INFORMATION:
Additional authors of the study are Chase J. Boyer and Andrea C. Buhler-Wassmann, doctoral student researchers, and Blake J. Shaw, master's degree student researcher.
The full study is available here:
https://psycnet.apa.org/fulltext/2021-03003-001.html
Latina mothers, often essential workers, report COVID-19 took toll
UC Davis researchers found stimulus didn't relieve burdens
2021-01-08
(Press-News.org) More than half of Latina mothers surveyed in Yolo and Sacramento counties reported making economic cutbacks in response to the pandemic shutdown last spring -- saying they bought less food and missed rent payments. Even for mothers who reported receiving the federal stimulus payment during this time, these hardships were not reduced, University of California, Davis, researchers found in a recent study.
"Latino families are fighting the pandemic on multiple fronts, as systemic oppression has increased their likelihood of contracting the virus, having complications from the virus and having significant economic hardship due to the virus," said Leah C. Hibel, associate professor of human development and family studies at UC Davis and lead author of the study. "These factors are likely to have a significant psychological toll on these families."
The study was published Jan. 7 in the journal Traumatology. Researchers administered surveys to 70 Latina mothers March 18 through June 5 of last spring, after the "shelter-in-place" orders went into effect in California in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The survey sample consisted of Latina mothers, all of whom are low-income, with 92 percent of the families having an essential worker (either the mother or her partner), in Yolo and Sacramento counties, researchers said. The survey respondents were identified through an earlier UC Davis study on Mexican-origin families living in the region. Yolo and Sacramento counties are in Northern California, which has a higher cost of living than most of the country, but has a relatively high level of social services available, researchers added.
Researchers said that although it has been reported that the stimulus checks may have kept some from falling below the poverty level, cutbacks due to other economic factors still had an effect on these low-income families.
"In other words, though the stimulus may have prevented some families from falling below the poverty line, our analyses suggest that many low-income families are still facing significant financial hardship," researchers said in the study. "This hardship appears to be placing families on a trajectory toward hunger and eviction."
Less food, higher stress
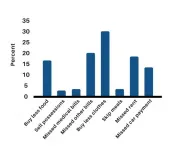
Mothers who engaged in cutbacks reported significantly higher levels of stress, depression, and anxiety. Further, receiving the federal stimulus money administered to those whose income was less than $99,000 a year (through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act) was not associated with lower cutbacks, stress, depression or anxiety. Of those surveyed, 65 percent had reported receiving their checks by the time the survey was administered.
Mothers' depressive symptoms were assessed through survey questions administered by phone. Most were in English, but in some cases, questions were asked in Spanish by native-speaking interviewers. Assessed on a five-point answer scale, mothers were asked such questions as:
"How stressed are you because of the virus outbreak?"
"How often have you felt or experienced depressed mood?"
"How often have you felt panicky?"
Mothers were also asked to indicate whether or not they made any of 12 listed cutbacks (food, rent, cutting back on air conditioning, etc.) in previous weeks because of the pandemic. Of these mothers, 52 percent reported being forced to make economic cutbacks, and they reported higher stress, depressive symptoms and anxiety than those who reported not cutting back.
Researchers noted that the immediate economic impacts of the pandemic on low-income Latina mothers' well-being suggests that alleviating families' economic hardship might benefit mothers psychologically. Though the researchers did not find the stimulus payment to buffer the economic or psychological impacts, they suggest the stimulus money was simply not enough.
"Without additional local, state or federal aid, the pandemic is likely to cause severe hardship marked by homelessness, hunger and mental illness. Additional recurring monthly stimulus payments could be a lifeline for families who are struggling to make ends meet," the researchers wrote.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Novel RNA factors may help cancer cells thrive
2021-01-08
Like Peter Pan, some cells never grow up. In cancer, undifferentiated stem cells may help tumors such as glioblastoma become more aggressive than other forms of the disease. Certain groups of genes are supposed to help cells along the path to maturity, leaving their youthful "stemness" behind. This requires sweeping changes in the microRNAome -- the world of small non-coding material, known as microRNAs, that control where and when genes are turned on and off. Many microRNAs are tumor-suppressive; in cancer, the microRNAome is distorted and disrupted. Recent work by researchers at Brigham and Women's Hospital pinpoints critical changes in an enzyme known as DICER, which create a cascade of effects on this microRNAome. ...
Peter Raven addresses earth's dwindling resources, the value of science-informed outreach
2021-01-08
The BioScience Talks podcast features discussions of topical issues related to the biological sciences.
In a career-spanning installment of the journal BioScience's In Their Own Words oral history series, Missouri Botanical Garden President Emeritus Peter Raven illuminates numerous topics, sharing insights related to the sustainability of human civilization, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the importance of science in addressing the world's greatest challenges.
Raven, a recent coauthor of "A Call to Action: Marshaling Science for Society," highlights the importance of public outreach in overcoming deeply rooted societal problems. Among them, he argues that our present economic system "sees natural productivity like every other ...
