Researchers featured in Medical Research Journal for Artificial Intelligence Studies
2021-01-06
(Press-News.org) Memphis, Tenn. (January 5, 2021) - A paper written by Arash Shaban-Nejad, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor, and Nariman Ammar, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow, both at the Center for Biomedical Informatics in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, was recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - Medical Informatics. The paper discussed how an artificial intelligence system developed by the researchers was used to diagnose and treat children and adults who suffer from Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs).
Their research study was named among the Top Milestones on Explainable AI In 2020.
Adverse Childhood Experiences, negative events and processes that an individual might encounter during childhood and adolescence, have been proven to be linked to increased risk of a multitude of negative health outcomes and conditions in adulthood. Drs. Shaban-Nejad and Ammar implemented an artificial intelligence platform called Semantic Platform for Adverse Childhood Experiences Surveillance (SPACES), which assists medical practitioners and health care workers with diagnosing ACEs in the early stages by using real-time data captured through conversations during in-person consultations.
Many AI platforms don't provide enough explanation to interpret and justify decisions, prolonging the diagnosis and treatment processes. The SPACES platform has functions that can mitigate many of these difficulties. It can detect patient health disparity variants (geographic location, sexual identity, socioeconomic status, etc.), recommend intervention plans to health professionals, and allocate resources as needed.
"Current treatment options are long, complex, costly, and most of the time a non-transparent process," Dr. Shaban-Nejad said. "We aim not only to assist health care practitioners in extracting, processing, and analyzing the information, but also to inform and empower patients to actively participate in their own health care decision-making process in close cooperation with medical and health care professionals."
INFORMATION:
The study was conducted in collaboration with the Family Resilience Initiative at Le Bonheur Children's Hospital in Memphis. This research was also partially supported through a grant from the Memphis Research Consortium.
The paper is titled, "Explainable Artificial Intelligence Recommendation System by Leveraging the Semantics of Adverse Childhood Experiences: Proof-of-Concept Prototype Development."
As Tennessee's only public, statewide, academic health system, the mission of the University of Tennessee Health Science Center is to bring the benefits of the health sciences to the achievement and maintenance of human health through education, research, clinical care, and public service, with a focus on the citizens of Tennessee and the region. The main campus in Memphis includes six colleges: Dentistry, Graduate Health Sciences, Health Professions, Medicine, Nursing and Pharmacy. UTHSC also educates and trains medicine, pharmacy, and/or health professions students, as well as medical residents and fellows, at major sites in Knoxville, Chattanooga and Nashville. For more information, visit uthsc.edu. Find us on Facebook: facebook.com/uthsc, on Twitter: twitter.com/uthsc and on Instagram: instagram.com/uthsc. END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-06
A new SFU-led study finds that less than half of media stories in early 2020 featuring COVID-19 "preprint" research--research that has not yet been peer-reviewed--accurately framed the studies as being preprints or unverified research.
SFU PhD student Alice Fleerackers, a researcher in the Scholarly Communications Lab, and publishing program professor Juan Pablo Alperin collaborated with an international team of researchers to analyze more than 500 mentions in over 450 stories from digital news outlets covering preprint COVID-19 research. The study was published this week in Health Communication.
Their analysis ...
2021-01-06
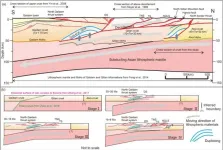
As the largest orogenic plateau on earth, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau was caused by a complex crustal deformation process during the continuous collision and compression process between the Indian and Eurasian continents starting at least 60-50 Ma ago. The formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau records the collision of the two continents and the deformation process and mechanism within the continents. Therefore, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is considered as a natural ideal laboratory for the study of continent-continent collision and dynamics. At present, the continuous collision between Eurasia and Indian continents is still ongoing, ...
2021-01-06
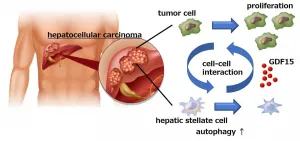
Osaka, Japan - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), frequently seen in patients with liver cirrhosis caused by alcohol abuse or chronic viral hepatitis, is the most common form of liver cancer worldwide. As such, it is the third-most common cause of cancer-related death and has a notoriously poor prognosis. At present, surgery is the most effective treatment for HCC, but is only successful in the 10%-20% of cases where cancer cells have not spread beyond the liver.
Given the lack of treatment options for HCC, a group of researchers led by Osaka University decided to focus on specific cells and processes that occur in the area around liver tumors in the hope of finding a novel target for drug development.
