(Press-News.org) Osaka - Organic light-emitting diode (OLED) displays are now very popular features of many mainstream products including smartphones and televisions. OLEDs have the advantages of being low cost, light, flexible, and easy to modify, making them ideal display materials. However, current OLEDs that achieve commercially viable quantum efficiencies contain rare metal atoms such as iridium and platinum that increase costs and reduce sustainability. Now, an international team including researchers from Osaka University has reported the best performing heavy-atom-free OLED of its kind.
Although OLEDs that do not contain heavy atoms--such as rare metals and halogens--are an obvious choice for reducing the cost and improving the long-term viability of products, the heavy-atom-free emitters that are currently available have limitations.
Materials known as thermally activated delayed fluorescence (TADF) emitters are efficient; however, they typically have broad emission spectra that make them more suitable for use as light sources than as the precise emitters required for display applications. Another type of heavy-atom-free emitter is room-temperature phosphorescence (RTP) emitters; however, the OLEDs using them show very low efficiencies of END
Exciting times for efficient heavy-atom-free OLEDs
An international team including researchers from Osaka University reports a novel hybrid emitter that could revolutionize the design of OLEDs
2021-01-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Singapore and US scientists uncover the structure of Wnt, Wntless proteins
2021-01-12
SINGAPORE, 12 January 2021 - Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School in Singapore and Columbia University in the US have solved how Wnt proteins, which play a fundamental role in cell proliferation and differentiation, hitch a ride to travel from their cellular factory to the cell surface. Drugs that interfere with Wnt transport, like the made-in-Singapore anti-cancer drug ETC-159, can be exploited to treat diseases with excess Wnt signalling, such as cancer and fibrosis.
"Since excessive Wnt signalling can drive cancer, supress immunity and trigger fibrosis, ...
Conflict between divorced parents can lead to mental health problems in children
2021-01-12
Conflict between divorced or separated parents increases the risk of children developing physical and mental health problems.
A new study from the Arizona State University Research and Education Advancing Children's Health (REACH) Institute has found that children experience fear of being abandoned when their divorced or separated parents engage in conflict. Worrying about being abandoned predicted future mental health problems in children. The work will be published in Child Development on January 12.
"Conflict is a salient stressor for kids, and the link between exposure to interparental conflict ...
Endocrine Society recommends government negotiation and other policies to lower out-of-pocket costs
2021-01-12
WASHINGTON--The Endocrine Society is calling on policymakers to include government negotiation as part of an overall strategy to reduce insulin prices in its updated position statement published today in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
More than 34 million Americans have diabetes, and another 88 million are at risk for developing the disease. The cost of insulin has nearly tripled in the past 15 years, and a lack of transparency in the drug supply chain has made it challenging to identify and address the causes of soaring costs.
Federal law currently prohibits Medicare, which accounts for a third of all drug spending, from negotiating directly with pharmaceutical companies over drug prices. Legislation empowering the ...
FAU develops simplified COVID-19 diagnostic method to ramp up widespread testing
2021-01-12
To properly monitor and help curb the spread of COVID-19, several millions of diagnostic tests are required daily in just the United States alone. There is still a widespread lack of COVID-19 testing in the U.S. and many of the clinical diagnostics protocols require extensive human labor and materials that could face supply shortages and present biosafety concerns.
The current gold standard for COVID-19 diagnostic testing in the U.S., developed by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), is quantitative PCR-based (qPCR) molecular tests that detect the presence of the viral ...
High levels of clinician burnout identified at leading cardiac centre
2021-01-12
Toronto (Jan. 12, 2021) - More than half the clinicians surveyed at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre reported burnout and high levels of distress according to a series of studies published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal Open (CMAJ-OPEN). In these studies carried out before the COVID-19 pandemic, 78% of nurses, 73% of allied health staff and 65% of physicians described experiencing burnout.
"In my 35 years as a physician I have never seen a more serious issue for clinicians than burnout," says lead author Dr. Barry Rubin, Chair and Medical Director, the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, ...
iCeMS makes highly conductive antiperovskites with soft anion lattices
2021-01-12
A new structural arrangement of atoms shows promise for developing safer batteries made with solid materials. Scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) designed a new type of 'antiperovskite' that could help efforts to replace the flammable organic electrolytes currently used in lithium ion batteries. Their findings were described in the journal Nature Communications.
Perovskite compounds are being tested and used in a wide range of technologies due to their excellent ability to conduct electricity, among other properties. They can be made from a large combination of atoms with the formula ABX3, where A and B are positively charged atoms and X is a negatively ...
Master designers: Architects of the brain revealed
2021-01-12
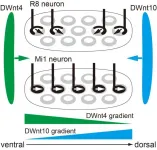
Brain cells often cluster and grow together creating three-dimensional columns. While this pillar-like pattern of neurons is established, the exact mechanism behind its formation is still elusive. Makoto Sato's team at Kanazawa University has been closely studying this phenomenon. Their recent findings explain how molecules in the brain work in conjunction to create the architectural marvels that are the columns.
The researchers base much of their work on the Drosophila (fruit fly) due to the organism's genetic similarities to humans. In this study they focused on the visual center of the fly's brain in a region known ...
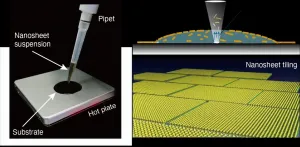
Nanosheet-based electronics could be one drop away
2021-01-12
Scientists at Japan's Nagoya University and the National Institute for Materials Science have found that a simple one-drop approach is cheaper and faster for tiling functional nanosheets together in a single layer. If the process, described in the journal ACS Nano, can be scaled up, it could advance development of next-generation oxide electronics.
"Drop casting is one of the most versatile and cost-effective methods for depositing nanomaterials on a solid surface," says Nagoya University materials scientist Minoru Osada, the study's corresponding author. "But it has serious drawbacks, one being the so-called coffee-ring effect: a pattern left by particles once the liquid they are in evaporates. We found, to our great surprise, that ...
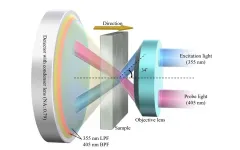
No disassembly required: Non-destructive method to measure carrier lifetime in SiC
2021-01-12
Silicon carbide (SiC), a versatile and resistant material that exists in multiple crystalline forms, has attracted much attention thanks to its unique electronic properties. From its use in the first LED devices, to its applications in high-voltage devices with low power losses, SiC displays exceptional semiconductor behavior. So far, the operating voltages for unipolar SiC devices are below 3.3 kV. Though useful for the electronic systems of cars, trains, and home appliances, unipolar SiC-based devices cannot be used in power generation and distribution systems, which operate at voltages above 10 kV.
Some researchers believe that the solution to this conundrum lies in bipolar SiC devices, which offer low on-resistance (and hence lower losses) ...
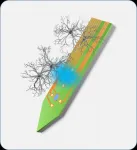
MicroLED neural probe for neuroscience
2021-01-12
Overview:
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi and Ph.D. candidate Hiroki Yasunaga in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a MicroLED neural probe for neuroscience. This MicroLED tool can optogenetically control and observe neural activity in the brain. Neural activity was successfully recorded using the neural probe, and sufficient light output was obtained from the MicroLED to activate neural activity. The developed MicroLED tool will contribute to the development of neuroscience research-purposed ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
[Press-News.org] Exciting times for efficient heavy-atom-free OLEDsAn international team including researchers from Osaka University reports a novel hybrid emitter that could revolutionize the design of OLEDs