(Press-News.org) A new class of protein material that interacts with living cells without being absorbed by them can influence cell signaling, a new study shows. The material does this by binding and sequestering cell surface receptors.
The discovery could have far-reaching implications for stem cell research and enable the development of new materials designed to modulate the behavior of living systems.
The research, reported in the January 6 edition of Nature, was led by the Baker lab at the University of Washington School of Medicine and the Derivery lab at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge, U.K. Their paper is titled, Design of Biologically Active Binary Protein 2D Materials.
Cells interact with their environment via receptors at their surface. These receptors can bind to hormones, neurotransmitters, drugs, and toxins. When such molecules bind to a receptor, this triggers a response inside the cell, a process known as signaling.
But for the cell, it is important that this response be transient, to still be responsive to the signal later on. To achieve this, cells will commonly terminate signaling by absorbing both an activated receptor and the molecule that stimulated it, thereby targeting both for destruction inside the cell.
"This tendency of cells to internalize receptors likely lowers the efficiency of immunotherapies," said Emmanuel Derivery, assistant professor at the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology. "Indeed, when antibody drugs bind their target receptors and then become internalized and degraded, more antibody must always be injected."
To create a way around this, Baker lab postdoctoral scholar Ariel Ben-Sasson designed new proteins that assemble into large, flat patches. This molecular scaffolding was then further engineered to contain signaling molecules.
Graduate student Joseph Watson of the Derivery lab showed that such protein materials could latch onto cells, activate surface receptors, and resist being absorbed by the cell for hours or even days.
"This work paves the way towards a synthetic cell biology, where a new generation of multi-protein materials can be designed to control the complex behavior of cells," said David Baker, professor of biochemistry at the UW School of Medicine and director of the UW Medicine Institute for Protein Design.
By swapping out which cell surface receptors were targeted by the patch, the researchers showed that different cell types could be activated.
"We now have a tool that can interact with any type of cells in a very specific way," said Ben-Sasson. "This is what is exciting about protein engineering: it opens fields that people may not expect."
According to co-author Hannele Ruohola-Baker, professor of biochemistry at the UW School of Medicine and associate director of the UW Medicine Institute for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine, versions of these new materials could eventually help physicians alleviate the dangers of sepsis by controlling the inflammatory response to infection.
They might even enable entirely new ways to treat COVID-19, heart disease, and diabetes, and perhaps mitigate the downstream effects of strokes, including Alzheimer's disease.
"This breakthrough helps pave the way for the use of synthetic cell biology in regenerative medicine," said Ruohola-Baker.
INFORMATION:
This news release was written by Ian Haydon of the UW Medicine Institute for Protein Design.
Full END
The westerlies--or westerly winds--play an important role in weather and climate both locally and on a global scale, by influencing precipitation patterns, impacting ocean circulation and steering tropical cyclones. So, finding a way to assess how they will change as the climate warms is crucial.
Typically, the westerlies blow from west to east across the planet's middle latitudes. But scientists have noticed that over the last several decades, these winds are changing, migrating poleward. Research suggests this is because of climate change. But, scientists have been debating whether the poleward movement of ...
What The Study Did: The findings of this survey study suggest that simply providing maps with COVID-19 case information wasn't necessarily associated with improved public knowledge, risk perception or reported intent to adhere to health guidelines.
Authors: Angela Fagerlin, Ph.D., of the University of Utah in Salt Lake City, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33538)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional ...
What The Study Did: Changes in out-of-hospital cardiac arrests and fatalities in the Detroit area during the COVID-19 pandemic are compared with year-earlier events for the same period in this observational study.
Authors: Adrienne V. Nickles, M.P.H., of the Michigan Department of Health and Human Services in Lansing, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32331)
Editor's Note: The article includes conflict of interest disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Writing, driving a screw or throwing darts are only some of the activities that demand a high level of skill. How the brain masters such exquisite movements has now been described in the journal "Nature" by a team of researchers at the University of Basel and the Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research. A map of brainstem circuits reveals which neurons control the fine motor skills of the arm and hand.
