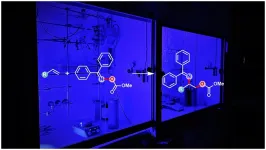
Chemists succeed in synthesis of aminoalcohols by utilizing light
New method for generating the least accessible form of vicinal aminoalcohols; study published in 'Nature Catalysis'
2021-01-04
(Press-News.org) Whether in beta-blockers to treat high blood pressure or in natural products: So-called vicinal aminoalcohols are high-quality organic compounds that are found in many everyday products. However, their production is difficult. For a long time, chemists are trying to develop efficient methods of synthesizing them. In their recent study published in the journal Nature Catalysis, scientists led by Prof. Dr. Frank Glorius of Münster University have found a solution for the production of a special variant of aminoalcohols. "The new method helps to study the properties of the substance and to find applications for these new compounds in the future", emphasizes Frank Glorius from the Organic Chemistry Institute at Münster University.
Vicinal aminoalcohols can occur in two different variants - called regioisomers - in which the amine and alcohol functional groups exchange positions. Although they are thus very similar, they often have different biochemical properties. Installation of both amine and alcohol groups in one step poses a major challenge. The discovery of the "Asymmetric Amino Hydroxylation Reaction" with which one of the regioisomers can be produced, even rewarded the chemist Barry Sharpless with a Nobel Prize in 2001. However, the other regioisomer cannot be synthesized by similar method and remained a long-standing problem - until now. With the help of the chemists' new photo-initiated reaction method, the synthesis of the other regioisomer has now also become efficiently possible.
Background and method:
Unactivated alkenes containing a carbon-carbon double bond are known as feedstock chemicals for reaction processes due to their good availability. In general, the installation of both amine and alcohol groups in one step via this carbon-carbon double bond of unactivated alkene is at all times initiated by the amine group, followed by the addition of the alcohol group. As a result, always a particular regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohol is formed. Now the scientists have identified a particular class of amine-like compounds that are reactive yet stable enough to allow first the addition of the alcohol group to the carbon-carbon double bond, followed by the addition of the amine group to generate the previously inaccessible opposite regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohols.
"Like plants use chlorophyll to convert light into energy, we use what is called a photocatalyst", explains Dr. Tuhin Patra, first author of this study. "This species can absorb the light from blue LEDs and transfer its energy into a molecule directly involved in the reaction. This simultaneously releases the amine and alcohol groups." This process, in which the molecules transfer electrons to each other, is called energy transfer, the scientist explains.
Fascinatingly, the new method generates the least accessible regioisomer of the vicinal aminoalcohols in such a manner that both the alcohol and amine groups are protected from further reactions. Depending on the user's needs, one of the two alcohol or amine groups can now be reactivated without affecting the other. However, even both groups can be enabled to react further at the same time, if that is necessary for the synthesis of further requirements. "Previous designs usually install only one group at a time in a complex multistep overall process. Our design not only allows the installation of two different groups in one step with desired protection, but also reliably generates the least accessible regioisomer, offering the chance to investigate future applications of this compound," concludes Frank Glorius.
INFORMATION:
Original publication:
T. Patra, M. Das, C. Daniliuc, F. Glorius (2021): Metal-free, photosensitized oxyimination of unactivated alkenes with bifunctional oxime carbonates. Nature Catalysis; DOI: 10.1038/s41929-020-00553-2.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-04
Assembling tiny chips into unique programmable surfaces, Princeton researchers have created a key component toward unlocking a communications band that promises to dramatically increase the amount data wireless systems can transmit.
The programmable surface, called a metasurface, allows engineers to control and focus transmissions in the terahertz band of the electromagnetic spectrum. Terahertz, a frequency range located between microwaves and infrared light, can transit much more data than current, radio-based wireless systems. With fifth generation (5G) communications systems offering speeds 10 to 100 times faster than the previous generation, demand for bandwidth is ever increasing. Facing the emergence of technologies such as self-driving cars and augmented reality ...
2021-01-04
What The Study Did: Changes were assessed in abortions performed and at what gestational age following a Texas order postponing nonmedically necessary surgeries due to the COVID-19 pandemic compared with abortions performed during the same months in 2019.
