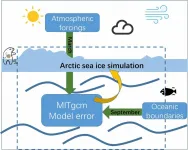
Scientists find the error source of a sea-ice model varies with the season
2021-01-02
(Press-News.org) Arctic sea ice has been rapidly declining in recent decades, and changes in arctic sea ice can have a significant impact on global weather and climate through interactions with the atmosphere and oceans. In addition, the Arctic shipping routes are a shortcut to connect the major countries in the Northern Hemisphere. The Arctic region is also rich in natural resources and biological resources. Simulation of the Arctic sea ice could provide valuable information for Arctic shipping as well as climate studies, and it is therefore urgent to evaluate the ability to simulate Arctic sea ice and diagnose the sources of simulation errors.
To address the issue of error source identification, Prof. Fei Zheng and his team from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, evaluated the sea-ice simulations of the Arctic regional ocean-ice coupling configuration of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology general circulation model (MITgcm).
"We evaluated the model's performance in the Arctic cold season (March) and warm season (September), and found the model performances are different in the two months," says Zheng. "Due to the uncertainty of the model, the model's insufficient response to the signal of atmospheric forcings, and the insufficient response to the ocean boundary signal, there were disagreements between the simulations and observations in both March and September."
According to their paper, published in Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, the characteristics of seasonally varying model error sources could be fully considered by means of an ensemble approach, so as to achieve the goal of improving the simulation and prediction of the Arctic sea ice in different seasons in future work.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-02
Experts in optical physics have developed a new way to see inside living cells in greater detail using existing microscopy technology and without needing to add stains or fluorescent dyes.
Since individual cells are almost translucent, microscope cameras must detect extremely subtle differences in the light passing through parts of the cell. Those differences are known as the phase of the light. Camera image sensors are limited by what amount of light phase difference they can detect, referred to as dynamic range.
"To see greater detail using the same image sensor, we must expand the dynamic range so that we can ...
2021-01-02
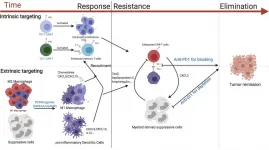
Activating an immune signaling pathway best known for fighting viral and bacterial infections can boost the ability of genetically engineered T cells to eradicate breast cancer in mice, according to a new study by researchers at the University of North Carolina. The study, to be published December 31 in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), suggests that CAR T cells, which are already used to treat certain blood cancers in humans, may also be successful against solid tumors if combined with other immunotherapeutic approaches.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells are a type of white blood cell that have been genetically engineered to recognize ...
2021-01-02
The Asian tiger mosquito does not pose a major risk for Zika virus epidemics, according to a study published December 31 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by Albin Fontaine of the Institut de Recherche Biomédicale des Armées, and colleagues.
Zika virus has triggered large outbreaks in human populations, in some cases causing congenital deformities, fetal loss, or neurological problems in adults. While the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti is considered the primary vector of Zika ...
2021-01-02
A novel computational drug screening strategy combined with lab experiments suggest that pralatrexate, a chemotherapy medication originally developed to treat lymphoma, could potentially be repurposed to treat Covid-19. Haiping Zhang of the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology in Shenzhen, China, and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
With the Covid-19 pandemic causing illness and death worldwide, better treatments are urgently needed. One shortcut could be to repurpose existing drugs that were originally developed to ...
2021-01-02
Multiple bouts of blood feeding by mosquitoes shorten the incubation period for malaria parasites and increase malaria transmission potential, according to a study published December 31 in the open-access journal PLOS Pathogens by Lauren Childs of Virginia Tech, Flaminia Catteruccia of the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, and colleagues. Given that mosquitoes feed on blood multiple times in natural settings, the results suggest that malaria elimination may be substantially more challenging than suggested by previous experiments, which typically involve a single blood meal.
Malaria ...
2021-01-02
The discovery of new drugs is vital to achieving the eradication of neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) in Africa and around the world. Now, researchers reporting in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases have identified traditional Ghanaian medicines which work in the lab against schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis, three diseases endemic to Ghana.
The major intervention for NTDs in Ghana is currently mass drug administration of a few repeatedly recycled drugs, which can lead to reduced efficacy and the emergence of drug resistance. Chronic infections of schistosomiasis, onchocerciasis and lymphatic filariasis ...
2021-01-02
In the ongoing arms race between humans and the parasite that causes malaria, Taane Clark and colleagues at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) report that new mutations that enhance resistance to a drug used to prevent malaria in pregnant women and children are already common in countries fighting the disease. The new results are published December 31 in PLOS Genetics.
Malaria causes about 435,000 deaths each year, primarily in young children in sub-Saharan Africa. Despite a long-term global response, efforts to control the disease are hampered by the rise of drug-resistant strains of the parasite species that cause malaria. Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP), ...
2021-01-02
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- A desalination membrane acts as a filter for salty water: push the water through the membrane, get clean water suitable for agriculture, energy production and even drinking. The process seems simple enough, but it contains complex intricacies that have baffled scientists for decades -- until now.
Researchers from Penn State, The University of Texas at Austin, Iowa State University, Dow Chemical Company and DuPont Water Solutions published a key finding in understanding how membranes actually filter minerals from water, online today (Dec. 31) in Science. The article will be featured on the print edition's cover, to be issued tomorrow (Jan. ...
2021-01-02
Predicting when and how collections of particles, robots, or animals become orderly remains a challenge across science and engineering.
In the 19th century, scientists and engineers developed the discipline of statistical mechanics, which predicts how groups of simple particles transition between order and disorder, as when a collection of randomly colliding atoms freezes to form a uniform crystal lattice.
More challenging to predict are the collective behaviors that can be achieved when the particles ...
2021-01-02
High in the clouds, atmospheric aerosols, including anthropogenic air pollutants, increase updraft speeds in storm clouds by making the surrounding air more humid, a new study finds. The results offer a new mechanism explaining the widely observed - but poorly understood - atmospheric phenomenon and provide a physical basis for predicting increasing thunderstorm intensity, particularly in the high-aerosol regions of the tropics. Observations worldwide have highlighted aerosols' impact on weather, including their ability to strengthen convection in deep convective clouds, like those ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists find the error source of a sea-ice model varies with the season