(Press-News.org) PULLMAN, Wash. - In what may be a sign of climate-change-induced conflict, researchers have captured rare photographic evidence of a jaguar killing another predatory wild cat at an isolated waterhole in Guatemala.
In the footage, a male jaguar arrives near the waterhole and apparently lies in wait for an hour. It lets a potentially dangerous prey animal, a large tapir, pass by, but when the ocelot stops to drink, the jaguar pounces and carries off the smaller predator.
The event, detailed in a recent study published in the journal Biotropica, was captured in the Maya Biosphere Reserve in March 2019, a dry month in a drought year for the tropical forest, by wildlife ecologists from Washington State University and the Wildlife Conservation Society.
"Although these predator-on-predator interactions may be rare, there may be certain instances when they become more prevalent, and one of those could be over contested water resources," said Daniel Thornton, a WSU assistant professor and co-author on the paper. "People don't often think of tropical systems as being dry, but in many parts of the world, tropical rains are quite seasonal, and with climate change, some of these tropical ecosystems are expected to become even more seasonal. The more isolated and rare water resources become, the more they're going to become hotspots of activity."
Jaguars which can weigh more than 200 pounds typically prey on small animals like armadillos or peccaries. Ocelots, also carnivores, are smaller than their larger jaguar cousins at around 18 to 44 pounds, and their activity patterns overlap with the jaguars particularly in twilight periods of the day.
While some research has noted signs of ocelot in jaguar feces, until now, no known images have been captured of a jaguar directly killing an ocelot.
"These dramatic camera trap images clearly show the fierce competition wildlife face for precious resources like water," said Rony García-Anleu of WCS's Guatemala Program and a co-author of the study. "Unfortunately, climate change and associated droughts are predicted to worsen, which means tough times are ahead for wildlife that depend on watering holes for their survival."
The researchers had placed cameras at 42 waterholes in the area in 2018 and 2019. In the 2019 dry season only 21 had water, and none of those were within 10 km (6.2 miles) of this particular waterhole. At this same remote spot, scientists also recorded a fight between two jaguars and a jaguar attempting to attack a young tapir. They also noted that seven different jaguars frequented this waterhole, which is unusual for a species that normally avoids its peers and sticks to its own territory.
The jaguar-ocelot kill was captured as part of a larger monitoring project looking at the distribution of animals across the entire landscape in northern Guatemala, especially in relation to human pressures. Ironically, this waterhole was one that was far from any human community, but that did not mean it was necessarily unaffected by human activity.
"We have evidence that many things are happening related to climate change, but we might not be aware of every detail, of every consequence," said Lucy Perera-Romero, a WSU doctoral student and lead author on the study. "For example, in these beautiful, green forests, we may not be aware that water flow is a serious issue. It could be another source of mortality--apart from deforestation, from hunting, and from everything else that we do."
The Maya Forest is one of Mesoamerica's 5 Great Forests, spanning from Mexico to Colombia, collectively covering an area three times the size of Switzerland. The 5 Great Forests are all transboundary and represent Mesoamerica's most critical bastions for jaguars and other wildlife, and provide services such as carbon sequestration, clean water and food security to five million people.
INFORMATION:
LA JOLLA--(January 5, 2021) Lithium is considered the gold standard for treating bipolar disorder (BD), but nearly 70 percent of people with BD don't respond to it. This leaves them at risk for debilitating, potentially life-threatening mood swings. Researchers at the Salk Institute have found that the culprit may lie in gene activity--or lack of it.
A new study led by Salk Professor and President Rusty Gage, which published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry on January 4, 2021, shows that decreased activation of a gene called LEF1 disrupts ordinary ...
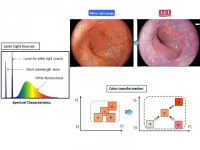
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) describe an endoscopic modality for detecting upper gastrointestinal tract neoplasms by Linked Color Imaging that innovatively mixes light of different wavelengths to better depict mucosal changes
Tokyo, Japan - Recently there have been significant advances on several fronts in the ongoing war against cancer of the alimentary tract. Now, Japanese researchers report the development of another weapon: Linked Color Imaging (LCI), a novel endoscopic technique that improves detection of cancer by viewing the upper digestive tract mucosa under illumination that combines specific wavelengths of light to intensify subtle color variations indicative of neoplastic change.
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) endoscopy ...