Picking up a pen and writing our name or reaching for a fork to eat spaghetti with tomato sauce are things we take for granted. However, holding a pen properly or bringing spaghetti to the mouth without making a mess requires precise ...
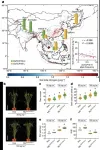
Chinese scientists from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have found a gene that plays an important role in helping rice adapt to low soil nitrogen.
Nitrogen fertilizer application is a strategic challenge for sustainable agriculture: On the one hand, it plays an indispensable role in increasing crop yields, thus ensuring global food security. On the other hand, it creates a severe threat to ecosystems. For this reason, breeding new crop varieties with high nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) is a high priority for both agricultural production and environmental protection.
Using a diversified rice population derived from different ecogeographical regions, the scientists carefully evaluated how various agronomic traits responded to ...
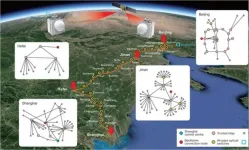
Chinese scientists have established the world's first integrated quantum communication network, combining over 700 optical fibers on the ground with two ground-to-satellite links to achieve quantum key distribution over a total distance of 4,600 kilometers for users across the country. The team, led by Jianwei Pan, Yuao Chen, Chengzhi Peng from the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, reported in Nature their latest advances towards the global, practical application of such a network for future communications.
Unlike conventional encryption, quantum communication is considered ...
SYRACUSE, N.Y. - There's no doubt the Earth's temperatures are going up. According to a December report by the World Meteorological Organization, 2020 is on track to be one of the three hottest years on record, already within the warmest decade to date. During the year's hottest months, many people rely on electricity-generated cooling systems to remain comfortable. But the power plants that keep air conditioners pushing out cold air could soon be in a vicious cycle in a warming world-not able to keep up with growing demands on hotter days and driving up greenhouse gas emissions ...
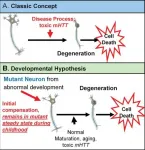
Amsterdam, NL, January 6, 2021 - There is growing evidence to support the hypothesis that there is a neurodevelopmental component to the late-onset neurodegeneration occurring in the brain of huntingtin gene (HTT gene) mutation carriers, and that this increased susceptibility to brain cell death begins during childhood. Experts discuss the evidence that the HTT gene mutation affects brain and body growth based on a unique study of children at risk for HD, the Kids-HD study, in a review paper and accompanying research article published in the Journal of Huntington's Disease.
The classic concept is that Huntington's disease is caused by toxic mutant huntingtin (mHTT) acting over time on mature brain cells. However, there is growing evidence for an alternative ...
Engineers at the University of Maryland (UMD) have created a new shape-changing or "morphing" 3D printing nozzle that was featured as a Frontispiece in the January 5th issue of the journal Advanced Materials Technologies.
The team's morphing nozzle offers researchers new means for 3D printing "fiber-filled composites" - materials made up of short fibers that boost special properties over traditional 3D-printed parts, such as enhancing part strength or electrical conductivity. The challenge is that these properties are based on the directions or "orientations" of the short fibers, which has been difficult to control during the 3D printing process, until now.
"When 3D printing with the morphing nozzle, the power lies on ...
A survey of approximately 5,000 Americans suggests that 31.1 percent of the U.S. public does not intend to get the COVID-19 vaccine once it becomes available to them - and the likelihood of vaccine refusal is highest among Black Americans, women and conservatives.
Timothy Callaghan, assistant professor at the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, led the study with the aim of better understanding the intentions of the American public regarding vaccines. The results were recently published in Social Science and Medicine.
According to the study, survey respondents answered a series of questions about their behaviors and attitudes about COVID-19, including why or why not they intend to pursue vaccination. Women are 71 percent ...