Authors: Kari White, Ph.D., M.P.H., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24096)
Editor's Note: The articles includes conflict of interest and funding/support ...
2021-01-04
What The Viewpoint Says: The rapid spread of scientific misinformation on social media platforms throughout the COVID-19 pandemic is discussed in this Viewpoint, which also proposes strategies to counteract its adverse effects including surveillance of digital data and partnering with trusted messengers to engage the public and advance scientifically sound public health measures.
Authors: Raina M. Merchant, M.D., M.S.H.P., of the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2020.24514)
Editor's Note: The ...
2021-01-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - From an observatory high above Chile's Atacama Desert, astronomers have taken a new look at the oldest light in the universe.
Their observations, plus a bit of cosmic geometry, suggest that the universe is 13.77 billion years old - give or take 40 million years. A Cornell University researcher co-authored one of two papers about the findings, which add a fresh twist to an ongoing debate in the astrophysics community.
The new estimate, using data gathered at the National Science Foundation's Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), matches the one provided by the standard ...
2021-01-04
All prediabetes is not the same: in people in the preliminary stages of type 2 diabetes, there are six clearly distinguishable subtypes, which differ in the development of the disease, diabetes risk, and the development of secondary diseases. This is shown in a study by the Institute for Diabetes Research and Metabolic Diseases (IDM) of Helmholtz Zentrum München at the University of Tübingen, Tübingen University Hospital and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD). The results have now been published in Nature Medicine. The new classification can help in the future to prevent the manifestation of diabetes ...
2021-01-04
A sugar-binding protein could fuel terrible inflammation and worsen sepsis, a disease that kills more than 270,000 people every year in the US alone, reports a team of researchers led by UConn Health in the 4 January issue of Nature Immunology.
Sepsis is caused mostly by bacterial infections. The immune system runs out of controls and triggers a cytokine storm, a condition in which inflammation-causing proteins flood the blood. Organs may break down, and death often follows.
Other diseases can also cause cytokine storms; medical historians believe cytokine storms were behind the lethality of the ...
2021-01-04
If you type into a search engine - "why do men have to wait before having sex again?" - you will very quickly come across Prolactin. This little hormone is thought to be involved in hundreds of physiological processes in the body. Among them is the male post-ejaculatory refractory period. This period begins when a male ejaculates and ends when he recovers his sexual capacity.
If you search a bit more, you'll see that this theory has even led to the development of so called "treatments". These promise to shorten the length of a person's refractory period by reducing their body's prolactin levels.
Well, here is some bad news for anyone who has bought any such merchandise. A new study in mice by scientists at the Champalimaud Centre for the Unknown ...
2021-01-04
A research study at the University of Chicago has found that in pregnancy, while the T cell response to a fetus becomes tolerant to allow for successful pregnancy, the part of the immune system that produces antibodies (known as the humoral response) becomes sensitized, creating memory B cells that can later contribute to the rejection of a transplanted organ.
The results help to clarify why it is that the immune system can tolerate a fetus during pregnancy, but later may be more likely to become sensitized to and reject an organ transplant. The study was published on January 4, 2021 in the END ...
2021-01-04
Polarons are fleeting distortions in a material's atomic lattice that form around a moving electron in a few trillionths of a second, then quickly disappear. As ephemeral as they are, they affect a material's behavior, and may even be the reason that solar cells made with lead hybrid perovskites achieve extraordinarily high efficiencies in the lab.
Now scientists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University have used the lab's X-ray laser to watch and directly measure the formation of polarons for the first time. They reported their findings in Nature ...
2021-01-04
Using a new combination of emitter molecules, researchers in Japan have demonstrated the promise of a novel approach to finally overcome a major challenge facing displays using organic light-emitting diodes: a blue light source matching the excellent performance of the red and green ones.
By splitting energy conversion and emission processes between two molecules, the researchers achieved devices that produce pure-blue emission with high efficiency, maintain brightness for relatively long times, and lack any expensive metal atoms--a set of properties that has so far been difficult ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Chemists succeed in synthesis of aminoalcohols by utilizing light
New method for generating the least accessible form of vicinal aminoalcohols; study published in 'Nature Catalysis'