Diabetes is a worldwide pandemic. Since 1980, the number of people with diabetes has quadrupled worldwide. In Germany alone, 7 million people suffer from it. And the trend is still rising. By 2040, the number of people with type 2 diabetes could increase to as many as 12 million. But type 2 diabetes does not develop from one day to the next. People often go through a longer preliminary stage of diabetes, in which blood glucose levels are already elevated but people are not yet ill. "For people with prediabetes it has not been possible until now to predict whether they would develop diabetes and be at risk for serious complications such as kidney failure, or whether they would only have a harmless form with slightly higher blood glucose levels but without significant risk," said Professor Hans-Ulrich Häring, who initiated the study 25 years ago. However, such a distinction is important for the targeted prevention of the metabolic disease and thus for counteracting the diabetes pandemic. Researchers from Tübingen have now achieved an important breakthrough. Using cluster analysis* in people with prediabetes, they have discovered six distinct subtypes with different diabetes risk. A differentiated classification of prediabetes and diabetes makes it possible to carry out individual and early prevention and therapy of diabetes and its secondary diseases in a way that is adapted to the development of the disease.
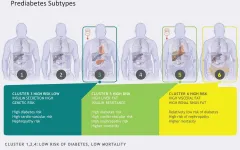
Prediabetes: Six different clusters identified The research group led by Professor Häring and Professor Fritsche at the University Hospital in Tübingen has conducted detailed studies of the metabolism of people with prediabetes who are still considered healthy. The test persons (n=899) are from the Tübingen Family Study and the study of the Tübingen Lifestyle Program. They have repeatedly undergone intensive clinical, laboratory chemical, magnetic resonance imaging and genetic examinations in Tübingen over the past 25 years. Based on key metabolic parameters such as blood glucose levels, liver fat, body fat distribution, blood lipid levels and genetic risk, the researchers were able to identify six subtypes of prediabetes. "As in manifest diabetes, there are also different disease types in the preliminary stage of diabetes, which differ in blood glucose levels, insulin action and insulin secretion, body fat distribution, liver fat and genetic risk," said first author Professor Robert Wagner from the DZD Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, summarizing the results of the study.
Three of these groups (clusters 1, 2 and 4) are characterized by a low diabetes risk. The study participants in clusters 1 and 2 were healthy. Slim people are the main members of cluster 2. They have a particularly low risk of developing complications. Cluster 4 consists of overweight people, whose metabolism is still relatively healthy. The three remaining subtypes (clusters 3, 5 and 6) are associated with an increased risk of diabetes and/or secondary diseases. People who belong to subtype 3 produce too little insulin and have a high risk of developing diabetes. People in cluster 5 have a pronounced fatty liver and a very high risk of diabetes because their bodies are resistant to the blood glucose lowering effect of insulin. In subtype 6, damage to the kidneys occurs even before diabetes is diagnosed. Here, mortality is also particularly high.
But can the classification into six prediabetes subtypes also be confirmed in other cohorts? To investigate this, the researchers extended the analysis to include almost 7000 subjects in the Whitehall II Cohort in London and there, too, identified the six prediabetes subtypes.
More targeted prevention measures The researchers are already making further plans. "Next, in prospective studies, we will first seek to determine to what extent the new findings are applicable for the classification of individual persons into risk groups," said Professor Andreas Fritsche of Tübingen University Hospital. If this is the case, people with a high risk profile could be identified early on and receive specific treatment.
About the study These results are based on research conducted by the Diabetes Research Department at Tübingen University Hospital over the past 25 years to characterize people with an increased risk of diabetes. The study was funded by the German Research Foundation, the Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the State of Baden-Württemberg.
"One of the DZD's goals is to develop precise prevention and therapy measures, i.e. the appropriate prevention or treatment for the right group of people at the right time. The combination of in-depth clinical and molecular research with state-of-the-art bioinformatics has made this internationally important result possible. The identification of subtypes in the preliminary stages of type 2 diabetes is an important step towards precision medicine in the prevention of diabetes and its complications," says DZD Executive Director Prof. Martin Hrab? de Angelis.
