(Press-News.org) Toronto (Jan. 12, 2021) - More than half the clinicians surveyed at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre reported burnout and high levels of distress according to a series of studies published today in the Canadian Medical Association Journal Open (CMAJ-OPEN). In these studies carried out before the COVID-19 pandemic, 78% of nurses, 73% of allied health staff and 65% of physicians described experiencing burnout.
"In my 35 years as a physician I have never seen a more serious issue for clinicians than burnout," says lead author Dr. Barry Rubin, Chair and Medical Director, the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, UHN.
Completed in 2019, the study used the Well-Being Index, a survey tool developed by the Mayo Clinic, a globally recognized academic medical centre. 414 physicians, nurses and allied health staff answered a series of questions about the level of stress they experienced in the previous month.
The index measured fatigue, depression, burnout, anxiety or stress, mental and physical quality of life, work-life integration, meaning in work and distress.
The study also evaluated the respondent's perception of the adequacy of staffing levels, and of fair treatment in the workplace. The results were then compared to outcomes for corresponding healthcare professionals at academic health science centres in the United States.
Main Findings and Impact:
78% of nurses, 73% of allied health staff and 65% of physicians described burnout in the month prior to when the survey was administered.
79% of nurses, 56% of allied health staff and 55% of physicians had high levels of distress.
Lower levels of distress among all clinicians were associated with a perception of fair treatment at work and a perception of adequate staffing levels.
The impact of burnout on clinicians can include extreme fatigue, professional dissatisfaction, job turnover, decreased quality of life, and thoughts of suicide.
"Burnout also has a negative impact on the care we provide," says Dr. Rubin. "It is associated with an increased incidence of medical errors, serious safety events, readmission to hospital, worse patient outcomes and in some situations even increased patient mortality. Clinician burnout is a public health crisis that we must address now."
The findings of these studies are the first step in acknowledging the existence, depth, and degree of distress and burnout among clinicians at the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre.
"Our next steps will be to meet with nurses, doctors and allied health staff, so that we can understand the key drivers of burnout in the PMCC and develop targeted intervention strategies," says Dr. Rubin. "It is critical we address these issues and work together to bring about much-needed change. Healthcare workers give their all to care for others, it is time they are cared for too."
INFORMATION:
These studies were funded by the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre Innovation Fund.
About the Peter Munk Cardiac Centre
The Peter Munk Cardiac Centre, established through the generous support of The Peter and Melanie Munk Charitable Foundation, is the premier cardiac centre in Canada. Each year, over 163,000 patients receive innovative and compassionate care from a multidisciplinary team who treat some of the most complex cases of heart and vascular disease. Our clinical and research expertise has improved the lives of patients around the world, while we continue to train more cardiologists, cardiovascular surgeons, and vascular surgeons than any other hospital in Canada. The Peter Munk Cardiac Centre is based at Toronto General Hospital, Toronto Western Hospital and Toronto Rehabilitation Institute - all members of University Health Network. For more information, visit http://www.petermunkcardiaccentre.ca
About the University Health Network
University Health Network consists of Toronto General, recently voted one of the Top 5 Hospitals in the World according to Newsweek Magazine, and Toronto Western Hospital, the Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute, and the Michener Institute of Education at UHN. The scope of research and complexity of cases at University Health Network has made it a national and international source of discovery, education and patient care. It has the largest hospital-based research program in Canada, with major research in cardiology, transplantation, neurosciences, oncology, surgical innovation, infectious diseases, genomic medicine and rehabilitation medicine. University Health Network is a research hospital affiliated with the University of Toronto.
Media Contact
Rosa Kim
Senior Public Affairs Advisor
Phone: 647 669 8416
Email: Rosa.kim@uhn.ca
A new structural arrangement of atoms shows promise for developing safer batteries made with solid materials. Scientists at Kyoto University's Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS) designed a new type of 'antiperovskite' that could help efforts to replace the flammable organic electrolytes currently used in lithium ion batteries. Their findings were described in the journal Nature Communications.
Perovskite compounds are being tested and used in a wide range of technologies due to their excellent ability to conduct electricity, among other properties. They can be made from a large combination of atoms with the formula ABX3, where A and B are positively charged atoms and X is a negatively ...
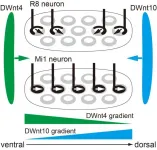
Brain cells often cluster and grow together creating three-dimensional columns. While this pillar-like pattern of neurons is established, the exact mechanism behind its formation is still elusive. Makoto Sato's team at Kanazawa University has been closely studying this phenomenon. Their recent findings explain how molecules in the brain work in conjunction to create the architectural marvels that are the columns.
