Spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocean: Along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia)
2021-01-12
(Press-News.org) Announcing a new publication for Marine Life Science & Technology journal. In this research article the authors Hungchia Huang, Jinpeng Yang, Shixiang Huang, Bowei Gu, Ying Wang, Lei Wang and Nianzhi Jiao from Xiamen University, Xiamen, China and Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China consider the spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocea: along a transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia).
Planktonic ciliates have been recognized as major consumers of nano- and picoplankton in pelagic ecosystems, playing pivotal roles in the transfer of matter and energy in the microbial loop. However, due to the difficulties in identification, the species composition of ciliate assemblages, especially for the small, fragile, and naked species that usually dominate the ciliate communities in the oceanic waters, remains largely unknown.
The authors sampled 22 stations along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia) for the enumeration of picoplankton and nanoflagellates. In addition, pigment analysis of major phytoplankton groups along with the measurements of environmental variables including temperature, salinity, and nutrients were also carried out. Ciliates were identified at species level using quantitative protargol stain to reveal the species composition and their distribution patterns from offshore to open ocean. Ciliate abundance was positively correlated with phosphate, silicate, and pico-sized pigmented eukaryotes (PPEs), whereas the biomass was closely related with PPEs, heterotrophic nanoflagellates, and chlorophytes. The ciliate communities were separated into four groups showing a nearshore to open ocean trend.
The authors identified the combination of silicate and pigmented nanoflagellates as the major factor driving the ciliate community composition. This close relationship between silicate and ciliate abundance and community structure needs further validation based on more data collected from oceanic waters. The study demonstrates the necessity of using techniques that can reveal the community composition at higher taxonomic resolutions in future studies on ciliates.
INFORMATION:
Article reference: Hungchia Huang, Jinpeng Yang, Shixiang Huang, Bowei Gu, Ying Wang, Lei Wang, Nianzhi Jiao, Spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocean: along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia), Marine Life Science & Technology, 2020, ISSN 2662-1746, https://doi.org/10.1007/s42995-020-00075-7
Keywords: Community structure, Distribution pattern, Diversity, Nanoflagellates, Quantitative protargol stain
Marine Life Science & Technology (MLST) provides a platform that introduces new discoveries and theories associated with marine organisms, bioresources, and biotechnology. The journal is intended for marine scientists, biological oceanographers, conservation biologists, marine technologists, policy makers and legislators. Accordingly, we publish original research papers across a broad range of marine life sciences and technologies with an emphasis on synergistic interactions of multiple disciplines. Both theoretical and practical papers are welcome, including laboratory and field experimental studies relevant to marine life science and technology. Focused reviews, viewpoints, comments, and short communications are also accepted. As the journal's aim is to foster multidisciplinary approaches to marine sciences, authors are encouraged to emphasise the relevance of their work in relation across the journals key-disciplines.
For more information, please visit https://www.springer.com/journal/42995/
Editorial Board: https://www.springer.com/journal/42995/editors
MLST is available on SpringerLink (https://link.springer.com/journal/42995/volumes-and-issues).
Submissions to MLST may be made using ScholarOne ManuscriptsTM (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/mlst).
Abstracted and indexed in:
Astrophysics Data System (ADS)
CNKI
Dimensions
EBSCO Discovery Service
Google Scholar
Institute of Scientific and Technical Information of China
Meta
Naver
OCLC WorldCat Discovery Service
ProQuest-ExLibris Primo
ProQuest-ExLibris Summon
TD Net Discovery Service
ISSN 2662-1746 END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2021-01-12
COLUMBIA, Mo. - As a former school nurse in the Columbia Public Schools, Gretchen Carlisle would often interact with students with disabilities who took various medications or had seizures throughout the day. At some schools, the special education teacher would bring in dogs, guinea pigs and fish as a reward for good behavior, and Carlisle noticed what a calming presence the pets seemed to be for the students with disabilities.
Now a research scientist at the MU Research Center for Human-Animal Interaction (ReCHAI) in the MU College of Veterinary Medicine, Carlisle studies the benefits that companion animals can have on families. While there is plenty of ...
2021-01-12
New Orleans, LA - Catherine O'Neal, MD, Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine at LSU Health New Orleans School of Medicine's branch campus in Baton Rouge, is a co-author of a paper reporting that shortening the length of quarantine due to COVID exposure when supported by mid-quarantine testing may increase compliance among college athletes without increasing risk. The findings are published in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's January 8, 2021 Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (MMWR), available here.
CDC partnered with representatives of the NCAA conferences to analyze retrospective data collected by participating colleges and universities. De-identified data from a total of 620 ...
