Sustainable transportation: clearing the air on nitrogen doping
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba identify the active nitrogen atoms in the carbon catalyst of a technology that will help optimize a proposed renewable energy storage technology
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Tsukuba, Japan - Proton-exchange membrane (PEM) fuel cells are an energy storage technology that will help lower the environmental footprint of transportation. These fuel cells make use of a chemical reaction known as oxygen reduction. This reaction needs a low-cost catalyst for widespread commercial applications. Nitrogen-doped carbon is one such catalyst, but the chemical details of how nitrogen doping works are rather controversial. Such knowledge is important to improving the function of PEM fuel cells in future technologies.
In a study recently published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition, researchers from the University of Tsukuba reported chemical details for optimizing the oxygen reduction reaction in PEM fuel cells in acidic conditions. This configuration helps the carbon catalyst adsorb oxygen in a way that enables the fuel cell to function.
Nitrogen can adopt various bonding configurations, such as pyridinic, in nitrogen-doped carbon catalysts. For years, researchers have tried to determine which bonding configurations are the source of electrolytic activity in PEM fuel cells. The results of such studies may be unclear unless the reaction mechanisms are clarified with controlled bonding and crystallographic orientation of the nitrogen atom on the catalysts.
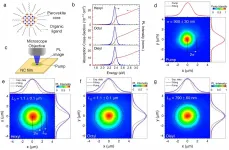
"We deposited seven nitrogenous molecules onto a paracrystalline carbon black catalyst to make model catalysts with homogeneous structures," says lead author Professor Kotaro Takeyasu. "We found that 1,10-phenanthroline, with two pyridinic nitrogen atoms at the armchair edges of the catalyst, had the highest activity with reference to current density."
Sulfuric acid fully acidifed the nitrogen atoms in the catalyst. Upon applying an appropriate voltage under oxygen-saturated conditions, the protonated nitrogen atoms in the catalyst were reduced. This was attributable to the simultaneous oxygen adsorption, because there was no reduction in nitrogen-saturated conditions.
"Density functional theory calculations also indicate that oxygen adsorption promotes the reduction of fully protonated nitrogen atoms," explains senior author, Professor Junji Nakamura. "Thus, oxygen absorbs onto the catalyst and at the same time, the nitrogen atoms are reduced for additional catalytic cycles."
Current PEM fuel cells use platinum catalysts. Because platinum is a rare metal it is not a realistic option for commercial applications in the long term. Thus, platinum catalysts will not enable PEM fuel cells to contribute to a low-carbon economy. The findings described here will help researchers improve the performance of carbon-based catalysts for PEM fuel cells and improve the sustainability of transportation.
INFORMATION:
The article, "Role of pyridinic nitrogen in the mechanism of the oxygen reduction reaction on carbon electrocatalysts," was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition at DOI: 10.1002/anie.202014323
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
In a major register-based study, scientists at University of Gothenburg, Sweden, have now demonstrated a connection between inferior physical fitness in young adults and elevated risk of the autoimmune disease psoriasis. For the male recruits to compulsory military training who were rated as the least fit, the risk of developing psoriasis later was 35 percent higher than for the fittest.
The study was based on data on more than 1.2 million men conscripted, aged 18, into the Swedish Armed Forces between the years 1968 and 2005. During the enrollment ...
2021-01-12
Nausea and vomiting symptoms during pregnancy start within a three day timeframe for most women, according to new study from University of Warwick
More accurate measurement achieved by calculating start of pregnancy from date of ovulation - rather than last menstrual period
Points to a potential biological cause for nausea and vomiting, and supports the view that the condition has been trivialised
Researchers from the University of Warwick have narrowed the time frame that nausea and vomiting during pregnancy will potentially start to just three days for most women, opening up the possibility for scientists to identify ...
2021-01-12
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and other organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy, has been a major player during the evolution of life and our planet's atmosphere. Although most of the ins and outs of photosynthesis are understood, how the necessary mechanisms evolved is still a topic of debate. The answer to this question, however, may actually lie buried in the mineral world.
