(Press-News.org) A new computational analysis suggests that a vaccine or medication that could shorten the infectious period of COVID-19 may potentially prevent millions of cases and save billions of dollars. The study was led by Bruce Lee along with colleagues in the Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research (PHICOR) team headquartered at the CUNY Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy and the Lundquist Research Institute at Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, and publishes in the open-access journal PLOS Computational Biology.
While much of the public conversation surrounding COVID-19 vaccines and medications has focused on preventing or curing the infection, the vaccines and medications that may emerge could have subtler effects. Those that can't necessarily prevent or cure may still reduce how long someone is contagious.
To clarify the potential value of shortening the infectious period, Lee and colleagues created a computational model that simulates the spread of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. They used the model to explore how a vaccine or medication that can reduce the contagious period might alleviate the clinical and economic impact of the disease.
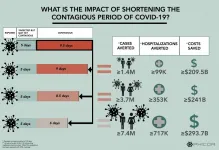
The simulations suggest that reducing the contagious period by half a day could avert up to 1.4 million cases and over 99,000 hospitalizations, saving $209.5 billion in direct medical and indirect costs--even if only a quarter of people with symptoms were treated--and incorporating conservative estimates of how contagious the virus may be. Under the same circumstances, cutting the contagious period by 3.5 days could avert up to 7.4 million cases. Expanding such treatment to 75 percent of everyone infected could avert 29.7 million cases and save $856 billion.
These findings could help guide research and investments into development of vaccines or medications that reduce the infectious period of SARS-CoV-2. They could also help government agencies plan rollout of such products and provide cost insights to guide reimbursement policies for third-party payers.
"There may be a tendency to overlook vaccines and other treatments that don't prevent a COVID-19 infection or cure disease," says Lee. "But this study showed that even relatively small changes in how long people are contagious can significantly affect the transmission and spread of the virus and thus save billions of dollars and avert millions of new cases."
"This study shows that vaccine and medication development efforts for COVID-19 should focus on the impact to actually help curb the spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, not just benefits of a single patient," says James McKinnell, a co-author of the study. "Widespread treatment, in combination with other prevention efforts, could prove to be the tipping point."
INFORMATION:
Peer-reviewed; Simulation / modeling
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Computational Biology:
https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008470
Citation: Lee BY, Bartsch SM, Ferguson MC, Wedlock PT, O'Shea KJ, Siegmund SS, et al. (2020) The value of decreasing the duration of the infectious period of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. PLoS Comput Biol 16(12): e1008470.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008470
Funding: This work was supported in part by City University of New York (CUNY) Graduate School of Public Health and Health Policy (BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC), the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) as part of the Models of Infectious Disease Agent Study (MIDAS) network under grant 1 R01 GM127512-01A1 (BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC). It was also supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) via grant R01HS023317 (BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC), United States Agency for International Development (USAID) under agreement number AID-OAA-A-15-00064 (BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC), and the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) via grant U01HD086861(BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC), and 5R01HD086013-02(BYL, SMB, MCF, PTW, KJO, SSS, SNC). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. The authors of this manuscript are responsible for its content, including data analysis. Statements in the manuscript do not necessarily represent the official views of, or imply endorsement by, National Institute of Health, AHRQ or HHS.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
The fatal threat from diarrhoea and pneumonia to young children in the world's poorer countries can be drastically reduced by using traditional performing arts to encourage mothers to provide youngsters with safe food and water, a new study reveals.
The Gambia, like many other Low- and Middle-income Countries (LMICs) faces high rates of under-five deaths due to diarrhoea and pneumonia - the two highest causes of death in this age group in this country and globally.
Children transitioning from breastfeeding to eating food are at most risk, as complementary food becomes contaminated. Researchers working in The Gambia discovered that mothers' food safety and hygiene behaviours were massively improved by a low-cost behaviour change community ...
ANN ARBOR--A team of researchers has discovered an antibody that blocks the ability of the dengue virus to cause disease in mice. The findings open the potential for developing effective treatments and designing a vaccine for dengue and similar diseases.
Dengue virus, a member of a group of viruses called flaviviruses, causes 50 to 100 million cases of dengue disease each year, with no effective treatment or vaccine. Other members of this group include the viruses that cause Zika, yellow fever and West Nile fever.