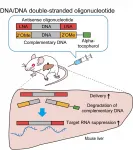
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, USA, report a modification wherein replacing the RNA strand of a heteroduplex oligonucleotide with DNA may enhance the efficacy of antisense oligonucleotide-based drugs
Tokyo, Japan - Antisense oligonucleotides (ASO) hold great promise for pharmacotherapy. Now, researchers at Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, advancing their earlier work on a heteroduplex oligonucleotide (HDO) model, have demonstrated augmentation of ASO-based ...
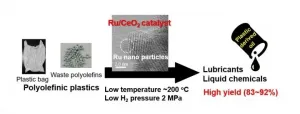
For the first time, researchers have used a novel catalyst process to recycle a type of plastic found in everything from grocery bags and food packaging to toys and electronics into liquid fuels and wax.
The team published their results on Dec. 10 in Applied Catalysis B: Environmental.
"Plastics are essential materials for our life because they bring safety and hygiene to our society," said paper co-authors Masazumi Tamura, associate professor in the Research Center for Artificial Photosynthesis in the Advanced Research Institute for Natural Science and Technology in Osaka City University, and Keiichi Tomishige, professor in the Graduate School of Engineering in Tohoku University. "However, the growth of the global ...
An imbalance of the body's oxygen producing free radicals and its antioxidant cells could be the reason why gum disease and chronic kidney disease affect each other, a new study led by the University of Birmingham has found.
Periodontitis - or gum disease - is a common, inflammatory disease which causes bleeding gums, wobbly or drifting teeth and can eventually result in tooth loss.
Previous studies have shown a link between the severe oral inflammation caused by gum disease and chronic kidney disease (CKD) which demonstrated that those with worse inflammation of the gums have worse kidney function.
Previous research also showed that patients with CKD and periodontitis experience ...
Practicing gratitude and looking to the future will help safeguard our mental wellbeing during Covid-19 lockdowns, a new study in the Journal of Positive Psychology reports.
In the first study of its kind, researchers from the University of Surrey investigated the effectiveness of three psychological interventions -- nostalgia, a sentimentality for the past; gratitude, recognising the good things currently in our life; and best possible self, thinking about positive elements of the future -- and how they each affect wellbeing during lockdowns.
Personal characteristics such as emotion regulation (the ability to respond ...
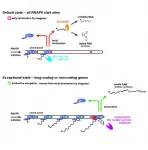
In a joint collaboration, Danish and German researchers have characterized a cellular activity that protects our cells from potentially toxic by-products of gene expression. This activity is central for the ability of multicellular organisms to uphold a robust evolutionary 'reservoir' of gene products.
Manufacturing processes need quality control systems in order to ensure proper assembly of functional products. Moreover, space-consuming, and perhaps even toxic, by-products of such processes need to be properly discarded or recycled by efficient waste handling systems.
By analogy, transcription of our genome is an imperfect process that produces large quantities of non-functional and potentially harmful transcripts both from within and ...
Researchers at the Francis Crick Institute and the University of Western Australia have developed a new imaging method to see where antibiotics have reached bacteria within tissues. The method could be used to help develop more effective antibiotic treatments, reducing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
During bacterial infections like tuberculosis, bacteria enter human cells, which poses a challenge for treatment, as antibiotics must reach and enter all infected cells in order to be effective. If researchers could select for or develop more effective antibiotics based on where they reach, this may reduce the length of treatment ...
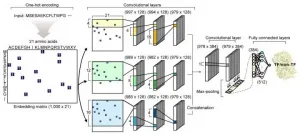
A joint research team from KAIST and UCSD has developed a deep neural network named DeepTFactor that predicts transcription factors from protein sequences. DeepTFactor will serve as a useful tool for understanding the regulatory systems of organisms, accelerating the use of deep learning for solving biological problems.
A transcription factor is a protein that specifically binds to DNA sequences to control the transcription initiation. Analyzing transcriptional regulation enables the understanding of how organisms control gene expression in response to genetic or environmental changes. In this regard, finding the transcription factor of an organism is the first step in the analysis ...
While glass is a truly ubiquitous material that we use on a daily basis, it also represents a major scientific conundrum. Contrary to what one might expect, the true nature of glass remains something of a mystery, with scientific inquiry into its chemical and physical properties still underway. In chemistry and physics, the term glass itself is a mutable concept: It includes the substance we know as window glass, but it may also refer to a range of other materials with properties that can be explained by reference to glass-like behaviour, including, for instance, ...