(Press-News.org) Scientists have used a "galaxy-sized" space observatory to find possible hints of a unique signal from gravitational waves, or the powerful ripples that course through the universe and warp the fabric of space and time itself.
The new findings, which appeared recently in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, hail from a U.S. and Canadian project called the North American Nanohertz Observatory for Gravitational Waves (NANOGrav).
For over 13 years, NANOGrav researchers have pored over the light streaming from dozens of pulsars spread throughout the Milky Way Galaxy to try to detect a "gravitational wave background." That's what scientists call the steady flux of gravitational radiation that, according to theory, washes over Earth on a constant basis. The team hasn't yet pinpointed that target, but it's getting closer than ever before, said Joseph Simon, an astrophysicist at the University of Colorado Boulder and lead author of the new paper.
"We've found a strong signal in our dataset," said Simon, a postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences. "But we can't say yet that this is the gravitational wave background."
In 2017, scientists on an experiment called the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO) won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the first-ever direct detection of gravitational waves. Those waves were created when two black holes slammed into each other roughly 130 million lightyears from Earth, generating a cosmic shock that spread to our own solar system.
That event was the equivalent of a cymbal crash--a violent and short-lived blast. The gravitational waves that Simon and his colleagues are looking for, in contrast, are more like the steady hum of conversation at a crowded cocktail party.
Detecting that background noise would be a major scientific achievement, opening a new window to the workings of the universe, he added. These waves, for example, could give scientists new tools for studying how the supermassive black holes at the centers of many galaxies merge over time.
"These enticing first hints of a gravitational wave background suggest that supermassive black holes likely do merge and that we are bobbing in a sea of gravitational waves rippling from supermassive black hole mergers in galaxies across the universe," said Julie Comerford, an associate professor of astrophysical and planetary science at CU Boulder and NANOGrav team member.
Simon will present his team's results at a virtual press conference on Monday at the 237th meeting of the American Astronomical Society.
Galactic lighthouses
Through their work on NANOGrav, Simon and Comerford are part of a high stakes, albeit collaborative, international race to find the gravitational wave background. Their project joins two others out of Europe and Australia to make up a network called the International Pulsar Timing Array.
Simon said that, at least according to theory, merging galaxies and other cosmological events produce a steady churn of gravitational waves. They're humungous--a single wave, Simon said, can take years or even longer to pass Earth by. For that reason, no other existing experiments can detect them directly.
"Other observatories search for gravitational waves that are on the order of seconds," Simon said. "We're looking for waves that are on the order of years or decades."
He and his colleagues had to get creative. The NANOGrav team uses telescopes on the ground not to look for gravitational waves but to observe pulsars. These collapsed stars are the lighthouses of the galaxy. They spin at incredibly fast speeds, sending streams of radiation hurtling toward Earth in a blinking pattern that remains mostly unchanged over the eons.
Simon explained that gravitational waves alter the steady pattern of light coming from pulsars, tugging or squeezing the relative distances that these rays travel through space. Scientists, in other words, might be able to spot the gravitational wave background simply by monitoring pulsars for correlated changes in the timing of when they arrive at Earth.
"These pulsars are spinning about as fast as your kitchen blender," he said. "And we're looking at deviations in their timing of just a few hundred nanoseconds."
Something there
To find that subtle signal, the NANOGrav team strives to observe as many pulsars as possible for as long as possible. To date, the group has observed 45 pulsars for at least three years and, in some cases, for well over a decade.
The hard work seems to be paying off. In their latest study, Simon and his colleagues report that they've detected a distinct signal in their data: Some common process seems to be affecting the light coming from many of the pulsars.
"We walked through each of the pulsars one by one. I think we were all expecting to find a few that were the screwy ones throwing off our data," Simon said. "But then we got through them all, and we said, 'Oh my God, there's actually something here.'"
The researchers still can't say for sure what's causing that signal. They'll need to add more pulsars to their dataset and observe them for longer periods to determine if it's actually the gravitational wave background at work.
"Being able to detect the gravitational wave background will be a huge step but that's really only step one," he said. "Step two is pinpointing what causes those waves and discovering what they can tell us about the universe."
INFORMATION:
NANOGrav is a U.S. National Science Foundation Physics Frontiers Center. It is co-directed by Maura McLaughlin of West Virginia University and Xavier Siemens of Oregon State University.
Nothing in biology is static. Biological processes fluctuate over time, and if we are to put together an accurate picture of cells, tissues, organs etc., we have to take into account their temporal patterns. In fact, this effort has given rise to an entire field of study known as "chronobiology".
