Groundwater drives rapid erosion of the Canterbury coastline, New Zealand
An outcome of the MARCAN project, led by the University of Malta
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Groundwater flow and seepage can form large gullies along coastal cliffs in the matter of days, it has been discovered, as per a recently-published paper.
An international team of scientists from Malta, Germany, Romania, New Zealand and USA has used drones and satellite imagery to monitor a stretch of coastline near Ashburton (South Island, New Zealand). They found that gullies up to 30m in length can develop in less than a week.
Field observations and numerical models have shown that groundwater plays a key role in forming these gullies, by either eroding tunnels or triggering landslides.
Gullies are an important coastal hazard. There is an average of one gully every 250m along the Canterbury coastline, and their formation leads to the loss of precious agricultural land.
Similar coastal gullies have been documented in South Taranaki (North Island, New Zealand), as well as other countries such as the USA, Japan and Brazil.
When and where coastal gullies form can be partly predicted. The study has shown that gullies form when more than 40mm of rain fall per day, and that they are preferentially located above buried, old river channels.
INFORMATION:
This study was led by Prof. Aaron Micallef from the Department of Geosciences, and is an outcome of the MARCAN project, which is funded by the European Research Council.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
To resolve the energy crisis and environmental issues, research to move away from fossil fuels and convert to eco-friendly and sustainable hydrogen energy is well underway around the world. Recently, a team of researchers at POSTECH has proposed a way to efficiently produce hydrogen fuel via water-electrolysis using inexpensive and readily available nickel as an electrocatalyst, greenlighting the era of hydrogen economy.
A POSTECH research team led by Professor Jong Kyu Kim and Ph.D. candidate Jaerim Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and a team led by Professor Jeong Woo Han and Ph.D. candidate Hyeonjung Jung of the Department of Chemical Engineering have jointly developed a highly efficient nickel-based catalyst system doped with oxophilic transition metal atoms ...
2021-01-12
Researchers at Tampere University, Finland, have published new results in collaboration with an international research network that help to understand the biological phenomena mediated by cell membrane integrin receptors and contribute to the development of methods for the treatment of cancer.
In the cell membrane, integrins form the connection between the cytoskeleton and the extracellular matrix. The regulation of integrin activity is essential for the function of tissues and individual cells.
The studies investigated the structure and function of talin, a cytoskeletal protein, which is important in the regulation of the integrin receptor activity. Talin binds to integrin via its "head" and connects it to the cytoskeleton, thereby acting as a part of the ...
2021-01-12
Researchers at the University of York are calling for more stringent regulatory measures to reduce the health burden of smokeless tobacco, a product often found in UK stores without the proper health warnings and as a result of illicit trading.
Smokeless tobacco is particularly popular in Asia and Africa and includes chewing tobacco as well as various types of nasal tobacco. They contain high levels of nicotine as well as cancer producing toxic chemicals, making head and neck cancers common in those who consume smokeless tobacco products.
In a study of 25 wards across five boroughs - Birmingham, Bradford, Blackburn, Leicester, and ...
2021-01-12
If you were an owner of a newly set-up company, you would most likely be focused on building brand awareness to reach out to as many people as possible. But how can you do so with budget constraints?
These days, businesses have turned to a select group of people who are active on social media platforms as a cost efficient way to drive their promotional efforts. Also referred to as 'influencers', they have the ability to influence the opinions or buying decisions of others.
The company would then focus their efforts on influencing the influencers, hoping that, in turn, their product information gets disseminated to the largest possible number of people through these influencers' wide ...
2021-01-12
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition caused by the weakening of the heart muscle, affecting the ventricles (chambers in the heart that push blood around the body as it contracts). If allowed to progress unchecked, DCM can lead to heart failure and death, especially in children. The only cure, at present, is a heart transplant, which comes with its own challenges: long waiting times to secure a suitable donor heart, the possibility of organ rejection, long hospitalizations and recovery times, among others.
In recent decades, stem cells have become the cornerstone ...
2021-01-12
Tsukuba, Japan - Proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells are an energy storage technology that will help lower the environmental footprint of transportation. These fuel cells make use of a chemical reaction known as oxygen reduction. This reaction needs a low-cost catalyst for widespread commercial applications. Nitrogen-doped carbon is one such catalyst, but the chemical details of how nitrogen doping works are rather controversial. Such knowledge is important to improving the function of PEM fuel cells in future technologies.
In a study recently published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, researchers ...
2021-01-12
In a major register-based study, scientists at University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have now demonstrated a connection between inferior physical fitness in young adults and elevated risk of the autoimmune disease psoriasis. For the male recruits to compulsory military training who were rated as the least fit, the risk of developing psoriasis later was 35 percent higher than for the fittest.
The study was based on data on more than 1.2 million men conscripted, aged 18, into the Swedish Armed Forces between the years 1968 and 2005. During the enrollment ...
2021-01-12
Nausea and vomiting symptoms during pregnancy start within a three day timeframe for most women, according to new study from University of Warwick
More accurate measurement achieved by calculating start of pregnancy from date of ovulation - rather than last menstrual period
Points to a potential biological cause for nausea and vomiting, and supports the view that the condition has been trivialised
Researchers from the University of Warwick have narrowed the time frame that nausea and vomiting during pregnancy will potentially start to just three days for most women, opening up the possibility for scientists to identify ...
2021-01-12
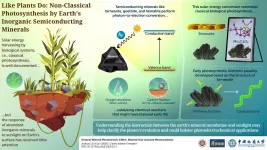
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and other organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy, has been a major player during the evolution of life and our planet's atmosphere. Although most of the ins and outs of photosynthesis are understood, how the necessary mechanisms evolved is still a topic of debate. The answer to this question, however, may actually lie buried in the mineral world.
In a recent study published in Earth Science Frontiers (10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.12.3), scientists from Peking University, China, shifted the focus in photosynthesis research from plants and bacteria one step further back to rocks and substances found in what's ...
2021-01-12
UK government plans to widen the roll out of the Innova lateral flow test without supporting evidence risks serious harm, warn experts in The BMJ today.
More than £1 billion have been spent on purchasing lateral flow tests, but Professor Jon Deeks and colleagues argue that the public is being misled about their accuracy, as well as the risks and implications of false negative results, and they call on the government urgently to change course.
Mass testing may be helpful and necessary in certain circumstances if delivered to high quality, they explain, but the Innova lateral flow test is not fit for this purpose.
For example, in the Liverpool pilot study, 60% of infected symptomless people went undetected, including 33% of those with ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Groundwater drives rapid erosion of the Canterbury coastline, New Zealand
An outcome of the MARCAN project, led by the University of Malta