In a new study scheduled to publish Jan. 8 in the journal Science, researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, and the University of Michigan revealed how an antibody called 2B7 neutralizes one specific protein made ...
Christina Krienke and colleagues have designed an mRNA vaccine that delayed the onset of and reduced the severity of multiple sclerosis-like disease in mice. The vaccine restores the body's tolerance to its own proteins, suppressing the characteristic immune overreactivity of the disease. The vaccine developed by Krienke et al. works in a targeted fashion to promote tolerance to specific disease-related proteins, an improvement over other approaches to treating the disease that induce systemic immune suppression that can leave an individual vulnerable to other ...
Policymakers around the world tend to reference new and highly cited COVID-19 research papers in their policy documents regarding the pandemic, Yian Yin and colleagues conclude after analyzing publications of both types from the first half of 2020. "Overall, this result shows that the coronavirus research used by policymakers aligns with what scientists heavily engage themselves," they write in a Policy Forum. Although government agencies produced more COVID-19 documents compared to think tanks and intergovernmental organizations such as the World Health Organization, Yin et al. found that governmental agencies are the least likely to cite science. Organizations like WHO are the most likely institutions to cite science, they write, suggesting that these organizations can act ...
Social contact can transfer the feeling of pain or fear in several animal species, including humans, but the exact neural mechanisms for this transmission are still being studied. Now, Monique Smith and colleagues demonstrate that the social transmission of pain and pain relief in mice is mediated by neural projections from the brain's anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) to the nucleus accumbens. The transfer of fear, however, is mediated by the ACC's projections into a different area of the brain called the basolateral amygdala. The findings help untangle the distinct neural circuits involved ...
Richard Tyser and colleagues have mapped the origins of the embryonic mouse heart at single-cell resolution, helping to define the cell types that make up the heart in the earliest days of development. Their techniques allowed them to identify for a first time a pool of progenitor cells that contributes to the formation of heart muscle cells as well as the early epicardium, the outermost layer of the heart. This layer provides cells and other proteins that guide the development and repair of heart tissue, so a better understanding of its origins could better inform regenerative heart therapies as well as improve ...
New treatments to cut the global death rate from dengue, Zika and West Nile viruses could result from research led by The University of Queensland.
Associate Professor Daniel Watterson from UQ's School of Chemistry and Molecular Biosciences said the team identified an antibody that improved survival rates in laboratory trials and reduced the presence of virus in the blood.
"We made a discovery in 2015 in the wake of the Zika outbreak that identified a new target for flavivirus treatments, a viral protein called NS1," Dr Watterson said.
"Now we've shown for the first time that a single NS1 antibody can be protective against multiple flaviviruses including dengue, Zika and West Nile.
"No other antibody reported has shown such a broad range of protection.
"The improved ...
One essential component of each eukaryotic cell is the cytoskeleton. Microtubules, tiny tubes consisting of a protein called tubulin, are part of this skeleton of cells. Cilia and flagella, which are antenna-like structures that protrude from most of the cells in our body, contain many microtubules. An example of flagell is the sperm tail, which is essential for male fertility and thus for sexual reproduction. The flagellum has to beat in a very precise and coordinated manner to allow progressive swimming of the sperm. Failure to do so can lead to male infertility. Researchers at the Institut Curie in Paris, the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology ...
Boulder, Colo., USA: The Yellowstone hotspot is well known for generating supereruptions in the geologic past that are far more explosive than historic examples. The origin and sustained longevity of the hotspot is less understood but is focused on two competing models, where the ascent of hot mantle is derived from either a deep-seated mantle plume or a shallow mantle source.
In their study published this month in GSA Today, Vic Camp and Ray Wells use an integrated database that supports the idea of a deep mantle-plume origin for the Yellowstone hotspot with a robust history of magmatism that extends to at least 56 million years ago, far older than previously thought. In this scenario, hotspot ...
Large perennial grasses like miscanthus are a primary target for use as bioenergy crops because of their sustainability advantages, but they take several years to establish and aren't ideal for crop rotation. Maize and other annual crops are easier to manage with traditional farming but are tougher on the environment.
Energy sorghum, a hefty annual plant with the ecological benefits of a perennial, may combine the best of both crops.
A study by researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Center for Advanced Bioenergy and Bioproducts Innovation (CABBI) found that energy sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) behaves more like miscanthus in the way it efficiently captures light and uses water to produce abundant biomass. ...