INFORMATION:
Article reference: Caiwen Li, Meng Li and Qian Huang, The parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium infects marine crustaceans, Marine Life Science & Technology, 2020, ISSN 2662-1746, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00061-z
Keywords: Parasitic dinoflagellate, Diversity, Life cycle, Pathogenesis, Outbreak mechanism, Ecological control
Marine Life Science & Technology (MLST) provides a platform that introduces new discoveries and theories associated with marine organisms, bioresources, and biotechnology. The journal is intended for marine scientists, biological oceanographers, conservation biologists, marine technologists, policy makers and legislators. Accordingly, we publish original research papers across a broad range of marine life sciences and technologies with an emphasis on synergistic interactions of multiple disciplines. Both theoretical and practical papers are welcome, including laboratory and field experimental studies relevant to marine life science and technology. Focused reviews, viewpoints, comments, and short communications are also accepted. As the journal's aim is to foster multidisciplinary approaches to marine sciences, authors are encouraged to emphasise the relevance of their work in relation across the journals key-disciplines.
For more information, please visit https://www.springer.com/journal/42995/
Editorial Board: https://www.springer.com/journal/42995/editors
MLST is available on SpringerLink (https://link.springer.com/journal/42995/volumes-and-issues).
Submissions to MLST may be made using ScholarOne ManuscriptsTM (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/mlst).
Abstracted and indexed in:
Astrophysics Data System (ADS)
CNKI
Dimensions
EBSCO Discovery Service
Google Scholar
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China
Meta
Naver
OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
ProQuest-ExLibris Primo
ProQuest-ExLibris Summon
TD Net Discovery Service
ISSN 2662-1746
The parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium infects marine crustaceans
2021-01-11
(Press-News.org) Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this review article the authors Caiwen Li, Meng Li and Qian Huang from Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, China consider the impact of the parasitic dinoflagellate Hematodinium on aquaculture of marine crustaceans in China.
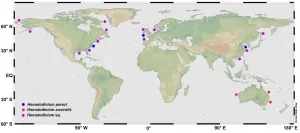
Hematodinium is a type of parasitic dinoflagellate that infects marine crustaceans globally. The parasite lives mainly in the hemolymph or hemocoels of affected hosts, and results in mortalities due to malfunction or loss of functions of major organs.
In recent years, the parasite has developed into an emerging epidemic pathogen not only affecting wild populations of economically valuable marine crustaceans in western countries but also the sustainable yield of aquaculture of major crabs in China. Epidemics of the parasitic disease have expanded recently in the coastal waters of China causing frequent outbreaks in aquaculture of major crab species, especially Portunus trituberculatus and Scylla paramamosain. The pathogen also infected two species of co-cultured shrimps and multiple cohabitating wild crabs, suggesting it is a significant threat to the sustainable culture of commercially valuable marine crustaceans. The polyculture system that is widely used along the coast of China may facilitate the spread and transmission of the pathogen.
To provide a better understanding of the biological and ecological characteristics of the parasitic dinoflagellate and highlight important directions for future research, the authors of this article review the current knowledge on the taxonomy, life cycle, pathogenesis, transmission and epidemiology of Hematodinium spp. proposing ecological countermeasures for the prevention and control of this emerging infectious disease.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NUS researchers concoct probiotic coffee and tea drinks
2021-01-11
Good news for those who need a cuppa to start the day. Researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) have created new probiotic coffee and tea drinks that are packed with gut-friendly live probiotics.
Supervised by Associate Professor Liu Shao Quan from the Department of Food Science and Technology at the NUS Faculty of Science, the two doctoral students who worked on these two new beverages assert that their drinks have a great taste, and can be stored chilled or at room temperature for more than 14 weeks without compromising on their probiotic viability.
Traditional probiotic carriers like yoghurts and cultured milks are dairy-based products. The rise in veganism, along with common health issues like lactose intolerance, high ...
Liquid metal ink liberates form
2021-01-11
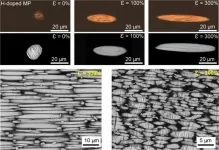
Today's electronic devices strive for new form factors - to make them foldable, stretchable, and deformable. To produce such devices that are highly stretchable or deformable, it is necessary to develop electrodes and circuit lines whose electrical properties can withstand harsh deformation or mechanical damage. To this, POSTECH-Yonsei University joint research team has recently developed liquid metal ink to accelerate printed electronic devices that can be changed into any shape.
Professor Unyong Jeong and Dr. Selvaraj Veerapandian of POSTECH's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, with Professor Aloysius Soon and Dr. Woosun Jang of Yonsei University's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, have developed liquid metal microparticles ...
Physician-pharmacist collaboration may increase adherence to opioid addiction treatment
2021-01-11
NIH-supported pilot study found team-based approach may improve buprenorphine care.
