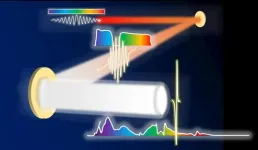
(Press-News.org) Osaka, Japan -- Ultra-intense lasers with ultra-short pulses and ultra-high energies are powerful tools for exploring unknowns in physics, cosmology, material science, etc. With the help of the famous technology "Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA)" (2018 Nobel Prize in Physics), the current record has reached 10 Petawatts (or 10^16 Watts). In a study recently published in Scientific Reports, researchers from Osaka University proposed a concept for next-generation ultra-intense lasers with a simulated peak power up to the Exawatt class (1 Exawatt equals 1000 Petawatts).
The laser, which was invented by Dr. T. H. Maiman in 1960, has one important characteristic of high intensity (or high peak power for pulse lasers): historically, laser peak power has experienced two-stage development. Just after the birth of the laser, Q-switching and mode-locking technologies increased laser peak power to Kilowatt (10^3 Watt) and Gigawatt (10^9 Watt) levels. After CPA technology was invented by Gérard Mourou and Donna Strickland in 1985, by which material damage and optical nonlinearity were avoided, laser peak power was dramatically increased to Terawatt (10^12 Watt) and Petawatt (10^15 Watt) levels. Today, two 10-Petawatt CPA lasers have been demonstrated in Europe (ELI-NP laser) and China (SULF laser), respectively.
At present, the facility scale of Petawatt lasers around the world is very large and project investment is also very high. The next step for future ultra-intense lasers is to further increase the peak power by compressing the pulse duration instead of increasing the pulse energy.
In their previous study (OSA Continuum, DOI: 10.1364/OSAC.2.001125), this group developed a new design, "Wide-angle Non-collinear Optical Parametric Chirped Pulse Amplification (WNOPCPA)," to increase the amplified spectrum and accordingly reduce the compressed pulse. The key mechanism of WNOPCPA is to increase the overall bandwidth by using a multiple-beam pump, which corresponds to different amplified spectra. "However, the pump interference, in addition to induced possible damage, is a potential problem in applying WNOPCPA to a huge project," explains corresponding author Zhaoyang Li.
In this newly improved design, by using a two-beam pumped WNOPCPA and carefully optimized phase-matching, pump interference is completely avoided, and an ultra-broadband bandwidth with two broad spectra is accomplished, resulting in END
Towards Exawatt-class lasers
Researchers from Osaka University propose a concept for next-generation ultra-intense lasers, possibly increasing the current record from 10 Petawatts to 500 Petawatts
2021-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NTU Singapore develops oral insulin nanoparticles that could be an alternative to jabs
2021-01-12
Scientists at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed insulin nanoparticles that may one day become the basis for an oral medicine, and an alternative to insulin injections for diabetic patients.
In a pre-clinical study, the NTU Singapore team fed insulin-containing nanoparticles to rats and found that insulin increased in their blood minutes later.
Insulin therapy is often an important part of treatment for diabetes, a metabolic disease that affects 422 million people globally . In Singapore, the number of diabetics is expected to grow to 1 million - almost a fifth of the population - in 2050 .
Delivering insulin orally would be preferable over insulin jabs for patients because it causes less ...
Anthropogenic heat flux increases the frequency of extreme heat events
2021-01-12
Anthropogenic, or human-made, heat flux in the near-surface atmosphere has changed urban thermal environments. Much of this fluctuation has been noted with rapid development of the global economy and urbanization since the turn of the 21st century. Meanwhile, the number of extreme temperature events in the first decade of the 21st century grew faster than in the last 10 years of the 20th century. During this period, urban extreme heat events have become more frequent, breaking temperature records more often.
"We found the relationships between anthropogenic heat flux and extreme temperature events..." said Prof. Zhenghui Xie, a scientist with the Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences. "...including ...
UTSW researchers identify new gene involved in breast cancer growth
2021-01-12
DALLAS - Jan. 12, 2021 - A team of UT Southwestern researchers has identified a gene involved in the growth of breast cancer, a finding that could lead to potential new targets for treatment.
"The gene ZMYND8 is increased in breast cancer conditions, and higher levels of the gene correlate with poor survival of breast cancer patients," says Yingfei Wang, Ph.D., assistant professor of pathology and neurology and corresponding author of the new study, published in Cancer Research. "It could be a promising target for antitumor immunotherapy."
In the U.S., about 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer at some point in their life. Worldwide, breast cancer is the most common cancer ...