The results of their study were published in a recent issue of Gastroenterology.
"Hepatic ...
2021-01-06
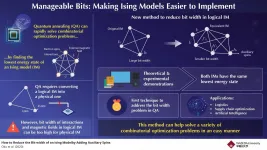
Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, how do you determine the shortest route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the starting location? This famous problem is called the "traveling salesman problem" and is an example of a combinatorial optimization problem. Solving these problems using conventional computers can be very time-consuming, and special devices called "quantum annealers" have been created for this purpose.
Quantum annealers are designed to find the lowest energy state (or "ground state") of what's known as an "Ising model." Such models are abstract representations of a quantum mechanical system involving interacting spins that are also influenced by external magnetic ...
2021-01-06
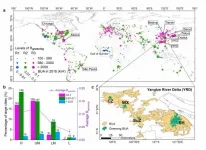
The world has experienced dramatic urbanization in recent decades. According to the latest report from the United Nations (UN), the global population in 2018 was 7.6 billion and the urban population was 4.2 billion. By 2050, the global population is expected to soar to 9.7 billion, with 68% of the population living in urban areas. (Note 1)
In the first-ever study on the characteristics of urbanization in large cities around the world, researchers at the Department of Civil Engineering of the University of Hong Kong (HKU) analyzed cities' urban built-up areas (BUAs) expansion, population growth and greening BUA changes, and revealed a hugely uneven ...
2021-01-06
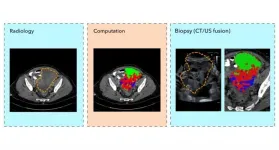
A new advanced computing technique using routine medical scans to enable doctors to take fewer, more accurate tumour biopsies, has been developed by cancer researchers at the University of Cambridge.
This is an important step towards precision tissue sampling for cancer patients to help select the best treatment. In future the technique could even replace clinical biopsies with 'virtual biopsies', sparing patients invasive procedures.
The research published in European Radiology shows that combining computed tomography (CT) scans with ultrasound images creates a visual guide for doctors to ensure they sample the full complexity of ...
2021-01-06
In the future, the Antarctic could become a greener place and be colonised by new species. At the same time, some species will likely disappear. 25 researchers recently presented these and many other findings in a major international project, in which they analysed hundreds of articles on the Antarctic published in the past ten years. By doing so, the team have provided an exceptionally comprehensive assessment of the status quo and future of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean that surrounds it.
Never before have researchers arrived at so many new findings on the biological and biochemical processes at work in the Antarctic than in the past ten years. Now 25 experts, led by the Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), have analysed and compiled these ...
2021-01-06
Smoking is associated with an increased risk of COVID-19 symptoms and smokers are more likely to attend hospital than non-smokers, a study has found.
The study published today in Thorax, by researchers from King's College London, investigates the association between smoking and the severity of the COVID-19.
Researchers analysed data from the ZOE COVID Symptom Study App. Of the participants of the app, 11% were smokers. This is a lower proportion than the overall UK population of 14.7%, however, it reflects the demographics of the self-selected sample of the ZOE COVID Symptom Study.
While more than a third of users reported not feeling physically well during the period of study (24th March and April 2020), current smokers were 14% more likely to develop the classic triad of ...
2021-01-06
DALLAS, Jan. 6, 2021 -- Statins, common cholesterol-lowering medications, may protect women's hearts from damage caused during chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access journal of the American Heart Association.
"Two types of cancer medications, anthracyclines and trastuzumab, are effective treatments for many women with breast cancer, however, the risk of heart muscle damage has limited their use, particularly in women who are at higher risk for heart problems because of their age or other medical issues," said Husam Abdel-Qadir, M.D., Ph.D., lead author of the study, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Toronto's ...
2021-01-06
Toronto - New research from UHN's Peter Munk Cardiac Centre (PMCC) shows statins, commonly prescribed to lower cholesterol and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke, may also protect the heart from damaging side-effects of early breast cancer treatment.
Published Jan. 6, 2021 in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an observational study found women already taking statins and treated with either anthracyclines or trastuzumab were half as likely to be hospitalized or visit an Emergency Department for heart failure within five years after chemotherapy.
"Our job is to protect the heart and ensure it has the greatest fighting chance to get through chemotherapy," says Dr. Husam Abdel-Qadir, lead author of the paper and a cardiologist at the PMCC and Women's College ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers featured in Medical Research Journal for Artificial Intelligence Studies