Link between dietary fiber and depression partially explained by gut-brain interactions
New study suggests that higher daily dietary fiber intake is linked to lower risk for depression in premenopausal women
2021-01-06
(Press-News.org) CLEVELAND, Ohio (January 5, 2021)--Fiber is a commonly recommended part of a healthy diet. That's because it's good for your health in so many ways--from weight management to reducing the risk of diabetes, heart disease, and some types of cancer. A new study also finds that it might be linked with a reduced risk of depression, especially in premenopausal women. Study results are published online in Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS).
Depression is a common and serious mental health condition that not only affects a person's ability to perform daily activities but can also lead to suicide. It's estimated that more than 264 million people worldwide have depression, with numbers increasing over time. This debilitating condition is much more common in women, and there are a number of theories as to why this is the case. Changes in hormone levels in perimenopausal women have been linked to depression.
Because of the serious consequences and prevalence of depression, numerous studies have been undertaken to evaluate treatment options beyond the use of antidepressants. Lifestyle interventions, including diet, exercise, and mindfulness, may help to reduce the risk for depression. In this new study involving more than 5,800 women of various ages, researchers specifically sought to investigate the relationship between dietary fiber intake and depression in women by menopause status. Dietary fiber is found mainly in fruit, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
Previous studies have already suggested the benefits of fiber for mental health, but this is the first known study to categorize the association in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. It also included a broader range of ages in participants and involved women who underwent natural, as well as surgical, menopause.
The study confirmed an inverse association between dietary-fiber intake and depression in premenopausal women after adjusting for other variables, but no significant difference was documented in postmenopausal women. Research has suggested that estrogen depletion may play a role in explaining why postmenopausal women don't benefit as much from increased dietary fiber, because estrogen affects the balance of gut microorganisms found in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. The link between dietary fiber and depression may be partially explained by gut-brain interactions, because it is theorized that changes in gut-microbiota composition may affect neurotransmission. Fiber improves the richness and diversity of gut microbiota.
Results are published in the article "Inverse association between dietary fiber intake and depression in premenopausal women: a nationwide population-based survey."
"This study highlights an important link between dietary fiber intake and depression, but the direction of the association is unclear in this observational study, such that women with better mental health may have had a healthier diet and consumed more fiber, or a higher dietary fiber intake may have contributed to improved brain health by modulating the gut microbiome or some combination. Nonetheless, it has never been more true that 'you are what you eat,' given that what we eat has a profound effect on the gut microbiome which appears to play a key role in health and disease," says Dr. Stephanie Faubion, NAMS medical director.
INFORMATION:
For more information about menopause and healthy aging, visit http://www.menopause.org.
Founded in 1989, The North American Menopause Society (NAMS) is North America's leading nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting the health and quality of life of all women during midlife and beyond through an understanding of menopause and healthy aging. Its multidisciplinary membership of 2,000 leaders in the field--including clinical and basic science experts from medicine, nursing, sociology, psychology, nutrition, anthropology, epidemiology, pharmacy, and education--makes NAMS uniquely qualified to serve as the definitive resource for health professionals and the public for accurate, unbiased information about menopause and healthy aging. To learn more about NAMS, visit http://www.menopause.org.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-06
Most forms of life -- species of mammals, birds, plants, reptiles, amphibians, etc. -- are most diverse at Earth's equator and least diverse at the poles. This distribution is called the latitudinal gradient of biodiversity.
A group of Santa Fe Institute collaborators was intrigued by the fact that human cultural diversity shows exactly the same distribution with latitude: human cultures are more diverse near the equator and least at the poles. Their big question was: why? Life is more diverse within richer environments, but it's not clear why human cultural diversity would show this pattern too.
To find answers, the group conducted a biogeographic and macroecological study of the distribution of mammal species ...
2021-01-06
A systematic review and meta-analysis of international COVID-19 literature, led by UNSW Sydney, has confirmed that while children under five years old were likely to recover from the infection, half of those infected were infants and almost half of the infected under-fives were asymptomatic.
These findings will help to inform future policy and decision-making about potential COVID-19 vaccination for young children and maternal immunisation programs during pregnancy - but the scientists say future research is needed to explore the potential risk of transmission from infants to their mothers, families and other caregivers, and to find out more about whether asymptomatic under-fives can spread the disease.
The collaborative study between researchers from UNSW Sydney, Telethon ...
2021-01-06
Memphis, Tenn. (January 5, 2021) - A paper written by Arash Shaban-Nejad, PhD, MPH, an assistant professor, and Nariman Ammar, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow, both at the Center for Biomedical Informatics in the Department of Pediatrics at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center, was recently published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research - Medical Informatics. The paper discussed how an artificial intelligence system developed by the researchers was used to diagnose and treat children and adults who suffer from Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs).
