Master designers: Architects of the brain revealed
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Brain cells often cluster and grow together creating three-dimensional columns. While this pillar-like pattern of neurons is established, the exact mechanism behind its formation is still elusive. Makoto Sato's team at Kanazawa University has been closely studying this phenomenon. Their recent findings explain how molecules in the brain work in conjunction to create the architectural marvels that are the columns.
The researchers base much of their work on the Drosophila (fruit fly) due to the organism's genetic similarities to humans. In this study they focused on the visual center of the fly's brain in a region known as the medulla. This region resembles the human cerebral cortex--the primary seat of reasoning. Developing columns in the medulla were photographed in real-time to find that a protein known as Fmi was abundant in the growing stages of the fly and vanished shortly after. Fmi also partakes in a process known as planar cell polarity (PCP) which drives the spatial orientation of a cell in two-dimensional space. Thus, it was purported that PCP was also at play in the development of columns. Indeed, deactivation of PCP components resulted in impaired column formation. What's more, a new candidate, Fz2, was found to be working closely with the individual PCP components.
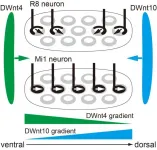
Fz2 is linked to a cellular pathway called Wnt signaling. A close inspection of the medulla revealed that prime regulators of the Wnt pathway, DWnt4 and DWnt10, were operational in the vicinity. When DWnt4 and DWnt10 were also disabled, a disruption of column structure in neighboring regions followed. Column construction was controlled by a complex chain of architects.
Makoto Sato and his co-workers have previously revealed three neurons types--R7, R8 and Mi1-- to comprise the columns. Thus, they then investigated the role of Wnt/PCP in these neurons. Switching PCP off resulted in the Mi1 and R8 neurons changing direction, confirming that orientation was controlled by this pathway. On the other hand, when Wnt signaling was turned off the Mi1 neurons also showed structural impairment. Wnt/PCP was, therefore, instrumental to proper spatial and structural development of the columns.
This study reveals the intertwined nature of the mechanisms that drive brain development. "[We] show that Wnt ligands globally regulate neuronal orientation and column arrangement through Fz2/planar cell polarity signaling in a three-dimensional space in the brain", summarize the researchers. These processes are key to monitoring healthy growth and tracking disorders in the developing brain.
Background:
Planar cell polarity (PCP) - Cell polarity is a phenomenon that enables spatial differences in shape and size within cells. Thus, cells may appear elongated at one end and oval at the other (as seen in the classic image of a neuron). This polarity occurs in a two-dimensional space and enables cells to carry out multiple functions simultaneously. A neuron can thus traverse distances at one end while the other end sustains essential life processes. Since the PCP is a complex process, multiple molecules are part of its chain. Until now, the role of PCP in regulating three-dimensional spatial orientation within neurons was elusive. This study elucidates how Wnt signaling works in conjunction with PCP to achieve this.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
Scientists at Japan's Nagoya University and the National Institute for Materials Science have found that a simple one-drop approach is cheaper and faster for tiling functional nanosheets together in a single layer. If the process, described in the journal ACS Nano, can be scaled up, it could advance development of next-generation oxide electronics.
"Drop casting is one of the most versatile and cost-effective methods for depositing nanomaterials on a solid surface," says Nagoya University materials scientist Minoru Osada, the study's corresponding author. "But it has serious drawbacks, one being the so-called coffee-ring effect: a pattern left by particles once the liquid they are in evaporates. We found, to our great surprise, that ...
2021-01-12
Silicon carbide (SiC), a versatile and resistant material that exists in multiple crystalline forms, has attracted much attention thanks to its unique electronic properties. From its use in the first LED devices, to its applications in high-voltage devices with low power losses, SiC displays exceptional semiconductor behavior. So far, the operating voltages for unipolar SiC devices are below 3.3 kV. Though useful for the electronic systems of cars, trains, and home appliances, unipolar SiC-based devices cannot be used in power generation and distribution systems, which operate at voltages above 10 kV.
Some researchers believe that the solution to this conundrum lies in bipolar SiC devices, which offer low on-resistance (and hence lower losses) ...
