(Press-News.org) COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care in the early months of the pandemic were subject to a significantly higher burden of delirium and coma than is typically found in patients with acute respiratory failure. Choice of sedative medications and curbs on family visitation played a role in increasing acute brain dysfunction for these patients.
That's according to an international study published Jan. 8 in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, led by researchers at Vanderbilt University Medical Center in coordination with researchers in Spain.
The study, which is far the largest of its kind to date, tracks the incidence of delirium and coma in 2,088 COVID-19 patients admitted before April 28, 2020, to 69 adult intensive care units across 14 countries.
ICU delirium is associated with higher medical costs and greater risk of death and long-term ICU-related dementia. Seminal studies at VUMC over the past two decades have spurred widespread interest in ICU delirium research, and the resulting body of evidence has come to inform critical care guidelines endorsed by medical societies in several countries. These guidelines include well calibrated pain management with prompt discontinuation of analgesics and sedatives, daily spontaneous awakening trials, daily spontaneous breathing trials, delirium assessments throughout the day, early mobility and exercise, and family engagement.
Some 82% of patients in this observational study were comatose for a median of 10 days, and 55% were delirious for a median of three days. Acute brain dysfunction (coma or delirium) lasted for a median of 12 days.
"This is double what is seen in non-COVID ICU patients," said VUMC's Brenda Pun, DNP, RN, co-first author on the study with Rafael Badenes MD, PhD, of the University of Valencia in Spain. The authors cite a previous large, multi-site ICU study, also led by VUMC, where acute brain dysfunction lasted a median of five days, including four days of coma and one day of delirium.
The authors note that COVID-19 disease processes could predispose patient to a higher burden of acute brain dysfunction. But they also note that a number of patient care factors, some of which are related to pressures posed on health care by the pandemic, also appear to have played a significant role.
The study appears to show a reversion to outmoded critical care practices, including deep sedation, widespread use of benzodiazepine infusions (benzodiazepine is a nervous system depressant), immobilization, and isolation from families. The authors find that, where COVID-19 is concerned, there has been an apparent widespread abandonment of newer clinical protocols that are proven to help ward off the acute brain dysfunction that stalks many critically ill patients.
"It is clear in our findings that many ICUs reverted to sedation practices that are not in line with best practice guidelines," Pun said, "and we're left to speculate on the causes. Many of the hospitals in our sample reported shortages of ICU providers informed about best practices.
There were concerns about sedative shortages, and early reports of COVID-19 suggested that the lung dysfunction seen required unique management techniques including deep sedation. In the process, key preventive measures against acute brain dysfunction went somewhat by the boards."
Using electronic health records, investigators were able to closely examine patient characteristics, care practices and findings from clinical assessments. Some 88% of patients tracked in the study were invasively mechanical ventilated at some point during hospitalization, 67% on the day of ICU admission. Patients receiving benzodiazepine sedative infusions were at 59% higher risk of developing delirium. Patients who received family visitation (in-person or virtual) were at 30% lower risk of delirium.
"There's no reason to think that, since the close of our study, the situation for these patients has changed," said one of the study's senior authors, Pratik Pandharipande, MD, MSCI, professor of Anesthesiology.
"These prolonged periods of acute brain dysfunction are largely avoidable. Our study sounds an alarm: as we enter the second and third waves of COVID-19, ICU teams need above all to return to lighter levels of sedation for these patients, frequent awakening and breathing trials, mobilization and safe in-person or virtual visitation."
INFORMATION:
Pandharipande is co-director, with the study's other senior author, Wesley Ely, MD, MPH, of the Critical Illness, Brain Dysfunction, and Survivorship Center. Pun is director of data quality with the center. Other VUMC investigators on the study include Onur Orun, MS, Wencong Chen, PhD, Rameela Raman, PhD, Beata-Gabriela Simpson, MPH, Stephanie Wilson-Linville, BSN, Nathan Brummel, MD, and Timothy Girard, MD.
Hundreds of cancer patients have benefitted from using computer algorithms to manage their symptoms and improve their wellbeing in a unique UK trial.
The early stage colorectal, breast or gynecological cancer patients took part in the trial of the eRAPID system, developed by the University of Leeds, which allowed them to report online symptoms from home and receive instant advice on whether to self-manage or seek medical attention.
Patients reported better symptom control and physical wellbeing in the early weeks of treatment, with the system preventing symptom deterioration in about 9% of patients after 12 weeks. Patients reported more confidence in managing ...
A year ago, trying to find patients who would agree to see their University of Michigan mental health provider through a video screen felt like pulling teeth.
Only 26 video visits with a few early-adopters had happened in nearly six months, compared with more than 30,000 in-person visits.
But Jennifer Severe, M.D., one of the three psychiatrists who helped launch a test of telehealth initiatives in the U-M's outpatient psychiatry clinic, wasn't about to give up.
