agencies and other organizations, and we end up seeing images that have nothing to do with the safety message ...
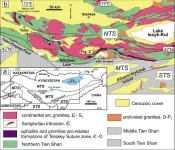
St Petersburg University scientists discover an ancient island arc in the Kyrgyz Tien Shan
2021-01-02
The scientists from St Petersburg University began to study the geology of Central Asia in the middle of the 20th century. Multi-year research and rich field experience have made it possible to create the world's leading school of thought in the geology of the Tien Shan at the University. At present, work continues with active collaboration with scientists throughout the world.
One of the recent discoveries of the international research team is the discovery of this specific rock assemblage that is characteristic of ...
Allergists offer reassurance regarding potential allergic reactions to COVID-19 vaccines
2021-01-02
BOSTON - Reports of possible allergic reactions to the COVID-19 vaccines produced by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, both recently approved for emergency use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), have raised public concern. A team of experts led by allergists at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now examined all relevant information to offer reassurance that the vaccines can be administered safely even to people with food or medication allergies. The group's review is published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
In response to accounts of potential allergic reactions in some people following COVID-19 ...
Clinical criteria for diagnosing autism inadequate for people with genetic conditions
2021-01-02
People with certain genetic conditions are likely to have significant symptoms of autism, even if they do not meet all diagnostic criteria, a study concludes.
Researchers at Cardiff University say their findings show clinical services need to adapt so that people diagnosed with autism-linked genetic conditions are not denied access to vital support and interventions.
Published in The American Journal of Psychiatry, the international study analysed data from 547 people who had been diagnosed with ...