In a recent study published in Earth Science Frontiers (10.13745/j.esf.sf.2020.12.3), scientists from Peking University, China, shifted the focus in photosynthesis research from plants and bacteria one step further back to rocks and substances found in what's ...
2021-01-12
UK government plans to widen the roll out of the Innova lateral flow test without supporting evidence risks serious harm, warn experts in The BMJ today.
More than £1 billion have been spent on purchasing lateral flow tests, but Professor Jon Deeks and colleagues argue that the public is being misled about their accuracy, as well as the risks and implications of false negative results, and they call on the government urgently to change course.
Mass testing may be helpful and necessary in certain circumstances if delivered to high quality, they explain, but the Innova lateral flow test is not fit for this purpose.
For example, in the Liverpool pilot study, 60% of infected symptomless people went undetected, including 33% of those with ...
2021-01-12
Scientists from the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a technique that will enable researchers to more efficiently isolate and identify rare T cells that are capable of targeting viruses, cancer and other diseases.
The approach could increase scientists' understanding of how these critical immune cells respond to a wide range of illnesses and advance the development of T cell therapies. This includes immunotherapies that aim to boost the function and quantity of cancer or virus-targeting T cells and therapies ...
2021-01-12
EUGENE, Ore. -- Jan. 12, 2020 -- Insufficient interactions with academic advisors and peers and financial problems are derailing career aspirations of women and minority groups pursing graduate degrees in the nation's highest-funded chemistry programs.
The challenges, tied to systemic gender and racial inequities, emerged from a deep analysis of data compiled in a 2013 American Chemical Society survey of 1,375 chemistry graduate students in the top 100 university chemistry departments in terms of research funding reported by the National Science Foundation.
The findings are detailed in a study, led by University of Oregon researchers, publishing this ...
2021-01-12
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. -- Wild bees are more affected by climate change than by disturbances to their habitats, according to a team of researchers led by Penn State. The findings suggest that addressing land-use issues alone will not be sufficient to protecting these important pollinators.
"Our study found that the most critical factor influencing wild bee abundance and species diversity was the weather, particularly temperature and precipitation," said Christina Grozinger, Distinguished Professor of Entomology and director of the Center for Pollinator Research, Penn State. "In the Northeastern United States, past trends and future predictions show a changing climate with warmer winters, more intense precipitation ...
2021-01-12
A major risk of being hospitalised is catching a bacterial infection.
Hospitals, especially areas including intensive care units and surgical wards, are teeming with bacteria, some of which are resistant to antibiotics - they are infamously known as 'superbugs'.
Superbug infections are difficult and expensive to treat, and can often lead to dire consequences for the patient.
Now, new research published today in the prestigious journal Nature Microbiology has discovered how to revert antibiotic-resistance in one of the most dangerous superbugs.
The strategy involves ...
2021-01-12
Producing clean energy and reducing the power consumption of illumination and personal devices are key challenges to reduce the impact of modern civilization on the environment. As a result, the surging demand for solar cells and light-emitting devices is driving scientists to explore new semiconductor materials and improve their performances, while lowering the production costs.
Semiconductor nanocrystals (materials with sizes about 10 nanometers, which is approximately 10,000 times thinner than our hair) hold great promise for these applications: they are cheap to produce, can be easily integrated in these devices and possess exceptionally enhanced properties upon interaction with ...
2021-01-12
Curtin University researchers have used ancient crystals from eroded rocks found in stream sediments in Greenland to successfully test the theory that portions of Earth's ancient crust acted as 'seeds' from which later generations of crust grew.
The findings not only advance an understanding of the production of the Earth's crust through deep time, along with its structure and composition, but reveal a planet-wide crustal growth spurt three billion years ago when mantle temperatures peaked.
Lead author Professor Chris Kirkland, from Curtin University's Timescales of Mineral Systems ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Sustainable transportation: clearing the air on nitrogen doping
Researchers from the University of Tsukuba identify the active nitrogen atoms in the carbon catalyst of a technology that will help optimize a proposed renewable energy storage technology