2021-01-12
Overview:
Associate Professor Hiroto Sekiguchi and Ph.D. candidate Hiroki Yasunaga in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering at Toyohashi University of Technology have developed a MicroLED neural probe for neuroscience. This MicroLED tool can optogenetically control and observe neural activity in the brain. Neural activity was successfully recorded using the neural probe, and sufficient light output was obtained from the MicroLED to activate neural activity. The developed MicroLED tool will contribute to the development of neuroscience research-purposed ...
2021-01-12
For other measures, however, the behaviour of the generations differs: "Of those under 40 years of age, 18 percent say they have food delivered more frequently", says BfR-President Professor Dr. Dr. Andreas Hensel. "In the age group 60 years and older, on the other hand, only seven percent make use of such offers."
https://www.bfr.bund.de/cm/349/210105-bfr-corona-monitor-en.pdf
In addition to more frequent ventilation, the respondents try to protect themselves from an infection mainly by wearing masks, keeping distance to other people and washing their hands more frequently. The mandatory use of masks was approved by 93 percent of the respondents, the distance regulation by 96 percent. ...
2021-01-12
In patients with anorexia, it could remain at the same level as before the start of the illness. The researchers led by Professor Martin Diers recommend a combination of cognitive behavioural therapy and the use of virtual reality to correct the distorted body schema. The study is published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders on 20 December 2020.
Understanding the unconscious
The distorted perception of one's own body is a characteristic symptom of anorexia nervosa. It has long been known that patients overestimate the dimensions of their body. "This ...
2021-01-12
Severe thunderstorms often produce lightning, heavy precipitation, hails, and wind gusts, and cause significant economic losses and casualties in the region they passed through. So, their prediction is one of the primary concerns of not only weather forecasters but also local government and public. However, the accurate forecasting on severe thunderstorm is still a great challenge because of its complicated mechanism of formation and enhancement.
Beijing metropolitan region is one of the most developed areas in China and is also influenced greatly by severe thunderstorms. ...
2021-01-12
Groundwater flow and seepage can form large gullies along coastal cliffs in the matter of days, it has been discovered, as per a recently-published paper.
An international team of scientists from Malta, Germany, Romania, New Zealand and USA has used drones and satellite imagery to monitor a stretch of coastline near Ashburton (South Island, New Zealand). They found that gullies up to 30m in length can develop in less than a week.
Field observations and numerical models have shown that groundwater plays a key role in forming these gullies, by either eroding tunnels or triggering landslides.
Gullies are an important coastal hazard. There ...
2021-01-12
To resolve the energy crisis and environmental issues, research to move away from fossil fuels and convert to eco-friendly and sustainable hydrogen energy is well underway around the world. Recently, a team of researchers at POSTECH has proposed a way to efficiently produce hydrogen fuel via water-electrolysis using inexpensive and readily available nickel as an electrocatalyst, greenlighting the era of hydrogen economy.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Jong Kyu Kim and Ph.D. candidate Jaerim Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and a team led by Professor Jeong Woo Han and Ph.D. candidate Hyeonjung Jung of the Department of Chemical Engineering have jointly developed a highly efficient nickel-based catalyst system doped with oxophilic transition metal atoms ...
2021-01-12
Researchers at Tampere University, Finland, have published new results in collaboration with an international research network that help to understand the biological phenomena mediated by cell membrane integrin receptors and contribute to the development of methods for the treatment of cancer.
In the cell membrane, integrins form the connection between the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. The regulation of integrin activity is essential for the function of tissues and individual cells.
The studies investigated the structure and function of talin, a cytoskeletal protein, which is important in the regulation of the integrin receptor activity. Talin binds to integrin via its "head" and connects it to the cytoskeleton, thereby acting as a part of the ...
2021-01-12
Researchers at the University of York are calling for more stringent regulatory measures to reduce the health burden of smokeless tobacco, a product often found in UK stores without the proper health warnings and as a result of illicit trading.
Smokeless tobacco is particularly popular in Asia and Africa and includes chewing tobacco as well as various types of nasal tobacco. They contain high levels of nicotine as well as cancer producing toxic chemicals, making head and neck cancers common in those who consume smokeless tobacco products.
In a study of 25 wards across five boroughs - Birmingham, Bradford, Blackburn, Leicester, and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Master designers: Architects of the brain revealed