2021-01-12
Gut microbes passed from female mice to their offspring, or shared between mice that live together, may influence the animals' bone mass, says a new study published today in eLife.
The findings suggest that treatments which alter the gut microbiome could help improve bone structure or treat conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis.
"Genetics account for most of the variability in human bone density, but non-genetic factors such as gut microbes may also play a role," says lead author Abdul Malik Tyagi, Assistant Staff Scientist at the Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism, and Lipids at Emory Microbiome Research Center, Emory University, Georgia, US. "We wanted to investigate the influence of the microbiome on skeletal growth and bone mass development."
To ...
2021-01-12
Using both mouse and human brain tissue, researchers at Yale School of Medicine have discovered that SARS-CoV-2 can directly infect the central nervous system and have begun to unravel some of the virus's effects on brain cells. The study, published today in the Journal of Experimental Medicine (JEM), may help researchers develop treatments for the various neurological symptoms associated with COVID-19.
Though COVID-19 is considered to primarily be a respiratory disease, SARS-CoV-2 can affect many other organs in the body, including, in some patients, the central nervous system, where infection is associated with ...
2021-01-12
The first step in treating cancer is understanding how it starts, grows and spreads throughout the body. A relatively new cancer research approach is the study of metabolites, the products of different steps in cancer cell metabolism, and how those substances interact.
To date, research like this has focused mostly on cancerous tissues; however, normal tissues that surround tumors, known as the extratumoral microenvironment (EM), may have conditions favorable for tumor formation and should also be studied.
In a new study published in the journal PLOS ONE, researchers investigated the metabolites involved in the growth and spread of melanoma, a rare but deadly ...
2021-01-12
Almost 18,000 Americans experience traumatic spinal cord injuries every year. Many of these people are unable to use their hands and arms and can't do everyday tasks such as eating, grooming or drinking water without help.
Using physical therapy combined with a noninvasive method of stimulating nerve cells in the spinal cord, University of Washington researchers helped six Seattle area participants regain some hand and arm mobility. That increased mobility lasted at least three to six months after treatment had ended. The research team published these findings Jan. 5 in the journal ...
2021-01-12
A recent study finds that, in the wake of a mass shooting, National Rifle Association (NRA) employees, donors and volunteers had extremely mixed emotions about the organization - reporting higher levels of both positive and negative feelings about the NRA, as compared to people with no NRA affiliation.
"We wanted to see what effect 'in-group' affiliation and political identity had on how people responded to the NRA's actions after a mass shooting," says Yang Cheng, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of communication at North Carolina State University. "The political findings were predictable - Republicans thought more favorably of the NRA than Democrats did. But the in-group affiliation was a lot more complex than ...
2021-01-12
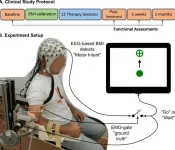
Stroke survivors who had ceased to benefit from conventional rehabilitation gained clinically significant arm movement and control by using an external robotic device powered by the patients' own brains.
The results of the clinical trial were described in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical.
Jose Luis Contreras-Vidal, director of the Non-Invasive Brain Machine Interface Systems Laboratory at the University of Houston, said testing showed most patients retained the benefits for at least two months after the therapy sessions ended, suggesting the potential for long-lasting gains. He is also Hugh Roy and Lillie Cranz Cullen Distinguished Professor of electrical and computer engineering.
The trial involved training stroke survivors with limited movement in one arm to use a brain-machine interface ...
2021-01-12
GAINESVILLE, Fla. --- Entomologist Akito Kawahara's message is straightforward: We can't live without insects. They're in trouble. And there's something all of us can do to help.
Kawahara's research has primarily focused on answering fundamental questions about moth and butterfly evolution. But he's increasingly haunted by studies that sound the alarm about plummeting insect numbers and diversity.
Kawahara has witnessed the loss himself. As a child, he collected insects with his father every weekend, often traveling to a famous oak outside Tokyo ...
2021-01-12
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- Kyle Goerl, the medical director of Kansas State University's Lafene Health Center, is part of a collaborative team that is providing research-based guidance during the COVID-19 pandemic. The team's latest research contributed to the updated quarantine guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Goerl is a co-author of the publication "Time from Start of Quarantine to SARS-CoV-2 Positive Test Among Quarantined College and University Athletes." The publication appeared in the Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report from the CDC on Friday, Jan. 8, and involved researchers from multiple organizations and universities.
The publication was one of many that the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Spatial distribution of planktonic ciliates in the western Pacific Ocean: Along the transect from Shenzhen (China) to Pohnpei (Micronesia)