Their research study was named among the Top Milestones on Explainable AI In 2020.
Adverse ...
2021-01-06
A new SFU-led study finds that less than half of media stories in early 2020 featuring COVID-19 "preprint" research--research that has not yet been peer-reviewed--accurately framed the studies as being preprints or unverified research.
SFU PhD student Alice Fleerackers, a researcher in the Scholarly Communications Lab, and publishing program professor Juan Pablo Alperin collaborated with an international team of researchers to analyze more than 500 mentions in over 450 stories from digital news outlets covering preprint COVID-19 research. The study was published this week in Health Communication.
Their analysis ...
2021-01-06
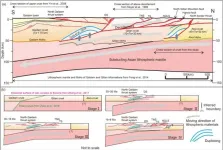
As the largest orogenic plateau on earth, the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau was caused by a complex crustal deformation process during the continuous collision and compression process between the Indian and Eurasian continents starting at least 60-50 Ma ago. The formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau records the collision of the two continents and the deformation process and mechanism within the continents. Therefore, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is considered as a natural ideal laboratory for the study of continent-continent collision and dynamics. At present, the continuous collision between Eurasia and Indian continents is still ongoing, ...
2021-01-06
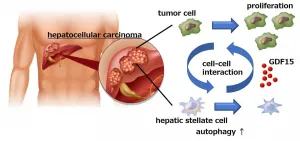
Osaka, Japan - Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), frequently seen in patients with liver cirrhosis caused by alcohol abuse or chronic viral hepatitis, is the most common form of liver cancer worldwide. As such, it is the third-most common cause of cancer-related death and has a notoriously poor prognosis. At present, surgery is the most effective treatment for HCC, but is only successful in the 10%-20% of cases where cancer cells have not spread beyond the liver.
Given the lack of treatment options for HCC, a group of researchers led by Osaka University decided to focus on specific cells and processes that occur in the area around liver tumors in the hope of finding a novel target for drug development.
The results of their study were published in a recent issue of Gastroenterology.
"Hepatic ...
2021-01-06
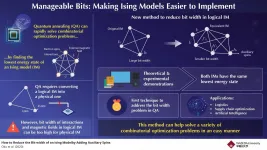
Given a list of cities and the distances between each pair of cities, how do you determine the shortest route that visits each city exactly once and returns to the starting location? This famous problem is called the "traveling salesman problem" and is an example of a combinatorial optimization problem. Solving these problems using conventional computers can be very time-consuming, and special devices called "quantum annealers" have been created for this purpose.
Quantum annealers are designed to find the lowest energy state (or "ground state") of what's known as an "Ising model." Such models are abstract representations of a quantum mechanical system involving interacting spins that are also influenced by external magnetic ...
2021-01-06
The world has experienced dramatic urbanization in recent decades. According to the latest report from the United Nations (UN), the global population in 2018 was 7.6 billion and the urban population was 4.2 billion. By 2050, the global population is expected to soar to 9.7 billion, with 68% of the population living in urban areas. (Note 1)
In the first-ever study on the characteristics of urbanization in large cities around the world, researchers at the Department of Civil Engineering of the University of Hong Kong (HKU) analyzed cities' urban built-up areas (BUAs) expansion, population growth and greening BUA changes, and revealed a hugely uneven ...
2021-01-06
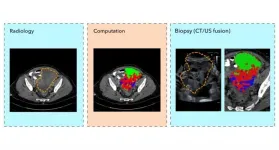
A new advanced computing technique using routine medical scans to enable doctors to take fewer, more accurate tumour biopsies, has been developed by cancer researchers at the University of Cambridge.
This is an important step towards precision tissue sampling for cancer patients to help select the best treatment. In future the technique could even replace clinical biopsies with 'virtual biopsies', sparing patients invasive procedures.
The research published in European Radiology shows that combining computed tomography (CT) scans with ultrasound images creates a visual guide for doctors to ensure they sample the full complexity of ...
2021-01-06
In the future, the Antarctic could become a greener place and be colonised by new species. At the same time, some species will likely disappear. 25 researchers recently presented these and many other findings in a major international project, in which they analysed hundreds of articles on the Antarctic published in the past ten years. By doing so, the team have provided an exceptionally comprehensive assessment of the status quo and future of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean that surrounds it.
Never before have researchers arrived at so many new findings on the biological and biochemical processes at work in the Antarctic than in the past ten years. Now 25 experts, led by the Alfred Wegener Institute Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI), have analysed and compiled these ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Link between dietary fiber and depression partially explained by gut-brain interactions
New study suggests that higher daily dietary fiber intake is linked to lower risk for depression in premenopausal women