The liver is a prime example. Everything we eat or drink is eventually processed there to separate nutrients from waste and regulate the body's metabolic balance. In fact, the liver as a whole is extensively time-regulated, and this pattern is orchestrated by the so-called ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. - Michigan State University is leading a global research effort to offer the first worldwide view of how climate change could affect water availability and drought severity in the decades to come.
By the late 21st century, global land area and population facing extreme droughts could more than double -- increasing from 3% during 1976-2005 to 7%-8%, according to Yadu Pokhrel, associate professor of civil and environmental engineering in MSU's College of Engineering, and lead author of the research published in Nature Climate Change.
"More and more people will suffer from extreme droughts if a medium-to-high level of global warming ...
Researchers at Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health developed an infectious disease early warning system that includes areas lacking health clinics participating in infectious disease surveillance. The approach compensates for existing gaps by optimally assigning surveillance sites that support better observation and prediction of the spread of an outbreak, including to areas remaining without surveillance. Details are published in the journal Nature Communications.
The research team, including Jeffrey Shaman and Sen Pei, have been at the forefront of forecasting and analyzing the spread of COVID-19. Their ...
Fast facts:
This study describes essential differences between marine and freshwater species and the contributions of viruses to such differences
The results may help guide future bioengineering efforts to develop plant strains adapted to grow in salt-water, which is of local and regional food security interest
Microalgae are fundamental to global ecosystems due to their ability to sustain coral reef species and produce atmospheric oxygen
Before this study, many important algal phyla did not have sequenced representatives
Viruses have contributed to the evolution of algae and their genome makeups
Abu Dhabi, UAE, January 11, 2021: NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) ...
It is well known that the expansion of the universe is accelerating due to a mysterious dark energy. Within galaxies, stars also experience an acceleration, though this is due to some combination of dark matter and the stellar density. In a new study to be published in Astrophysical Journal Letters researchers have now obtained the first direct measurement of the average acceleration taking place within our home galaxy, the Milky Way. Led by Sukanya Chakrabarti at the Institute for Advanced Study with collaborators from Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Rochester, and ...
Moms are not more likely than other women to support gun control efforts. In fact, a new study finds that parenthood doesn't have a substantial effect on the gun control views of men or women.
"Everybody 'knows' that moms are more politically liberal on gun control issues," says Steven Greene, corresponding author of the study and a professor of political science at North Carolina State University. "We wanted to know if that's actually true. And, as it turns out, it's not true - which was surprising."
To explore the impact of parenthood on people's gun control views, the researchers drew on data collected by the Pew Center for Research in 2017 as part of Pew's nationally ...
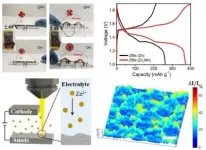
Lithium-ion batteries are critical for modern life, from powering our laptops and cell phones to those new holiday toys. But there is a safety risk - the batteries can catch fire.
Zinc-based aqueous batteries avoid the fire hazard by using a water-based electrolyte instead of the conventional chemical solvent. However, uncontrolled dendrite growth limits their ability to provide the high performance and long life needed for practical applications.
Now researchers have reported in Nature Communications that a new 3D zinc-manganese nano-alloy anode has overcome the limitations, resulting in a stable, high-performance, dendrite-free aqueous battery using seawater ...
In diseases characterized by bone loss -such as periodontitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and osteoporosis- there is a lot that scientists still don't understand. What is the role of the immune response in the process? What happens to the regulatory mechanisms that protect bone?
In a paper published recently in Scientific Reports, researchers from the Forsyth Institute and the Universidad de Chile describe a mechanism that unlocks a piece of the puzzle. Looking at periodontal disease in a mouse model, scientists found that a specific type of T cell, known as regulatory T cells, start behaving in unexpected ways. These cells lose their ability to regulate bone ...
WASHINGTON -- As LEDs replace traditional lighting systems, they bring more smart capabilities to everyday lighting. While you might use your smartphone to dim LED lighting at home, researchers have taken this further by tapping into dynamically controlled LEDs to create a simple illumination system for 3D imaging.
"Current video surveillance systems such as the ones used for public transport rely on cameras that provide only 2D information," said Emma Le Francois, a doctoral student in the research group led by Martin Dawson, Johannes Herrnsdorf and Michael Strain at the University of Strathclyde in the ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Scientists have known for years that mutations in the MLL4 gene can cause Kabuki syndrome, a rare developmental disorder.
But a study published on Jan. 11 in Nature Communications illuminates new details regarding how this occurs. (Images are available by contacting Charlotte Hsu in UB Media Relations at chsu22@buffalo.edu.)
The research suggests that MLL4 controls the production of neurons that secrete growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) in a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Mice without working copies of the MLL4 gene in this area had stunted growth and markedly fewer GHRH neurons. Mice with only one functioning ...