Three-site study highlight effectiveness of FEND nasal calcium rich salts
2021-01-12
In a paper published in Molecular Frontiers Journal, researchers from Cambridge, Massachusetts and Bangalore, India study the effectiveness of FEND product to significantly improve airway hygiene by reducing and suppressing respiratory droplets potentially containing airborne pathogens and other contaminants. The study's findings further highlight why the FEND product is an important new daily hygiene protocol that joins century-old hand washing, masking and distancing measures as a fourth protective layer of defense against aerosolized particles.
The new study examined two nasal salines: ...
Master of disguise is new genus and species of cylindrical bark beetle
2021-01-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. - A resemblance to moss, lichens and fungi made for fantastic cover by a new genus and species of cylindrical bark beetle described by an Oregon State University College of Science researcher.
"If you can't beat your enemies or run away, then hide, and that is what this Cretaceous beetle is doing," said OSU's George Poinar Jr. "He is hiding under a spectacular camouflage of his own making, allowing him to blend into a mossy background."
Poinar, an international expert in using plant and animal life forms preserved in amber to learn more about the biology and ecology of the distant past, and collaborator Fernando ...
Knowledge of cycad branching behavior improves conservation
2021-01-12
Research on cycad trees in Colombia, Guam, and the Philippines has illuminated how knowledge of their branching behavior may benefit conservation decisions for the endangered plants. In a study published in the December issue of the journal Horticulturae, scientists from the University of Guam and the Montgomery Botanical Center in Florida show that the number of times a cycad tree produces a branch can be used to infer the sex of the tree. The findings have practical applications for use of the sexual dimorphism that is described.
Cycads are unique seed-producing plants. Conservation actions are being implemented for many species around the world as cycads are being threatened by human activity.
The arborescent cycad stem is constructed using ...
Progress made on youth drowning in Aust, NZ, Canada - but more work required
2021-01-12
Ten years of data from Australia, New Zealand and Canada reveals a drop in drowning deaths among people under 20 - but a large increase in drowning for adolescent females and First Nations peoples.
Associate Professor Richard Franklin from James Cook University in Queensland, Australia, said an international collaboration of researchers looked at drowning in the under 20s between 2005 and 2014.
"Globally, drowning is a leading cause of unintentional death among children and young people, with the greatest toll among children under the age of five years. Many more children are impacted by non-fatal drowning, some experiencing long-term health impacts," said Dr Franklin.
He said children aged 0-19 years account for an average ...
Penn Medicine surgeons develop universal patient-reported outcomes tool to improve hernia care
2021-01-12
PHILADELPHIA--Patient-reported outcomes have become a critical part of improving surgical care because of their ability to capture patient experiences, such as quality of life and satisfaction, that can help inform treatment. However, for patients undergoing abdominal hernia repair -- a common procedure performed on about 400,000 patients a year in the United States -- a tool to effectively and practically measure those outcomes has not been widely accepted and implemented by clinics.
Now, researchers from the division of Plastic Surgery in the department of Surgery in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, have successfully developed, tested, and implemented a first-of-its-kind, patient-informed ...
Exciting times for efficient heavy-atom-free OLEDs
2021-01-12
Osaka - Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays are now very popular features of many mainstream products including smartphones and televisions. OLEDs have the advantages of being low cost, light, flexible, and easy to modify, making them ideal display materials. However, current OLEDs that achieve commercially viable quantum efficiencies contain rare metal atoms such as iridium and platinum that increase costs and reduce sustainability. Now, an international team including researchers from Osaka University has reported the best performing heavy-atom-free OLED of its kind.
Although OLEDs that do not contain heavy atoms--such as rare metals and halogens--are ...
Singapore and US scientists uncover the structure of Wnt, Wntless proteins
2021-01-12
SINGAPORE, 12 January 2021 - Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore and Columbia University in the US have solved how Wnt proteins, which play a fundamental role in cell proliferation and differentiation, hitch a ride to travel from their cellular factory to the cell surface. Drugs that interfere with Wnt transport, like the made-in-Singapore anti-cancer drug ETC-159, can be exploited to treat diseases with excess Wnt signalling, such as cancer and fibrosis.
"Since excessive Wnt signalling can drive cancer, supress immunity and trigger fibrosis, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
Study finds early imaging after pediatric UTIs may do more harm than good
UC San Diego Health joins national research for maternal-fetal care
New biomarker predicts chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer
Treatment algorithms featured in Brain Trauma Foundation’s update of guidelines for care of patients with penetrating traumatic brain injury
Over 40% of musicians experience tinnitus; hearing loss and hyperacusis also significantly elevated
Artificial intelligence predicts colorectal cancer risk in ulcerative colitis patients
Mayo Clinic installs first magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia system for cancer research in the US
[Press-News.org] Towards Exawatt-class lasersResearchers from Osaka University propose a concept for next-generation ultra-intense lasers, possibly increasing the current record from 10 Petawatts to 500 Petawatts