The researchers base much of their work on the Drosophila (fruit fly) due to the organism's genetic similarities to humans. In this study they focused on the visual center of the fly's brain in a region known ...
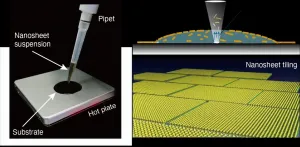
Scientists at Japan's Nagoya University and the National Institute for Materials Science have found that a simple one-drop approach is cheaper and faster for tiling functional nanosheets together in a single layer. If the process, described in the journal ACS Nano, can be scaled up, it could advance development of next-generation oxide electronics.
"Drop casting is one of the most versatile and cost-effective methods for depositing nanomaterials on a solid surface," says Nagoya University materials scientist Minoru Osada, the study's corresponding author. "But it has serious drawbacks, one being the so-called coffee-ring effect: a pattern left by particles once the liquid they are in evaporates. We found, to our great surprise, that ...
Silicon carbide (SiC), a versatile and resistant material that exists in multiple crystalline forms, has attracted much attention thanks to its unique electronic properties. From its use in the first LED devices, to its applications in high-voltage devices with low power losses, SiC displays exceptional semiconductor behavior. So far, the operating voltages for unipolar SiC devices are below 3.3 kV. Though useful for the electronic systems of cars, trains, and home appliances, unipolar SiC-based devices cannot be used in power generation and distribution systems, which operate at voltages above 10 kV.
Some researchers believe that the solution to this conundrum lies in bipolar SiC devices, which offer low on-resistance (and hence lower losses) ...
Overview:
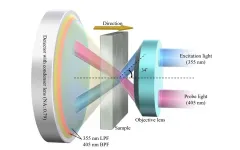
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi and Ph.D. candidate Hiroki Yasunaga in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a MicroLED neural probe for neuroscience. This MicroLED tool can optogenetically control and observe neural activity in the brain. Neural activity was successfully recorded using the neural probe, and sufficient light output was obtained from the MicroLED to activate neural activity. The developed MicroLED tool will contribute to the development of neuroscience research-purposed ...
For other measures, however, the behaviour of the generations differs: "Of those under 40 years of age, 18 percent say they have food delivered more frequently", says BfR-President Professor Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel. "In the age group 60 years and older, on the other hand, only seven percent make use of such offers."
https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/210105-bfr-corona-monitor-en.pdf
In addition to more frequent ventilation, the respondents try to protect themselves from an infection mainly by wearing masks, keeping distance to other people and washing their hands more frequently. The mandatory use of masks was approved by 93 percent of the respondents, the distance regulation by 96 percent. ...
In patients with anorexia, it could remain at the same level as before the start of the illness. The researchers led by Professor Martin Diers recommend a combination of cognitive behavioural therapy and the use of virtual reality to correct the distorted body schema. The study is published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders on 20 December 2020.
Understanding the unconscious
The distorted perception of one's own body is a characteristic symptom of anorexia nervosa. It has long been known that patients overestimate the dimensions of their body. "This ...
Severe thunderstorms often produce lightning, heavy precipitation, hails, and wind gusts, and cause significant economic losses and casualties in the region they passed through. So, their prediction is one of the primary concerns of not only weather forecasters but also local government and public. However, the accurate forecasting on severe thunderstorm is still a great challenge because of its complicated mechanism of formation and enhancement.
Beijing metropolitan region is one of the most developed areas in China and is also influenced greatly by severe thunderstorms. ...
Groundwater flow and seepage can form large gullies along coastal cliffs in the matter of days, it has been discovered, as per a recently-published paper.
An international team of scientists from Malta, Germany, Romania, New Zealand and USA has used drones and satellite imagery to monitor a stretch of coastline near Ashburton (South Island, New Zealand). They found that gullies up to 30m in length can develop in less than a week.
Field observations and numerical models have shown that groundwater plays a key role in forming these gullies, by either eroding tunnels or triggering landslides.
Gullies are an important coastal hazard. There ...
To resolve the energy crisis and environmental issues, research to move away from fossil fuels and convert to eco-friendly and sustainable hydrogen energy is well underway around the world. Recently, a team of researchers at POSTECH has proposed a way to efficiently produce hydrogen fuel via water-electrolysis using inexpensive and readily available nickel as an electrocatalyst, greenlighting the era of hydrogen economy.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Jong Kyu Kim and Ph.D. candidate Jaerim Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and a team led by Professor Jeong Woo Han and Ph.D. candidate Hyeonjung Jung of the Department of Chemical Engineering have jointly developed a highly efficient nickel-based catalyst system doped with oxophilic transition metal atoms ...