She prepared to give a talk at the beginning of April of 2020, hoping to convince more of her colleagues to give telepsychiatry a try, now that a major insurance ...
Eating a healthy diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, has a positive impact on health, but little is known about the effects of including unhealthy foods in an otherwise healthy diet. Now researchers at Rush University Medical Center have reported diminished benefits of a Mediterranean diet among those with high frequency of eating unhealthy foods. The results of their study were published in Alzheimer's & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer's Association on Jan. 7.
"Eating a diet that emphasizes vegetables, fruit, fish and whole grains may positively affects a person's health," said Puja Agarwal, PhD, a nutritional epidemiologist and assistant professor in the Department of Internal Medicine at Rush Medical College. "But when it is combined with fried food, ...
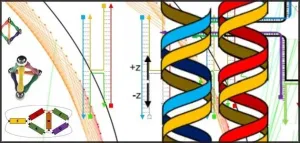
In a technique known as DNA origami, researchers fold long strands of DNA over and over again to construct a variety of tiny 3D structures, including miniature biosensors and drug-delivery containers. Pioneered at the California Institute of Technology in 2006, DNA origami has attracted hundreds of new researchers over the past decade, eager to build receptacles and sensors that could detect and treat disease in the human body, assess the environmental impact of pollutants, and assist in a host of other biological applications.
Although the principles of DNA origami are straightforward, the technique's tools and methods for designing new structures are not always easy to grasp and have not been well documented. In addition, scientists new to the method have had no single reference they ...
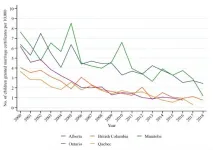
Canada is at the forefront of global efforts to end child marriage abroad. Yet this practice remains legal and persists across the country. In Canada, more than 3,600 marriage certificates were issued to children, usually girls, under the age of 18 between 2000 and 2018, according to a new study from researchers at McGill University. In recent years, an increasing number of child marriages have been common-law unions.
Child marriage, defined as formal or informal (common-law) marriage before the age of 18, is a globally-recognized indicator of gender inequality because the negative consequences for ...
BOSTON - Patients with tuberous sclerosis complex, a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of noncancerous tumors in multiple organs of the body, have limited treatment options. A team led by investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) has now shown that gene therapy can effectively treat mice that express one of the mutated genes that cause the disease. The research is published in Science Advances.
The gene, called TSC2, codes for tuberin, a protein that acts to inhibit cell growth and proliferation. When mutations occur in TSC2, resulting in a lack of tuberin in cells, the cells enlarge ...
ORLANDO, Jan. 8, 2021 - Florida's threatened coral reefs have a more than $4 billion annual economic impact on the state's economy, and University of Central Florida researchers are zeroing in on one factor that could be limiting their survival - coral skeleton strength.
In a new study published in the journal Coral Reefs, UCF engineering researchers tested how well staghorn coral skeletons withstand the forces of nature and humans, such as impacts from hurricanes and divers.
The researchers subjected coral skeletons to higher stresses than those caused by ocean waves, says Mahmoud Omer, a doctoral student in UCF's Department ...
A research team at the University of Basel has discovered immune cells resident in the lungs that persist long after a bout of flu. Experiments with mice have shown that these helper cells improve the immune response to reinfection by a different strain of the flu virus. The discovery could yield approaches to developing longer-lasting vaccinations against quickly-mutating viruses.
At the start of the coronavirus pandemic, some already began to raise the question of how long immunity lasts after weathering SARS-CoV-2. The same question has now arisen regarding the COVID-19 vaccination. A key role is played by immunological memory - a complex interplay of immune cells, antibodies and signaling ...
Humans have them, so do other animals and plants. Now research reveals that bacteria too have internal clocks that align with the 24-hour cycle of life on Earth.
The research answers a long-standing biological question and could have implications for the timing of drug delivery, biotechnology, and how we develop timely solutions for crop protection.
Biological clocks or circadian rhythms are exquisite internal timing mechanisms that are widespread across nature enabling living organisms to cope with the major changes that occur from day to night, even across seasons.
Existing inside cells, these molecular rhythms use external cues such as daylight and temperature to synchronise ...
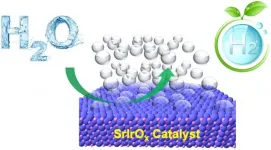
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Efficiently mass-producing hydrogen from water is closer to becoming a reality thanks to Oregon State University College of Engineering researchers and collaborators at Cornell University and the Argonne National Laboratory.
The scientists used advanced experimental tools to forge a clearer understanding of an electrochemical catalytic process that's cleaner and more sustainable than deriving hydrogen from natural gas.
Findings were published today in Science Advances.
Hydrogen is found in a wide range of compounds on Earth, most commonly combining with oxygen to make water, and it has many scientific, industrial and energy-related roles. It also occurs in the form of hydrocarbons, compounds consisting of hydrogen and carbon such ...