INFORMATION:
Original Publication:
Robert Wagner et al: Pathophysiology-based subphenotyping of individuals at elevated risk for type 2 diabetes. Nature Medicine. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.10.12.20210062
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-020-1116-9
Scientific Contact:
Prof. Dr. Robert Wagner
Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of the Helmholtz Zentrum München at the Eberhard-Karls-University of Tuebingen
72076 Tübingen
Phone: 07071/29-82910
robert.wagner@uni-tuebingen.de
* Cluster analysis:
Cluster analysis is a method through which the objects of investigation (e.g. persons) can be grouped on the basis of given criteria and characteristics. The groups found in this way - also called clusters - then contain cases that are similar to each other. A formed cluster should be maximally homogeneous in itself, but at the same time it should differ as much as possible from the other clusters. Here, six different clusters could be identified in test persons with pre-diabetes on the basis of eight core parameters important for metabolism (including blood glucose levels, liver fat, body fat distribution, blood lipid levels and genetic risk).
Further Information
In the German Diabetes Study, researchers from the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) and Lund University in Sweden have discovered various clusters that allow diabetes to be divided into subtypes. By means of cluster analysis, five different subtypes with different risks for secondary diseases were identified.
https://www.dzd-ev.de/en/latest/news/news/article/a-new-diabetes-classification-subgroups-of-type-2-diabetes-have-specific-risk-of-diabetes-associate/index.html
The German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) e.V. is one of six German Centers for Health Research. It brings together experts in the field of diabetes research and combines basic research, epidemiology and clinical application. By adopting an innovative, integrative approach to research, the DZD aims to make a substantial contribution to the successful, personalized prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. The members of the association are Helmholtz Zentrum München - German Research Center for Environmental Health, the German Diabetes Center (DDZ) in Düsseldorf, the German Institute of Human Nutrition (DIfE) in Potsdam-Rehbrücke, the Institute of Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, and the Paul Langerhans Institute Dresden of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University Medical Center Carl Gustav Carus of TU Dresden, associated partners at the universities in Heidelberg, Cologne, Leipzig, Lübeck and Munich, and other project partners. Further information: http://www.dzd-ev.de
As German Center for Environmental Health, Helmholtz Zentrum München pursues the goal of developing personalized medical approaches for the diagnosis, therapy and prevention of major common diseases such as diabetes mellitus and lung diseases. To achieve this, it investigates the interaction of genetics, environmental factors and lifestyle. The head office of the center is located in Neuherberg to the north of Munich. Helmholtz Zentrum München has approximately 2300 staff members and is a member of the Helmholtz Association, a German research organization comprised of 18 scientific-technical and medical-biological research centers with a total of about 37,000 staff members. http://www.helmholtz-muenchen.de
Founded in 1805, Tübingen University Hospital is one of the leading centers of German university medicine. As one of the 33 university hospitals in Germany, it contributes to the successful combination of high-performance medicine, research and teaching. Well over 400,000 inpatients and outpatients from all over the world benefit annually from this combination of science and practice. The clinics, institutes and centers unite all specialists under one roof. The experts work together across disciplines and offer every patient optimal treatment based on the latest research results. Tübingen University Hospital conducts research for better diagnoses, therapies and chances of cure, many new treatment methods are clinically tested and applied here. Neurosciences, oncology, immunology, infection research, vascular medicine and diabetes research are the main areas of research in Tübingen. The Chair of Diabetology /Endocrinology has been the centre of interdisciplinary research over the last 25 years, especially involving surgery, radiology and laboratory medicine. This excellent discovery of the pre-diabetes subtypes was only made possible by the interdisciplinary cooperation has the discovery of the pre-diabetes subtypes at the University Hospital. The University Hospital is a reliable partner in four of the six German Centers for Health Research initiated by the German government. http://www.medizin.uni-tuebingen.de