Nanoparticle vaccine for COVID-19
2021-01-08
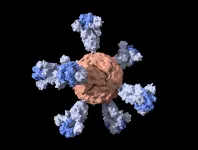
Before the pandemic, the lab of Stanford University biochemist Peter S. Kim focused on developing vaccines for HIV, Ebola and pandemic influenza. But, within days of closing their campus lab space as part of COVID-19 precautions, they turned their attention to a vaccine for SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. Although the coronavirus was outside the lab's specific area of expertise, they and their collaborators have managed to construct and test a promising vaccine candidate.
"Our goal is to make a single-shot vaccine that does not require a cold-chain for storage or transport. If we're successful at doing it ...
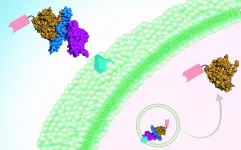
Botulism breakthrough? Taming botulinum toxin to deliver therapeutics
2021-01-08
While rare, botulism can cause paralysis and is potentially fatal. It is caused by nerve-damaging toxins produced by Clostridium botulinum -- the most potent toxins known. These toxins are often found in contaminated food (home canning being a major culprit). Infants can also develop botulism from ingesting C. botulinum spores in honey, soil, or dust; the bacterium then colonizes their intestines and produces the toxin.
Once paralysis develops, there is no way to reverse it, other than waiting for the toxins to wear off. People with serious cases of botulism may need to be maintained on ventilators for weeks or months. But a new treatment approach and delivery vehicle, ...
More than half of people using cannabis for pain experience multiple withdrawal symptoms
2021-01-08
More than half of people who use medical marijuana products to ease pain also experience clusters of multiple withdrawal symptoms when they're between uses, a new study finds.
And about 10% of the patients taking part in the study experienced worsening changes to their sleep, mood, mental state, energy and appetite over the next two years as they continued to use cannabis.
Many of them may not recognize that these symptoms come not from their underlying condition, but from their brain and body's reaction to the absence of substances in the cannabis products they're smoking, vaping, eating or applying to their skin, says the University of Michigan Addiction Center psychologist who led the study.
When someone ...
Tiny wireless device sheds light on combating obesity
2021-01-08
Gastric bypass surgery is sometimes the last resort for those who struggle with obesity or have serious health-related issues due to their weight. Since this procedure involves making a small stomach pouch and rerouting the digestive tract, it is very invasive and prolongs the recovery period for patients. In a new study, researchers at Texas A&M University have described a medical device that might help with weight loss and requires a simpler operative procedure for implantation.
Researchers said their centimeter-sized device provides the feeling of fullness by stimulating the endings of the vagus nerve with light. Unlike other devices that require a power cord, their device is wireless and can be controlled ...
Study reveals jellyfish create a 'virtual wall' to enhance performance
2021-01-08
TAMPA, Fla. (Jan. 8, 2021)- New research led by the University of South Florida has uncovered one of the reasons jellyfish have come to be known as the "world's most efficient swimmer." Brad Gemmell, associate professor of integrative biology, found jellyfish produce two vortex rings, which are donut-shaped bodies of fluid underneath their translucent bodies, that spin in opposite directions. They appear as jellyfish squeeze and reopen throughout each swim cycle, providing a "ground effect" force as if they were to be pushing off the seafloor.
The "ground effect" is most widely understood ...
Scientists from St. Petersburg University discovered the virus-like particles in Bryozoa
2021-01-08
Scientists from Russia, Austria, and the USA have discovered virus-like particles in the bacterial symbionts of Bryozoa - a phylum of colonial aquatic invertebrates - filter-feeders dominating in many bottom ecosystems. The research project was planned and supervised by scientists from St Petersburg University. Some of the virus-like particles resemble red blood cells, while others have a sea-urchin-like appearance. Although viruses have never been reported inside symbiotic bacteria in bryozoans, scientists suggest that this "matryoshka doll" may have a prominent effect on the bacterial ...
Measuring racial inequities in COVID-19 testing
2021-01-08
What The Study Did: This study adapted a well-established tool for measuring inequity from economics--the Lorenz curve--to measure racial inequities in COVID-19 testing.
Author: Aaloke Mody, M.D., of the Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32696)
Editor's Note: The article includes funding/support disclosures. Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
INFORMATION:
Media ...
Study: Religion, psychology share methods for reducing distress
2021-01-08
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. -- Religious people facing life crises rely on emotion-regulation strategies that psychologists also use, a new study finds. They look for positive ways of thinking about hardship, a practice known to psychologists as "cognitive reappraisal." They also tend to have confidence in their ability to cope with difficulty, a trait called "coping self-efficacy." Both have been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression.
The new findings are reported in the Journal of Religion and Health.
"It appears that religious people are making use of some of the same tools that psychologists have systematically identified as effective in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
Electric field tunes vibrations to ease heat transfer
[Press-News.org] Latina mothers, often essential workers, report COVID-19 took tollUC Davis researchers found stimulus didn't relieve burdens