(Press-News.org) ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- If everything moved 40,000 times faster, you could eat a fresh tomato three minutes after planting a seed. You could fly from New York to L.A. in half a second. And you'd have waited in line at airport security for that flight for 30 milliseconds.
Thanks to machine learning, designing materials for new, advanced technologies could accelerate that much.
A research team at Sandia National Laboratories has successfully used machine learning -- computer algorithms that improve themselves by learning patterns in data -- to complete cumbersome materials science calculations more than 40,000 times faster than normal.
Their results, published Jan. 4 in END
Advanced materials in a snap
Sandia Labs shows machine learning could lop a year off technology design cycle
2021-01-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New clues to prostate cancer
2021-01-05
Australian research has identified a new mechanism in which prostate cancer cells can 'switch' character and become resistant to therapy.
These findings, just published in Cell Reports, are an important development in unravelling how an aggressive subtype of prostate cancer, neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC), develops after hormonal therapies.
It is well established that some tumours show increased cellular 'plasticity' in response to new or stressful conditions, such as cancer therapy, says lead researcher Associate Professor Luke Selth, from the Flinders ...
Estimation of US SARS-CoV-2 infections, symptomatic infections, hospitalizations, deaths
2021-01-05
What The Study Did: Data from public health surveillance of reported COVID-19 cases and seroprevalence surveys were used in this observational study that reports an estimated 46.9 million SARS-CoV-2 infections, 28.1 million symptomatic infections, 956,174 hospitalizations and 304,915 deaths occurred in the U.S. through November 15, 2020.
Authors: Frederick J. Angulo, D.V.M., Ph.D., of Medical Development and Scientific/Clinical Affairs of Pfizer Vaccines, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33706)
Editor's ...
Imminent sudden stratospheric warming to occur, bringing increased risk of snow over coming weeks
2021-01-05
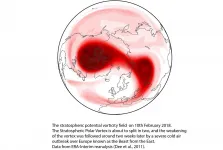
A new study led by researchers at the Universities of Bristol, Exeter, and Bath helps to shed light on the winter weather we may soon have in store following a dramatic meteorological event currently unfolding high above the North Pole.
Weather forecasting models are predicting with increasing confidence that a sudden stratospheric warming (SSW) event will take place today, 5 January 2021.
The stratosphere is the layer of the atmosphere from around 10-50km above the earth's surface. SSW events are some of the most extreme of atmospheric phenomena and can see polar stratospheric temperature increase by up to 50°C over the course of a few days. Such events ...
Novel method identifies areas most suitable for conservation of black lion tamarin
2021-01-05
By André Julião | Agência FAPESP - The black lion tamarin (Leontopithecus chrysopygus) once inhabited most forest areas in the state of São Paulo, Southeast Brazil, but currently occupies only some Atlantic Rainforest remnants there. In recent years, after various studies of the endangered species, environmental NGO Instituto de Pesquisas Ecológicas (IPÊ) moved groups of these animals to areas from which the species had disappeared.
Similar initiatives have now been reinforced by a group of researchers at IPÊ, São Paulo State University (UNESP) and the Federal University of Mato Grosso (UFMT), who cross-tabulated climate data and data on landscape (forest cover) to determine the sites best suited for future ...
Leaf fossils show severe end-Cretaceous plant extinction in southern Argentina
2021-01-05
The asteroid impact 66 million years ago that ushered in a mass extinction and ended the dinosaurs also killed off many of the plants that they relied on for food. Fossil leaf assemblages from Patagonia, Argentina, suggest that vegetation in South America suffered great losses but rebounded quickly, according to an international team of researchers.
"Every mass extinction event is like a reset button, and what happens after that reset depends on which organisms survive and how they shape the biosphere," said Elena Stiles, a doctoral student at the University of Washington who completed the research as part of her master's thesis at Penn State. "All the biodiversity ...
Remote sensing data sheds light on when and how asteroid Ryugu lost its water
2021-01-05
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- Last month, Japan's Hayabusa2 mission brought home a cache of rocks collected from a near-Earth asteroid called Ryugu. While analysis of those returned samples is just getting underway, researchers are using data from the spacecraft's other instruments to reveal new details about the asteroid's past.
In a study published in Nature Astronomy, researchers offer an explanation for why Ryugu isn't quite as rich in water-bearing minerals as some other asteroids. The study suggests that the ancient parent body from which Ryugu was formed had likely dried out in some kind of heating event before Ryugu came into being, which left Ryugu itself drier than expected.
"One of the ...
Repeated ketamine infusions reduce PTSD symptom severity
2021-01-05
Repeated intravenous (IV) ketamine infusions significantly reduce symptom severity in individuals with chronic post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and the improvement is rapid and maintained for several weeks afterwards, according to a study conducted by researchers from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. The study, published September XX in the American Journal of Psychiatry, is the first randomized, controlled trial of repeated ketamine administration for chronic PTSD and suggests this may be a promising treatment for PTSD patients.
"Our findings provide insight into the treatment efficacy of repeated ketamine ...
Protecting the global food supply chain
2021-01-05
As the world grows increasingly globalized, one of the ways that countries have come to rely on one another is through a more intricate and interconnected food supply chain. Food produced in one country is often consumed in another country -- with technological advances allowing food to be shipped between countries that are increasingly distant from one another.
This interconnectedness has its benefits. For instance, if the United States imports food from multiple countries and one of those countries abruptly stops exporting food to the United States, there are still other countries that can be relied on ...
Journal article reviews century of data showing COVID-19 likely to impact the brain
2021-01-05
SAN ANTONIO and CHICAGO - An article published Jan. 5 in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association cites decades of published scientific evidence to make a compelling case for SARS-CoV-2's expected long-term effects on the brain and nervous system.
Dementia researchers from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) are the first and senior authors of the report and are joined by coauthors from the Alzheimer's Association and Nottingham and Leicester universities in England.
"Since the flu pandemic of 1917 and 1918, many of the flulike diseases have been associated with brain disorders," said lead author ...
Self-controlled children tend to be healthier middle-aged adults
2021-01-05
DURHAM, N.C. -- Self-control, the ability to contain one's own thoughts, feelings and behaviors, and to work toward goals with a plan, is one of the personality traits that makes a child ready for school. And, it turns out, ready for life as well.
In a large study that has tracked a thousand people from birth through age 45 in New Zealand, researchers have determined that people who had higher levels of self-control as children were aging more slowly than their peers at age 45. Their bodies and brains were healthier and biologically younger.
In interviews, the higher self-control group also showed they may be better equipped to handle the health, financial and social challenges of later life as well. The researchers used structured interviews and credit checks ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Advanced materials in a snapSandia Labs shows machine learning could lop a year off technology design cycle