WHAT:
A collaborative approach to treating opioid use disorder that relies heavily on community pharmacists is feasible and may increase adherence and participant satisfaction, according to a pilot study published today in Addiction. The study was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), part of the National Institutes of Health, through the NIDA Center for the Clinical Trials Network.
Most people with opioid use disorder who would benefit from medication do not receive it. Buprenorphine is a safe and effective ...
Same difference: predicting divergent paths of genetically identical cells
2021-01-11
DALLAS - Jan. 11, 2021 - A set of biomarkers not traditionally associated with cell fate can accurately predict how genetically identical cells behave differently under stress, according to a UT Southwestern study. The findings, published by Cell Reports as a Dec. 1 cover story, could eventually lead to more predictable responses to pharmaceutical treatments.
Groups of the same types of cells exposed to the same stimuli often display different responses. Some of these responses have been linked to slight differences in genetics between individual cells. However, even genetically identical cells can diverge in ...
Impacts of climate change on our water and energy systems: it's complicated
2021-01-11
As the planet continues to warm, the twin challenges of diminishing water supply and growing energy demand are intensifying. But because water and energy are inextricably linked, as we try to adapt to one challenge - say, by getting more water via desalination or water recycling - we may be worsening the other challenge by choosing energy-intensive processes.
So, in adapting to the consequences of climate change, how can we be sure that we aren't making problems worse?
Now, researchers at the Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), UC Berkeley, and UC Santa Barbara have developed a science-based analytic framework to evaluate such complex connections between water and energy, and options for adaptations in response to an evolving ...
New nanostructured alloy for anode is a big step toward revolutionizing energy storage
2021-01-11
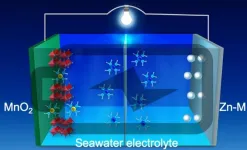
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers in the Oregon State University College of Engineering have developed a battery anode based on a new nanostructured alloy that could revolutionize the way energy storage devices are designed and manufactured.
The zinc- and manganese-based alloy further opens the door to replacing solvents commonly used in battery electrolytes with something much safer and inexpensive, as well as abundant: seawater.
Findings were published today in Nature Communications.
"The world's energy needs are increasing, but the development of next-generation electrochemical energy storage systems with high energy density and long cycling life ...
Biomarkers in fathers' sperm linked to offspring autism
2021-01-11
PULLMAN, Wash. - Biomarkers in human sperm have been identified that can indicate a propensity to father children with autism spectrum disorder. These biomarkers are epigenetic, meaning they involve changes to molecular factors that regulate genome activity such as gene expression independent of DNA sequence, and can be passed down to future generations.
In a study published in the journal Clinical Epigenetics on Jan. 7, researchers identified a set of genomic features, called DNA methylation regions, in sperm samples from men who were known to have autistic children. Then in a set of blind tests, the researchers were able to use the presence of these features to determine whether other men had fathered autistic children with 90% ...
Study shows meaningful lockdown activity is more satisfying than busyness
2021-01-11
New research shows people who pursue meaningful activities - things they enjoy doing - during lockdown feel more satisfied than those who simply keep themselves busy.
The study, published in PLOS ONE, shows you're better off doing what you love and adapting it to suit social distancing, like swapping your regular morning walk with friends for a zoom exercise session.
Simply increasing your level of activity by doing mindless busywork will leave you unsettled and unsatisfied.
Co-lead researcher Dr Lauren Saling from RMIT University in Melbourne, Australia said while novelty lockdown activities - like baking or painting - have their place, trying to continue what you enjoyed before lockdown can be more rewarding.
"Busyness might be distracting but it won't necessarily be fulfilling," ...
Latinx low-income workers hardest hit by SF COVID surge
2021-01-11
COVID-19 infections are once again rising at an alarming rate in San Francisco's Latinx community, predominantly among low-income essential workers, according to results of a massive community-based testing blitz conducted before and after the Thanksgiving holiday by Unidos En Salud -- a volunteer-led partnership between the Latino Task Force for COVID-19 (LTF), UC San Francisco , the Chan Zuckerberg Biohub (CZ Biohub), and the San Francisco Department of Public Health (SFDPH).
Unidos En Salud launched their "Healthy Holidays" initiative the weekend before Thanksgiving (Nov. 22-24) in San Francisco's Mission District, where they have been perfecting their community-based surveillance testing ...
Chloroplasts on the move
2021-01-11
The genetic material of plants, animals and humans is well protected in the nucleus of each cell and stores all the information that forms an organism. For example, information about the size or color of flowers, hair or fur is predefined here. In addition, cells contain small organelles that contain their own genetic material. These include chloroplasts in plants, which play a key role in photosynthesis, and mitochondria, which are found in all living organisms and represent the power plants of every cell. But is the genetic material actually permanently stored within one cell? No! As so far known, the genetic material can migrate from cell to cell and thus even be exchanged between different organisms. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology (MPI-MP) ...